|
Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture
The ARM Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture (AMBA) is an open-standard, on-chip interconnect specification for the connection and management of functional blocks in system-on-a-chip (SoC) designs. It facilitates development of multi-processor designs with large numbers of controllers and components with a bus architecture. Since its inception, the scope of AMBA has, despite its name, gone far beyond microcontroller devices. Today, AMBA is widely used on a range of ASIC and SoC parts including applications processors used in modern portable mobile devices like smartphones. AMBA is a registered trademark of ARM Ltd. AMBA was introduced by ARM in 1996. The first AMBA buses were the Advanced System Bus (ASB) and the Advanced Peripheral Bus (APB). In its second version, AMBA 2 in 1999, ARM added AMBA High-performance Bus (AHB) that is a single clock-edge protocol. In 2003, ARM introduced the third generation, AMBA 3, including Advanced eXtensible Interface (AXI) to reach even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Unit
In computer engineering, an execution unit (E-unit or EU) is a part of the central processing unit (CPU) that performs the operations and calculations as instructed by the computer program. It may have its own internal control sequence unit (not to be confused with the CPU's main control unit), some registers, and other internal units such as an arithmetic logic unit (ALU), address generation unit (AGU), floating-point unit (FPU), load-store unit (LSU), branch execution unit (BEU) or some smaller and more specific components. archived on the |
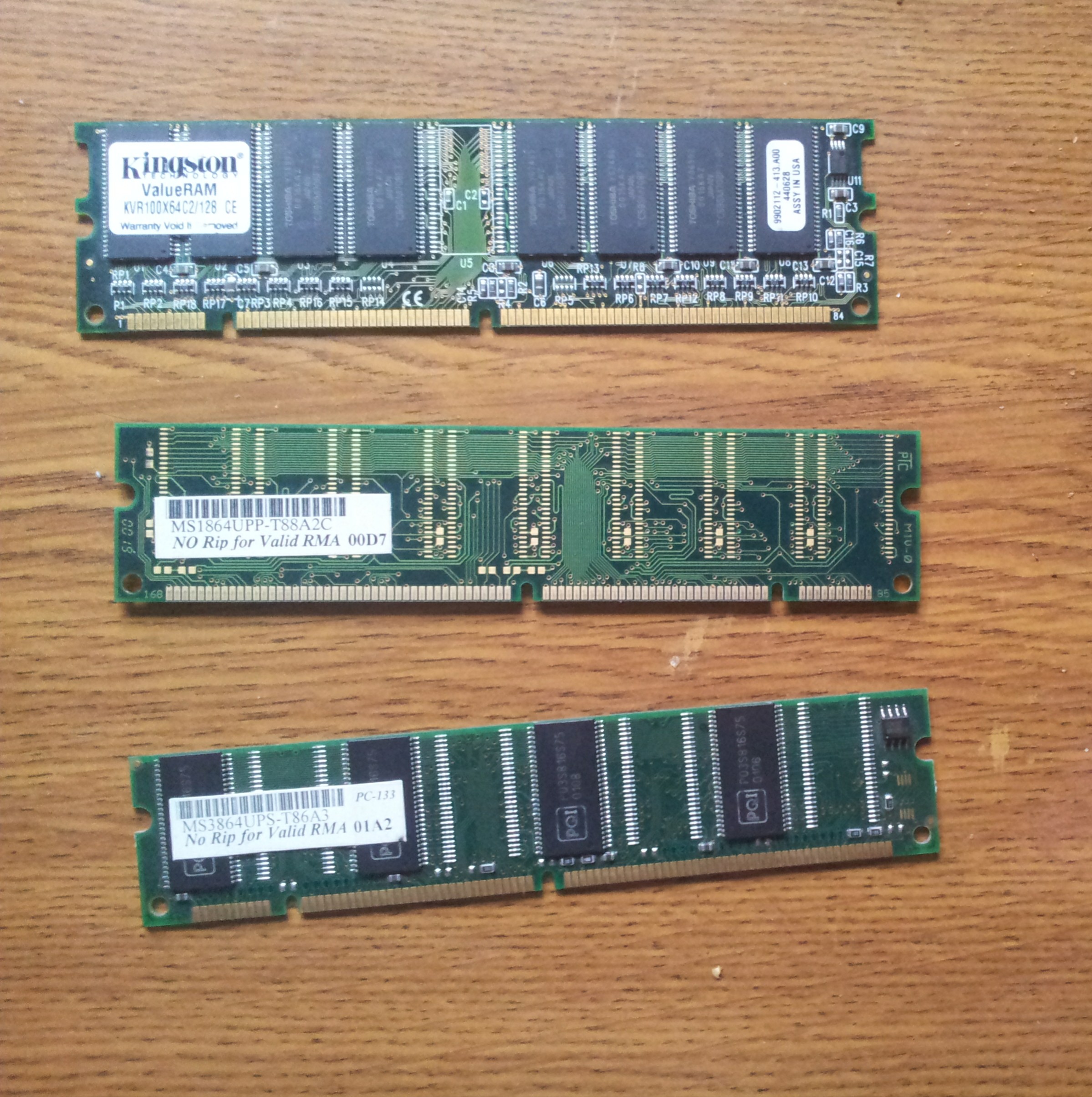
SDRAM
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to early 1990s used an ''asynchronous'' interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions only delayed by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a ''synchronous'' interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite-state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called ''banks'', allowing the device to operate on a memory a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altera
Altera Corporation was a manufacturer of programmable logic devices (PLDs) headquartered in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1983 and acquired by Intel in 2015. The main product lines from Altera were the flagship Stratix series, mid-range Arria series, and lower-cost Cyclone series system on a chip field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs); the MAX series complex programmable logic device and non-volatile FPGAs; Quartus design software; and Enpirion PowerSoC DC-DC power solutions. The company was founded in 1983 by semiconductor veterans Rodney Smith, Robert Hartmann, James Sansbury, and Paul Newhagen with $500,000 in seed money. The name of the company was a play on "alterable", the type of chips the company created. In 1984, the company formed a long-running design partnership with Intel, and 1988, became a public company via an initial public offering. In 1994, Altera acquired the PLD business of Intel for $50 million. On December 28, 2015, the company was acquired by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nios II
Nios II is a 32-bit embedded processor architecture designed specifically for the Altera family of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) integrated circuits. Nios II incorporates many enhancements over the original Nios architecture, making it more suitable for a wider range of embedded computing applications, from digital signal processing (DSP) to system-control. Nios II is a successor to Altera's first configurable 16-bit embedded processor Nios, introduced in 2000. Key features Like the original Nios, the Nios II architecture is a RISC soft-core architecture which is implemented entirely in the programmable logic and memory blocks of Altera FPGAs. Unlike its predecessor it is a full 32-bit design: * 32 general-purpose 32-bit registers, * Full 32-bit instruction set, data path, and address space, * Single-instruction 32 × 32 multiply and divide producing a 32-bit result. The soft-core nature of the Nios II processor lets the system designer specify and generate a custom Ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Device Technology
Integrated Device Technology, Inc., is an American corporation headquartered in San Jose, California, that designs, manufactures, and markets low-power, high-performance mixed-signal semiconductor solutions for the advanced communications, computing, and consumer industries. The company markets its products primarily to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). Founded in 1980, the company began as a provider of complementary metal-oxide semiconductors (CMOS) for the communications business segment and computing business segments. The company is focused on three major areas: communications infrastructure (wireless and wired), high-performance computing, and advanced power management. Business segments The communications segment offers communication clocks, serial RapidIO solutions for wireless base station infrastructure applications, radio frequency products, digital logic products, first-in and first-out (FIFO) memories, integrated communications processors, static random-acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xilinx
Xilinx, Inc. ( ) was an American technology and semiconductor company that primarily supplied programmable logic devices. The company was known for inventing the first commercially viable field-programmable gate array (FPGA) and creating the first fabless manufacturing model.Jonathan Cassell, iSuppli.A Forgettable Year for Memory Chip Makers: iSuppli releases preliminary 2008 semiconductor rankings." December 1, 2008. Retrieved January 15, 2009.John Edwards, EDN." June 1, 2006. Retrieved January 15, 2009. Xilinx was co-founded by Ross Freeman, Bernard Vonderschmitt, and James V. Barnett II, James V Barnett II in 1984 and the company went public on the NASDAQ in 1990. AMD announced its acquisition of Xilinx in October 2020 and the deal was completed on February 14, 2022 through an all-stock transaction worth an estimated $50 billion. Company overview Xilinx was founded in Silicon Valley in 1984 and headquartered in San Jose, California, San Jose, USA, with additional offices in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System On A Chip
A system on a chip or system-on-chip (SoC ; pl. ''SoCs'' ) is an integrated circuit that integrates most or all components of a computer or other electronic system. These components almost always include a central processing unit (CPU), memory interfaces, on-chip input/output devices, input/output interfaces, and secondary storage interfaces, often alongside other components such as radio modems and a graphics processing unit (GPU) – all on a single substrate or microchip. It may contain digital, analog, mixed-signal, and often radio frequency signal processing functions (otherwise it is considered only an application processor). Higher-performance SoCs are often paired with dedicated and physically separate memory and secondary storage (such as LPDDR and eUFS or eMMC, respectively) chips, that may be layered on top of the SoC in what's known as a package on package (PoP) configuration, or be placed close to the SoC. Additionally, SoCs may use separate wireless modems. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerPC
PowerPC (with the backronym Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC – Performance Computing, sometimes abbreviated as PPC) is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple Inc., Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM alliance, AIM. PowerPC, as an evolving instruction set, has been named Power ISA since 2006, while the old name lives on as a trademark for some implementations of Power Architecture–based processors. PowerPC was the cornerstone of AIM's PReP and Common Hardware Reference Platform (CHRP) initiatives in the 1990s. Originally intended for personal computers, the architecture is well known for being used by Apple's Power Macintosh, PowerBook, iMac, iBook, eMac, Mac Mini, and Xserve lines from 1994 until 2005, when Mac transition to Intel processors, Apple migrated to Intel's x86. It has since become a niche in personal computers, but remains popular for embedded system, embedded and high-performanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CoreConnect
__NOTOC__ CoreConnect is a microprocessor bus-architecture from IBM for system-on-a-chip (SoC) designs. It was designed to ease the integration and reuse of processor, system, and peripheral cores within standard and custom SoC designs. As a standard SoC design point, it serves as the foundation of IBM or non-IBM devices. Elements of this architecture include the processor local bus (PLB), the on-chip peripheral bus (OPB), a bus bridge, and a device control register (DCR) bus. High-performance peripherals connect to the high-bandwidth, low- latency PLB. Slower peripheral cores connect to the OPB, which reduces traffic on the PLB. CoreConnect has bridging capabilities to the competing AMBA bus architecture, allowing reuse of existing SoC-components. IBM makes the CoreConnect bus available as a no-fee, no-royalty architecture to tool-vendors, core IP-companies, and chip-development companies. As such it is licensed by over 1500 electronics companies such as Cadence, Ericsson, Luce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenCores
OpenCores is a community developing digital open-source hardware through electronic design automation (EDA), with a similar ethos as the free software movement. OpenCores hopes to eliminate redundant design work and slash development costs. A number of companies have been reported as adopting OpenCores IP in chips,Andrew Orlowski, "Flextronics demos open source chips", ''The Register'', 12 December 2003/ref> or as adjuncts to EDA tools. OpenCores is also cited from time to time in the electronics press as an example of open source in the electronics hardware community. OpenCores has always been a commercially owned organization. In 2015, the core active users of OpenCores established the independent Free and Open Source Silicon Foundation (FOSSi Foundation), and registered the libreCores.org website as the basis for all future development, independent of commercial control. History Damjan Lampret, one of the founders of OpenCores, stated on his website that it began in 1999. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wishbone (computer Bus)
The Wishbone Bus is an open source hardware computer bus intended to let the parts of an integrated circuit communicate with each other. The aim is to allow the connection of differing cores to each other inside of a chip. The Wishbone Bus is used by many designs in the OpenCores project. Wishbone is intended as a "logic bus". It does not specify electrical information or the bus topology. Instead, the specification is written in terms of "signals", clock cycles, and high and low levels. This ambiguity is intentional. Wishbone is made to let designers combine several designs written in Verilog, VHDL or some other logic-description language for electronic design automation (EDA). Wishbone provides a standard way for designers to combine these hardware logic designs (called "cores"). Wishbone is defined to have 8, 16, 32, and 64-bit buses. All signals are synchronous to a single clock but some slave responses must be generated combinatorially for maximum performance. Wishbone per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Cyclone_III_(cropped).jpg)


