|
Administrative Division Of The Second Polish Republic
Subdivisions of the Second Polish Republic became an issue immediately after the creation of the Second Polish Republic in 1918. The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth had been partitioned in the late 18th century. Various parts of new Polish territory had belonged to different administrative structures of Austrian Empire, Imperial Germany and Russian Empire. In 1919 the first voivodeships of interwar Poland were created; in addition, the capital of Warsaw had a status of an independent city-voivodeship. In the years 1919–1921 additional voivodeships were created, as borders of Poland were still fluid, with events such as the Silesian Uprisings in the West and Polish-Soviet War in the East. Eventually by 1921 Poland would have 15 voivodeships, Warsaw capital city-voivodeship and the Autonomous Silesian Voivodeship (the system known as 15+1+1). Additionally, creation of the new Sandomierz Voivodeship was planned for late 1939. The lower level of administration, below voivodeship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gmina
The gmina (Polish: , plural ''gminy'' , from German ''Gemeinde'' meaning ''commune'') is the principal unit of the administrative division of Poland, similar to a municipality. , there were 2,477 gminas throughout the country, encompassing over 43,000 villages. 940 gminas include cities and towns, with 302 among them constituting an independent urban gmina ( pl, gmina miejska) consisting solely of a standalone town or one of the 107 cities, the latter governed by a city mayor (''prezydent miasta''). The gmina has been the basic unit of territorial division in Poland since 1974, when it replaced the smaller gromada (cluster). Three or more gminas make up a higher level unit called powiat, except for those holding the status of a city with powiat rights. Each and every powiat has the seat in a city or town, in the latter case either an urban gmina or a part of an urban-rural one. Types There are three types of gmina: #302 urban gmina ( pl, gmina miejska) constituted either by a sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of the Vistula River and is about to the southeast of Warsaw by road. One of the events that greatly contributed to the city's development was the Polish-Lithuanian Union of Krewo in 1385. Lublin thrived as a centre of trade and commerce due to its strategic location on the route between Vilnius and Kraków; the inhabitants had the privilege of free trade in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The Lublin Parliament session of 1569 led to the creation of a real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, thus creating the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Lublin witnessed the early stages of Reformation in the 16th century. A Calvinist congregation was founded and groups of radical Arians appeared in the city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lublin Voivodeship (1919–1939)
Lublin Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo Lubelskie) was a unit of administrative division of the Second Polish Republic between the two world wars, in the years 1919–1939. The province's capital and biggest city was Lublin. Location and area The Voivodeship was founded by the decree of Polish Parliament ''Sejm'' of 14 August 1919.Act of Polish Parliament ''Sejm'' (2 August 1919) Dz. U. z 1919 r. Nr 65, poz. 395.Internetowy System Aktow Prawnych. Retrieved 25 October 2015. In the years 1919–1939 (unlike today), Lublin Voivodeship covered the central part of interwar Poland – the heartland of the country – bordering Białystok Voivodeship (1919–39) to the north, Warsaw Voivodeship and Kielce Voivodeship to the west, Lwów Voivodeship to the south and Polesie Voivodeship as well as Volhynian Voivodeship to the east. Its area, after April 1, 1938 (see: Territorial changes of Polish Voivodeships on April 1, 1938) was 26,555 km². Landscape was flat and hilly in the south, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 and has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, economic, cultural and artistic life. Cited as one of Europe's most beautiful cities, its Old Town with Wawel Royal Castle was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1978, one of the first 12 sites granted the status. The city has grown from a Stone Age settlement to Poland's second-most-important city. It began as a hamlet on Wawel Hill and was reported by Ibrahim Ibn Yakoub, a merchant from Cordoba, as a busy trading centre of Central Europe in 985. With the establishment of new universities and cultural venues at the emergence of the Second Polish Republic in 1918 and throughout the 20th century, Kraków reaffirmed its role as a major national academic and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraków Voivodeship (1919–1939)
Kraków Voivodeship ( pl, województwo krakowskie) was a unit of administrative division and local government in Poland in years 1919–1939. Back then, it covered a big chunk of the southern part of the country, including such cities as Kraków, Jaworzno and Tarnów. Capital city: Kraków. Location and area In early 1939, Voivodeship's area was 17 560 square kilometers. It was located in southern Poland, bordering Autonomous Silesian Voivodeship to the west, Kielce Voivodeship to the north, Lublin Voivodeship, Lwów Voivodeship to the east and Slovakia to the south. Landscape was hilly in the northern part and mountainous in south, with the Tatra Mountains located in the very south of the area. Forests covered 20.9%, with the national average 22.2% (as for January 1, 1937). Population According to the 1931 Polish census, the population was 2 300 100, with approximately 25% living in towns and cities. Poles were 91.3% of the population, Jews were 5.6%, and Ukrainians were 2.5% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kielce
Kielce (, yi, קעלץ, Keltz) is a city in southern Poland, and the capital of the Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship. In 2021, it had 192,468 inhabitants. The city is in the middle of the Świętokrzyskie Mountains (Holy Cross Mountains), on the banks of the Silnica River, in the northern part of the historical Polish province of Lesser Poland. Kielce has a history back over 900 years, and the exact date that it was founded remains unknown. Kielce was once an important centre of limestone mining and the vicinity is famous for its natural resources like copper, lead and iron, which, over the centuries, were exploited on a large scale. There are several fairs and exhibitions held in Kielce throughout the year. The city and its surroundings are also known for their historic architecture, green spaces and recreational areas like the Świętokrzyski National Park. In sports, the city is known as the home of the top-tier handball club, multiple Polish Champion and one-time EHF Champions Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kielce Voivodeship (1919–1939)
Kielce Voivodeship ( pl, województwo kieleckie) - a unit of administrative division and local government in Poland in years 1921–1939. At that time, it covered northern counties of the historic province of Lesser Poland, including such cities as Radom, Częstochowa and Sosnowiec. On 1 April 1938, its borders changed, see: Territorial changes of Polish Voivodeships on 1 April 1938. Capital city: Kielce. Location and area In early 1939, Voivodeship's area was 22 204 square kilometers. It was located in central Poland, bordering Germany and Autonomous Silesian Voivodeship to the west, Łódź Voivodeship and Warsaw Voivodeship to the north, Lublin Voivodeship and Lwów Voivodeship to the east and Kraków Voivodeship to the south. Landscape was flat in the northern part and hilly in mid and south, with the Świętokrzyskie Mountains located in the heart of the area. Forests covered 21.2%, with the national average 22.2% (as for January 1, 1937). Population According to the 193 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area. Białystok is located in the Białystok Uplands of the Podlachian Plain on the banks of the Biała River, by road northeast of Warsaw. It has historically attracted migrants from elsewhere in Poland and beyond, particularly from Central and Eastern Europe. This is facilitated by the nearby border with Belarus also being the eastern border of the European Union, as well as the Schengen Area. The city and its adjacent municipalities constitute Metropolitan Białystok. The city has a warm summer continental climate, characterized by warm summers and long frosty winters. Forests are an important part of Białystok's character and occupy around (18% of the administrative area of the city) which places it as the fifth-most forested city in Poland. The first settlers arrived in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
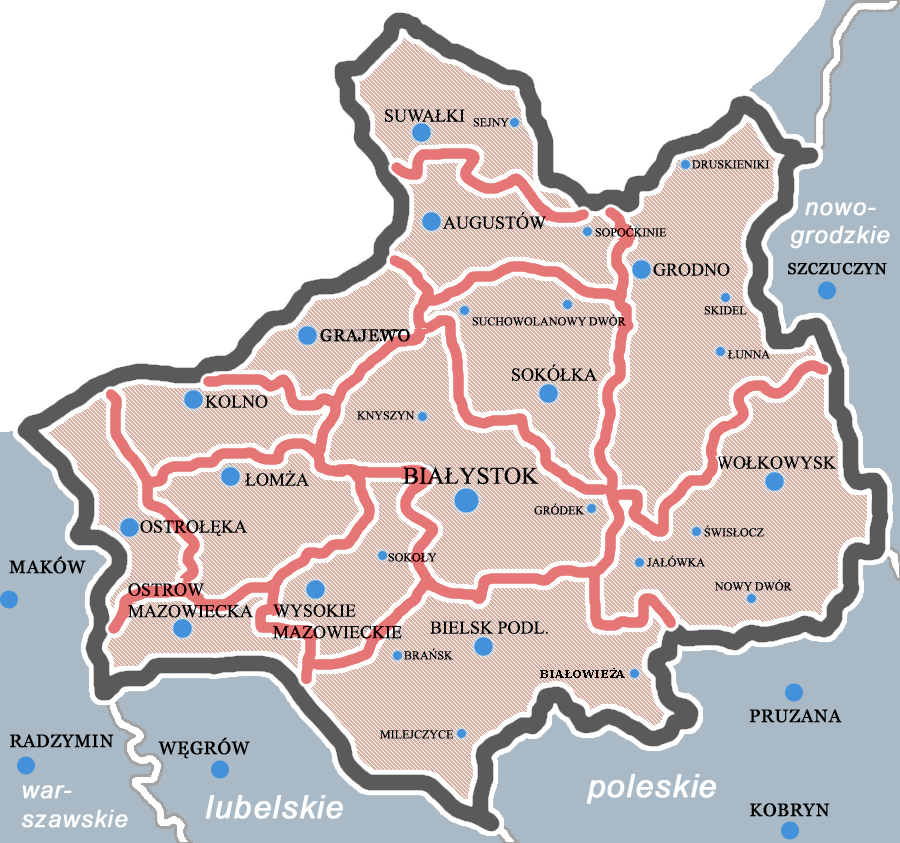
Białystok Voivodeship (1919–1939)
Białystok Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo białostockie) was an administrative unit of interwar Poland (1918–1939). The province's capital and its biggest city was Białystok with a population of over 91,000 people. Following the Nazi German and the Soviet invasion of Poland, the Voivodeship was occupied by both invading armies and divided according to Nazi-Soviet boundary treaty. Area and location In interwar Poland (1918–1939), Bialystok Voivodeship was located in the country's mid-northern part. It bordered Germany (East Prussia) to the north-west, Lithuania to the north-east, Wilno Voivodeship and Nowogródek Voivodeship to the east, Polesie Voivodeship and Lublin Voivodeship to the south and Warsaw Voivodeship to the west. Its area was 26 036 km². The landscape was flat, with the mighty Bialowieza Forest located right in the middle. Population Inhabited mostly by Poles (in 1931 they made up 66.9% of the population), it also had significant Belarusian (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw Voivodeship (1919–1939)
Warsaw Voivodeship ( pl, województwo warszawskie) was a voivodeship of Poland in the years 1919–1939. Its capital and biggest city was Warsaw. Location and area In the years 1919–1939, Warsaw Voivodeship covered north-central part of Poland, bordering East Prussia to the north, Pomorze Voivodeship and Łódź Voivodeship to the west, Kielce Voivodeship to the south and both Lublin Voivodeship and Białystok Voivodeship to the east. Its area, after April 1, 1938, was 31 656 km² (see: Territorial changes of Polish Voivodeships on 1 April 1938). The landscape was flat. Forests covered only 11.4% of the area, compared to the national average of 22.2%, as of January 1, 1937. Population According to the 1931 Polish census, the population was 2 460 900. Poles made up 88.3% of population, Jews - 9.7% and Germans - 1.6%. The Jews and the Germans preferred to live in the cities and towns, especially in Warsaw itself. In Warsaw, in 1931, only 70.7% of population was Polish, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital City Of Warsaw (1919–39)
Capital may refer to: Common uses * Capital city, a municipality of primary status ** List of national capital cities * Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences * Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used for further production *Economic capital * Financial capital, an economic resource measured in terms of money *Capital (Marxism), a central concept in Marxian critique of political economy *Capital good *Natural capital *Public capital *Human capital *Instructional capital *Social capital Architecture and buildings * Capital (architecture), the topmost member of a column or pilaster * Capital (fortification), a proportion of a bastion * The Capital (building), a commercial building in Mumbai, India Arts, entertainment and media Literature Books * ''Das Kapital'' ('Capital: Critique of Political Economy'), a foundational theoretical text by Karl Marx * '' Capital: The Eruption of Delhi'', a 2014 book by Rana Dasgupta * ''Capital'' (novel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |