|
Afro-Russians
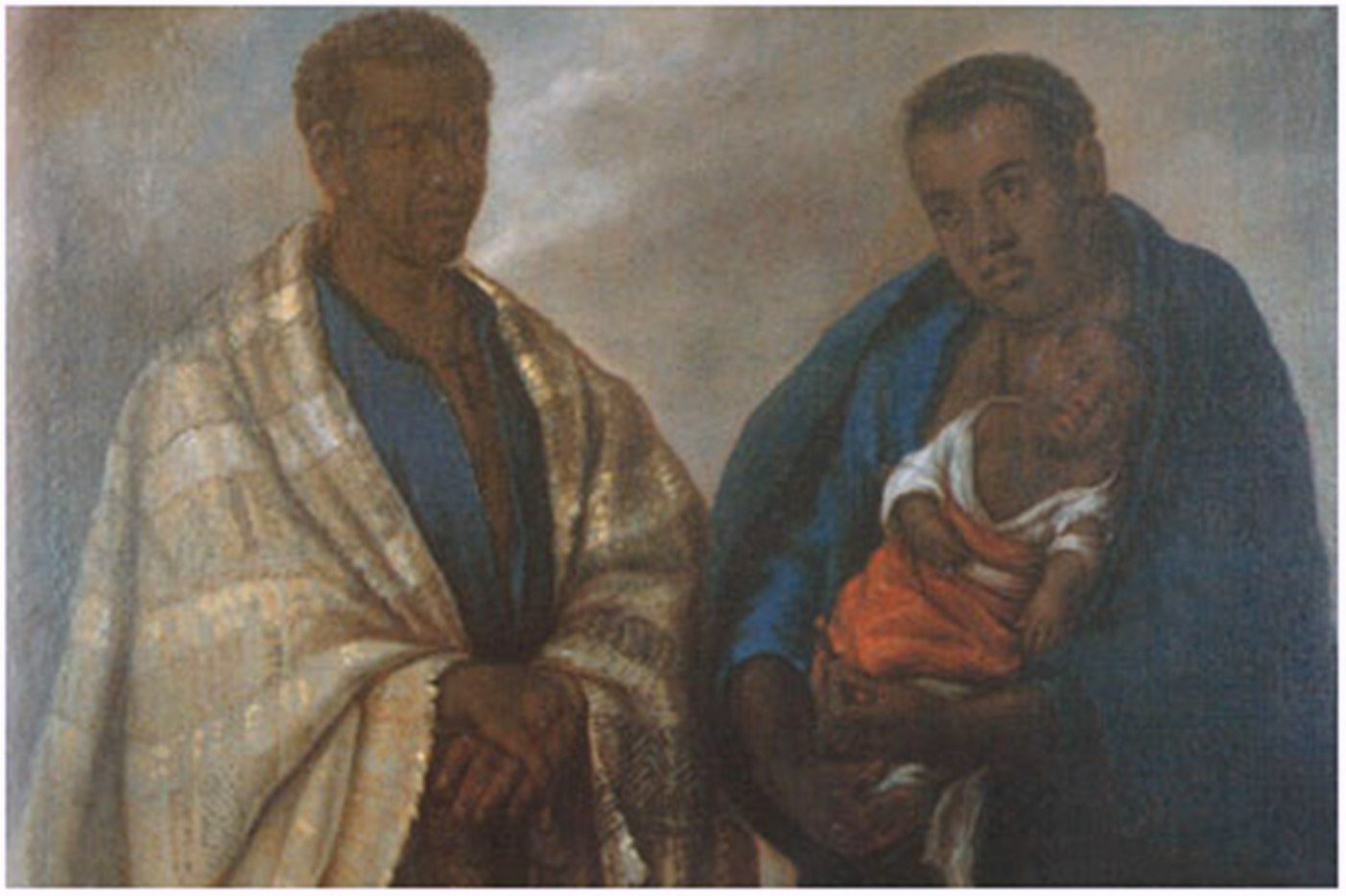
Afro-Russians (russian: Афророссияне, Afrorossiyane) are people of African descent that have migrated to and settled in Russia. The Metis Foundation estimates that there were about 30,000 Afro-Russians in 2013. Terminology Representatives of African peoples in the Russian language have been commonly called .; Negr // Dictionary of the Russian Language (Ozhegov): (first edition 1949, the reference to the edition of 1992 together with Natalia Shvedova). The word comes from es, negro (the color black in Spanish) through other European languages (german: Neger, french: nègre). In the Russian language the word does not carry a negative connotation, but that does not mean it is not offensive to others from other cultures. Russian Empire There was never an observable number of |
African Diaspora
The African diaspora is the worldwide collection of communities descended from native Africans or people from Africa, predominantly in the Americas. The term most commonly refers to the descendants of the West and Central Africans who were enslaved and shipped to the Americas via the Atlantic slave trade between the 16th and 19th centuries, with their largest populations in the United States, Brazil and Haiti. However, the term can also be used to refer to the descendants of North Africans who immigrated to other parts of the world. Some scholars identify "four circulatory phases" of this migration out of Africa. The phrase ''African diaspora'' gradually entered common usage at the turn of the 21st century. The term ''diaspora'' originates from the Greek (''diaspora'', literally "scattering") which gained popularity in English in reference to the Jewish diaspora before being more broadly applied to other populations. Less commonly, the term has been used in scholarship to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th World Festival Of Youth And Students
The 6th World Festival of Youth and Students was held from 28 July to 5 August 1957 in Moscow, capital city of the then Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. The festival attracted 34,000 people from 130 countries. This became possible after the political changes initiated by Nikita Khrushchev. It was the first World Festival of Youth and Students held in the Soviet Union.Moscow marks 50 years since youth festival The Khrushchev reforms, known as , resulted in some changes in the Soviet Union. Foreigners could come for a visit, and people were allowed to meet foreigners, albeit only in groups under supervision. Soviet foreign language students acted as interpre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abram Petrovich Gannibal
Abram Petrovich Gannibal, also Hannibal or Ganibal, or Abram Hannibal or Abram Petrov ( ru , Абра́м Петро́вич Ганниба́л; c. 1696 – 14 May 1781), was a Russian military engineer, general-in-chief, and nobleman of African origin. Kidnapped and enslaved as a child by Ottomans, Gannibal was traded to Russia and presented as a gift to Peter the Great, where he was freed, adopted and raised in the Emperor's court household as his godson.Phillips, Mike"Pushkin's African background – the Pushkins and the Gannibals."British Library. Retrieved May 26, 2016. Gannibal eventually rose to become a prominent member of the imperial court in the reign of Peter's daughter Elizabeth. He had 11 children, most of whom became members of the Russian nobility; he was a great-grandfather of the author and poet Alexander Pushkin. Early life The main reliable accounts of Gannibal's life come from ''The Moor of Peter the Great,'' Pushkin's unfinished biography of his great-g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
