|
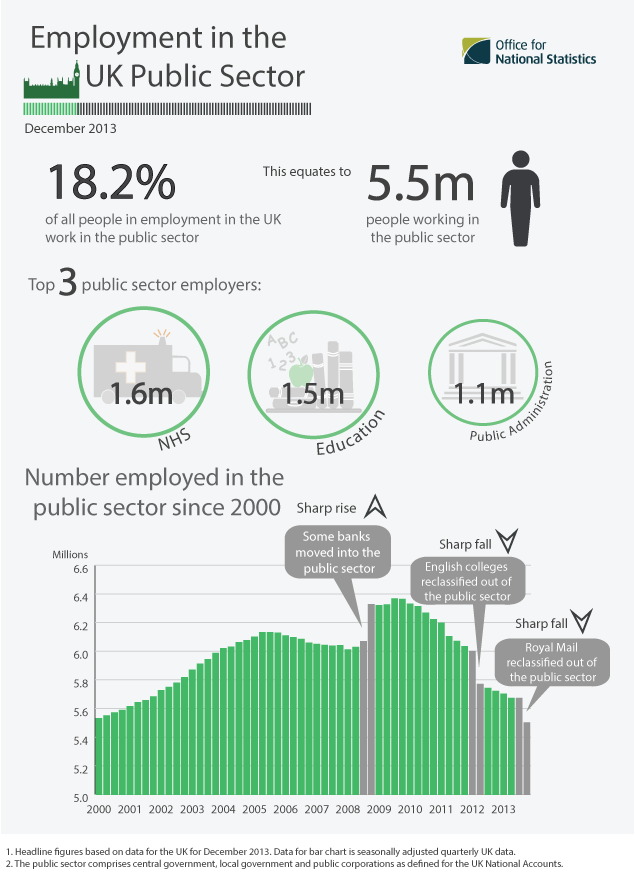
Affordable Medicines Facility-malaria
The Affordable Medicines Facility-malaria (AMFm) is a financing mechanism intended to expand access to affordable and effective antimalarial medication (artemisinin-based combination therapies, ACTs). It works primarily through the commercial private sector, in addition to the public and non-governmental organization sectors which are the more traditional routes for development assistance in malaria control. Its goal is to drive down the price of the most effective malaria medicines so that millions of people can afford to buy them. The program has been called "one of the most important recent advances in fighting malaria" and "a triumph of international cooperation." The AMFm is hosted and managed by the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria in Geneva, Switzerland. The premise of the AMFm is that a factory-gate global subsidy, with measures to support its implementation, will save lives and reduce malaria-related mortality by increasing access to ACTs, and delay t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimalarial Medication
Antimalarial medications or simply antimalarials are a type of antiparasitic chemical agent, often naturally derived, that can be used to treat or to prevent malaria, in the latter case, most often aiming at two susceptible target groups, young children and pregnant women. As of 2018, modern treatments, including for severe malaria, continued to depend on therapies deriving historically from quinine and artesunate, both parenteral (injectable) drugs, expanding from there into the many classes of available modern drugs. Incidence and distribution of the disease ("malaria burden") is expected to remain high, globally, for many years to come; moreover, known antimalarial drugs have repeatedly been observed to elicit resistance in the malaria parasite—including for combination therapies featuring artemisinin, a drug of last resort, where resistance has now been observed in Southeast Asia. As such, the needs for new antimalarial agents and new strategies of treatment (e.g., new combin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copenhagen Consensus
Copenhagen Consensus is a project that seeks to establish priorities for advancing global welfare using methodologies based on the theory of welfare economics, using cost–benefit analysis. It was conceived and organized around 2004 by Bjørn Lomborg, the author of ''The Skeptical Environmentalist'' and the then director of the Danish government's Environmental Assessment Institute. The project is run by the Copenhagen Consensus Center, which is directed by Lomborg and was part of the Copenhagen Business School, but it is now an independent 501(c)(3) non-profit organisation registered in the USA. The project considers possible solutions to a wide range of problems, presented by experts in each field. These are evaluated and ranked by a panel of economists. The emphasis is on rational prioritization by economic analysis. The panel is given an arbitrary budget constraint and instructed to use cost–benefit analysis to focus on a bottom line approach in solving/ranking presented pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amodiaquine
Amodiaquine (ADQ) is a medication used to treat malaria, including ''Plasmodium falciparum'' malaria when uncomplicated. It is recommended to be given with artesunate to reduce the risk of resistance. Due to the risk of rare but serious side effects, it is not generally recommended to prevent malaria. Though, the WHO in 2013 recommended use for seasonal preventive in children at high risk in combination with sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine. The side effects of amodiaquine are generally minor to moderate and are similar to those of chloroquine. Rarely liver problems or low blood cell levels may occur. When taken in excess headaches, trouble seeing, seizures, and cardiac arrest may occur. While not extensively studied as of 2007, it appeared to be safe in pregnancy. Amodiaquine is a 4-aminoquinoline compound related to chloroquine. Amodiaquine was first made in 1948. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. While not available in the United States, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine
Sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine, sold under the brand name Fansidar, is a combination medication used to treat malaria. It contains sulfadoxine (a sulfonamide) and pyrimethamine (an antiprotozoal). For the treatment of malaria it is typically used along with other antimalarial medication such as artesunate. In areas of Africa with moderate to high rates of malaria, three doses are recommended during the second and third trimester of pregnancy. Side effects include diarrhea, rash, itchiness, headache, and hair loss. Rarely a severe allergic reaction or rash such as toxic epidermal necrolysis, may occur. It is not generally recommended in people with a sulfonamide allergy or significant liver or kidney disease. It works by blocking malaria's ability to use folinic acid. Sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine was initially approved for medical use in the United States in 1981. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is not commercially available in the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroquine
Chloroquine is a medication primarily used to prevent and treat malaria in areas where malaria remains sensitive to its effects. Certain types of malaria, resistant strains, and complicated cases typically require different or additional medication. Chloroquine is also occasionally used for amebiasis that is occurring outside the intestines, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus erythematosus. While it has not been formally studied in pregnancy, it appears safe. It was studied to treat COVID-19 early in the pandemic, but these studies were largely halted in the summer of 2020, and is not recommended for this purpose. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include muscle problems, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and skin rash. Serious side effects include problems with vision, muscle damage, seizures, and low blood cell levels. Chloroquine is a member of the drug class 4-aminoquinoline. As an antimalarial, it works against the asexual form of the malaria parasite in the stage of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private Sector
The private sector is the part of the economy, sometimes referred to as the citizen sector, which is owned by private groups, usually as a means of establishment for profit or non profit, rather than being owned by the government. Employment The private sector employs most of the workforce in some countries. In private sector, activities are guided by the motive to earn money. A 2013 study by the International Finance Corporation (part of the World Bank Group) identified that 90 percent of jobs in developing countries are in the private sector. Diversification In free enterprise countries, such as the United States, the private sector is wider, and the state places fewer constraints on firms. In countries with more government authority, such as China, the public sector makes up most of the economy. Regulation States legally regulate the private sector. Businesses operating within a country must comply with the laws in that country. In some cases, usually involving multinatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Sector
The public sector, also called the state sector, is the part of the economy composed of both public services and public enterprises. Public sectors include the public goods and governmental services such as the military, law enforcement, infrastructure, public transit, public education, along with health care and those working for the government itself, such as elected officials. The public sector might provide services that a non-payer cannot be excluded from (such as street lighting), services which benefit all of society rather than just the individual who uses the service. Public enterprises, or state-owned enterprises, are self-financing commercial enterprises that are under public ownership which provide various private goods and services for sale and usually operate on a commercial basis. Organizations that are not part of the public sector are either part of the private sector or voluntary sector. The private sector is composed of the economic sectors that are intende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization (WHO)
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health". Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it has six regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. The WHO was established on 7 April 1948. The first meeting of the World Health Assembly (WHA), the agency's governing body, took place on 24 July of that year. The WHO incorporated the assets, personnel, and duties of the League of Nations' Health Organization and the , including the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Its work began in earnest in 1951 after a significant infusion of financial and technical resources. The WHO's mandate seeks and includes: working worldwide to promote health, keeping the world safe, and serve the vulnerable. It advocates that a billion more people should have: universal health care coverag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemisinin
Artemisinin () and its semisynthetic derivatives are a group of drugs used in the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum''. It was discovered in 1972 by Tu Youyou, who shared the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for her discovery. Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) are now standard treatment worldwide for ''P. falciparum'' malaria as well as malaria due to other species of ''Plasmodium''. Artemisinin is extracted from the plant ''Artemisia annua'', sweet wormwood, a herb employed in Chinese traditional medicine. A precursor compound can be produced using a genetically engineered yeast, which is much more efficient than using the plant. Artemisinin and its derivatives are all sesquiterpene lactones containing an unusual peroxide bridge. This endoperoxide 1,2,4-trioxane ring is responsible for their antimalarial properties. Few other natural compounds with such a peroxide bridge are known. Artemisinin and its derivatives have been used for the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combination Therapy
Combination therapy or polytherapy is therapy that uses more than one medication or modality. Typically, the term refers to using multiple therapies to treat a ''single'' disease, and often all the therapies are pharmaceutical (although it can also involve non-medical therapy, such as the combination of medications and talk therapy to treat depression). 'Pharmaceutical' combination therapy may be achieved by prescribing/administering separate drugs, or, where available, dosage forms that contain more than one active ingredient (such as fixed-dose combinations). Polypharmacy is a related term, referring to the use of multiple medications (without regard to whether they are for the same or separate conditions/diseases). Sometimes "polymedicine" is used to refer to pharmaceutical combination therapy. Most of these kinds of terms lack a universally consistent definition, so caution and clarification are often advisable. Uses Conditions treated with combination therapy include tuberculo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmodium Falciparum
''Plasmodium falciparum'' is a Unicellular organism, unicellular protozoan parasite of humans, and the deadliest species of ''Plasmodium'' that causes malaria in humans. The parasite is transmitted through the bite of a female ''Anopheles'' mosquito and causes the disease's most dangerous form, falciparum malaria. It is responsible for around 50% of all malaria cases. ''P. falciparum'' is therefore regarded as the deadliest parasite in humans. It is also associated with the development of blood cancer (Burkitt's lymphoma) and is classified as a List of IARC Group 2A carcinogens, Group 2A (probable) carcinogen. The species originated from the malarial parasite ''Laverania'' found in gorillas, around 10,000 years ago. Alphonse Laveran was the first to identify the parasite in 1880, and named it ''Oscillaria malariae''. Ronald Ross discovered its transmission by mosquito in 1897. Giovanni Battista Grassi elucidated the complete transmission from a female Anopheles, anopheline mosquit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)