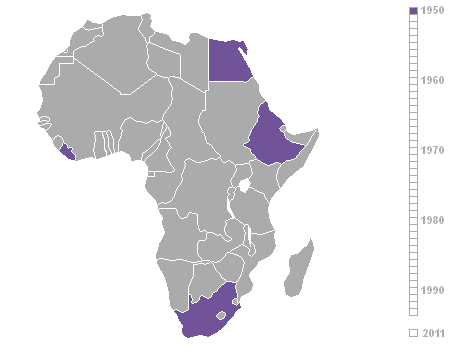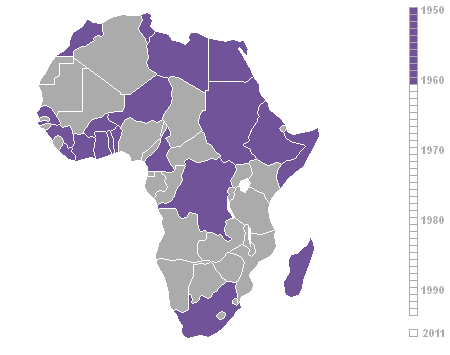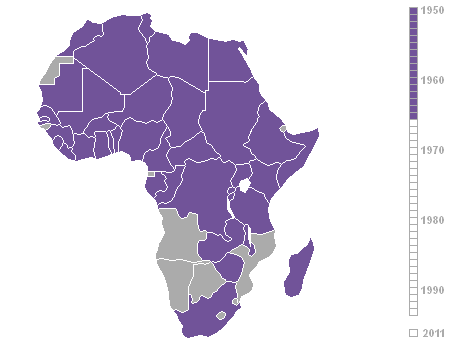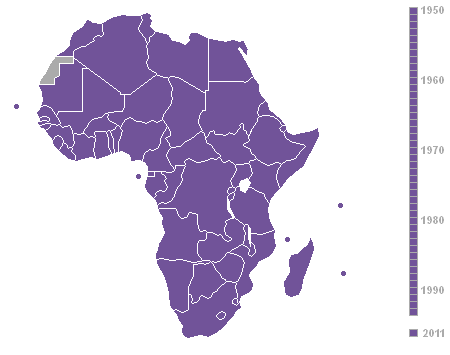
Decolonization Of Africa
The decolonisation of Africa was a process that took place in the Scramble for Africa, mid-to-late 1950s to 1975 during the Cold War, with radical government changes on the continent as Colonialism, colonial governments made the transition to Sovereign state, independent states. The process was often marred with violence, political turmoil, widespread unrest, and organised revolts in both northern and sub-Saharan countries including the Algerian War in French Algeria, the Angolan War of Independence in Portuguese Angola, the Congo Crisis in the Belgian Congo, the Mau Mau Uprising in Kenya Colony, British Kenya, the Zanzibar Revolution in the Sultanate of Zanzibar, and the Nigerian Civil War in the secessionist state of Biafra. Background The "Scramble for Africa" between 1870 and 1914 was a significant period of European imperialism in Africa that ended with almost all of Africa, and its natural resources, being controlled as colonies by a small number of European states. Racin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Robeson
Paul Leroy Robeson ( ; April 9, 1898 – January 23, 1976) was an American bass-baritone concert artist, stage and film actor, professional football player, and activist who became famous both for his cultural accomplishments and for his political stances. In 1915, Robeson won an academic scholarship to Rutgers College. While at Rutgers, he was twice named a consensus All-American in football and was the class valedictorian. He received his LL.B. from Columbia Law School while playing in the National Football League (NFL). After graduation, he became a figure in the Harlem Renaissance with performances in ''The Emperor Jones'' and '' All God's Chillun Got Wings''. Robeson performed in Britain in a touring melodrama, ''Voodoo'', in 1922, and in ''Emperor Jones'' in 1925. In 1928, he scored a major success in the London premiere of ''Show Boat''. Living in London for several years with his wife Eslanda, Robeson continued to establish himself as a concert artist and starred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langston Hughes
James Mercer Langston Hughes (February 1, 1901 – May 22, 1967) was an American poet, social activist, novelist, playwright, and columnist from Joplin, Missouri. One of the earliest innovators of the literary art form called jazz poetry, Hughes is best known as a leader of the Harlem Renaissance. He famously wrote about the period that "the Negro was in vogue", which was later paraphrased as "when Harlem was in vogue." Growing up in a series of Midwestern towns, Hughes became a prolific writer at an early age. He moved to New York City as a young man, where he made his career. He graduated from high school in Cleveland, Ohio, and soon began studies at Columbia University in New York City. Although he dropped out, he gained notice from New York publishers, first in ''The Crisis'' magazine and then from book publishers, and became known in the creative community in Harlem. He eventually graduated from Lincoln University. In addition to poetry, Hughes wrote plays and short sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comintern
The Communist International (Comintern), also known as the Third International, was a Soviet Union, Soviet-controlled international organization founded in 1919 that advocated world communism. The Comintern resolved at its Second Congress to "struggle by all available means, including armed force, for the overthrow of the international bourgeoisie and the creation of an international Soviet republic (system of government), Soviet republic as a transition stage to the complete abolition of the state". The Comintern was preceded by the 1916 dissolution of the Second International. The Comintern held seven World Congresses in Moscow between 1919 and 1935. During that period, it also conducted thirteen Enlarged Plenums of its governing Executive Committee of the Communist International, Executive Committee, which had much the same function as the somewhat larger and more grandiose Congresses. Joseph Stalin, leader of the Soviet Union, dissolved the Comintern in 1943 to avoid antag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin (; rus, links=no, Александр Сергеевич ПушкинIn pre-Revolutionary script, his name was written ., r=Aleksandr Sergeyevich Pushkin, p=ɐlʲɪkˈsandr sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈpuʂkʲɪn, a=ru-Pushkin.ogg; ) was a Russian poet, playwright, and novelist of the Romantic era.Basker, Michael. Pushkin and Romanticism. In Ferber, Michael, ed., ''A Companion to European Romanticism''. Oxford: Blackwell, 2005. He is considered by many to be the greatest Russian poetShort biography from University of Virginia . Retrieved 24 November 2006.Allan Rei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter The Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from to 1721 and subsequently the Russian Empire until his death in 1725, jointly ruling with his elder half-brother, Ivan V until 1696. He is primarily credited with the modernisation of the country, transforming it into a European power. Through a number of successful wars, he captured ports at Azov and the Baltic Sea, laying the groundwork for the Imperial Russian Navy, ending uncontested Swedish supremacy in the Baltic and beginning the Tsardom's expansion into a much larger empire that became a major European power. He led a cultural revolution that replaced some of the traditionalist and medieval social and political systems with ones that were modern, scientific, Westernised and based on the Enlightenment. Peter's reforms had a lasting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the term—a ruler with the same rank as a Roman emperor, holding it by the approval of another emperor or a supreme ecclesiastical official (the Pope or the Ecumenical Patriarch)—but was usually considered by western Europeans to be equivalent to "king". It lends its name to a system of government, tsarist autocracy or tsarism. "Tsar" and its variants were the official titles of the following states: * Bulgarian Empire (First Bulgarian Empire in 681–1018, Second Bulgarian Empire in 1185–1396), and also used in Kingdom of Bulgaria, Tsardom of Bulgaria, in 1908–1946 * Serbian Empire, in 1346–1371 * Tsardom of Russia, in 1547–1721 (replaced in 1721 by ''imperator'' in Russian Empire, but still re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fyodor Alexeyevich Golovin
Count Fyodor Alexeyevich Golovin (russian: Фёдор Алексеевич Головин; 1650 – ) was the last Russian boyar and the first Chancellor of the Russian Empire, he was also a field marshal, and general admiral (1700). He was perhaps the most influential of Peter the Great's associates until his death in 1706. Biography Golovin was descended from the family of Russian treasurers of Byzantine Greek descent. Military career During the regency of Sophia Alekseyevna, sister of Peter the Great, he was sent to the Amur to defend the new fortress of Albazin against the Chinese Qing Empire. In 1689, he ended with the Qing Empire the Treaty of Nerchinsk, by which the line of the Amur, as far as its tributary the Gorbitsa, was retroceded to China because of the impossibility of seriously defending it. In Peter's Grand Embassy to the West in 1697 Golovin occupied the second place immediately after Franz Lefort. It was his chief duty to hire foreign sailors and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |