|
Abu Talha Al-Ansari
Abū Ṭalḥa, Zayd ibn Sahl ibn al-Aswad ibn Ḥarām al-Khazrajī () was a renowned companion of the Islamic prophet Muḥammad and one of the Anṣār (the ‘Helpers’) of Medina. He was from Banu Khazraj, which after the Hijrah came to be known as the Ansar. He was mostly known as a valiant fighter and skilful archer of the early Islamic period. Abū Ṭalḥa was known to have been a horseman of Muhammad and was at Muhammad's side during the oath of allegiance at al- ʿAqaba and in the battles of Badr, Uḥud and Khandaq. He died at the age of 70 in the year 34/654 in Medina. Those who narrated from him include: Anas ibn Malik, Ibn Abbas, 'Abd al-Rahman ibn 'Abd al-Qari, 'Abd Allah ibn Abu Talha and Ishaq ibn 'Abd Allah ibn Abi Talha, with the penultimate and last of whom being his son and grandson.al-Dhahabi, Siyar A'lam al-Nubala', 2:27 Shuaib Al Arna'ut remarked the feat of Abu Talhah in battlefield which testified by Anas ibn Malik Anas ibn Mālik ibn Naḍr al-K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahabah
The Companions of the Prophet ( ar, اَلصَّحَابَةُ; ''aṣ-ṣaḥāba'' meaning "the companions", from the verb meaning "accompany", "keep company with", "associate with") were the disciples and followers of Muhammad who saw or met him during his lifetime, while being a Muslim and were physically in his presence. "Al-ṣaḥāba" is definite plural; the indefinite singular is masculine ('), feminine ('). Later Islamic scholars accepted their testimony of the words and deeds of Muhammad, the occasions on which the Quran was revealed and other various important matters of Islamic history and practice. The testimony of the companions, as it was passed down through trusted chains of narrators (''isnad''s), was the basis of the developing Islamic tradition. From the traditions (''hadith'') of the life of Muhammad and his companions are drawn the Muslim way of life (''sunnah''), the code of conduct (''sharia'') it requires, and the jurisprudence (''fiqh'') by which M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muḥammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monotheistic teachings of Adam, Abraham, Moses, Jesus, and other prophets. He is believed to be the Seal of the Prophets within Islam. Muhammad united Arabia into a single Muslim polity, with the Quran as well as his teachings and practices forming the basis of Islamic religious belief. Muhammad was born approximately 570CE in Mecca. He was the son of Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Amina bint Wahb. His father Abdullah was the son of Quraysh tribal leader Abd al-Muttalib ibn Hashim, and he died a few months before Muhammad's birth. His mother Amina died when he was six, leaving Muhammad an orphan. He was raised under the care of his grandfather, Abd al-Muttalib, and paternal uncle, Abu Talib. In later years, he would periodically seclude himsel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ansar (Islam)
The ''Ansar'' ( ar, الأنصار, al-Anṣār, The Helpers’ or ‘Those who bring victory) were the local inhabitants of Medina who, in Islamic tradition, took the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his followers (the '' Muhajirun'') into their homes when they emigrated from Mecca during the ''hijra''. They belonged to the tribes of Banu Khazraj and Banu Aus. Background The Medinese, which consisted of Aws and Khazraj, along with their Jewish allies, Banu Nadir, Banu Qurayza, and Banu Qaynuqa, were involved in degenerating years of warfare such as battle of Sumair, battle of Banu Jahjaha of Aus-Banu Mazin of Khazraj, battle of Sararah day, battle of Banu Wa'il ibn Zayd, battle of Zhufr-Malik, battle of Fari', battle of Hathib, battle of Rabi' day, first battle of Fijar in Yathrib (not Fijar war between Qays with Kinana in Mecca), battle of Ma'is, battle of Mudharras, and second battle of Fijar in Yathrib. The Medinese also even contacted against foreign invaders came from outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the Holiest sites in Islam, second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province of Saudi Arabia. , the estimated population of the city is 1,488,782, making it the List of cities and towns in Saudi Arabia, fourth-most populous city in the country. Located at the core of the Medina Province in the western reaches of the country, the city is distributed over , of which constitutes the city's urban area, while the rest is occupied by the Hijaz Mountains, Hejaz Mountains, empty valleys, Agriculture in Saudi Arabia, agricultural spaces and older dormant volcanoes. Medina is generally considered to be the "cradle of Islamic culture and civilization". The city is considered to be the second-holiest of three key cities in Islamic tradition, with Mecca and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Khazraj
The Banu Khazraj ( ar, بنو خزرج) is a large Arab tribe based in Medina. They were also in Medina during Muhammad's era. The Banu Khazraj are a South Arabian tribe that were pressured out of South Arabia in the Karib'il Watar 7th century BC war versus Awsan and its allies (Aws - Awsan), (Qataban - Ghatafan), when the Sabaeans were eventually defeated by the Himyarites, the settled tribes became the pre-Islamic Azd tribe and were known as ''Banū Qayla'' ( ) in pre-Islamic era. Early history Abu Muhammad Al-Hasan Ibn Ahmad Al-Hamdani mentioned that the Banu Khazraj and the Banu Aws settled the area of Yathrib around the 2nd century AD as part of the Pre-Islamic Exodus of Yemen because of the Great Marib Dam damage. However, all sources agree that the Banu Khazraj and Banu Aws became hostile to each other. Jewish chronicles state that they went to war against each other in the Battle of Bu'ath a few years before the Islamic prophet Muhammad migrated to Medina.jewishenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hijra (Islam)
The Hijrah or Hijra () was the journey of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his followers from Mecca to Medina. The year in which the Hijrah took place is also identified as the epoch of the Lunar Hijri and Solar Hijri calendars; its date equates to 16 July 622 in the Julian calendar. The Arabic word ''hijra'' means "departure" or "migration", among other definitions. It has been also transliterated as Hegira in medieval Latin, a term still in occasional use in English. Early in Muhammad's preaching of Islam, his followers only included his close friends and relatives. Following the spread of his religion, Muhammad and his small faction of Muslims faced several challenges including a boycott of Muhammad's clan, torture, killing, and other forms of religious persecution by the Meccans. Toward the end of the decade, Abu Talib, Muhammad's uncle, who supported him amidst the leaders of Mecca, died. Finally, the leaders of Mecca ordered the assassination of Muhammad, which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Pledge At Al-Aqabah
The second pledge at al-Aqabah was an important event in the mission of the Islamic prophet Muhammad where 75 residents of the city of Medina pledged their loyalty to Muhammad as their leader in an agreement known as a ''bay'ah''. It preceded the ''Hijrah'', or migration of Muhammad and his supporters to Medina where Muhammad became ruler, from Mecca where they were persecuted. The pledge occurred in 622 CE at a mountain pass (al-Aqabah) five kilometers from Mecca. Event Converts to Islam came from both non-Jewish Arab tribes present in Medina, such that by June of the subsequent year there were seventy-five Muslims coming to Mecca for pilgrimage and to meet Muhammad. Meeting him secretly by night, the group made what was known as the "''Second Pledge of al-`Aqaba''", or "The Second Pledge of Mount Aqabah" where the pledge was made. The guarantee of protection led Orientalists and Muslim scholars to describe it as "''Pledge of War''".Watt (1974) p. 83 Conditions of the pledge, many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
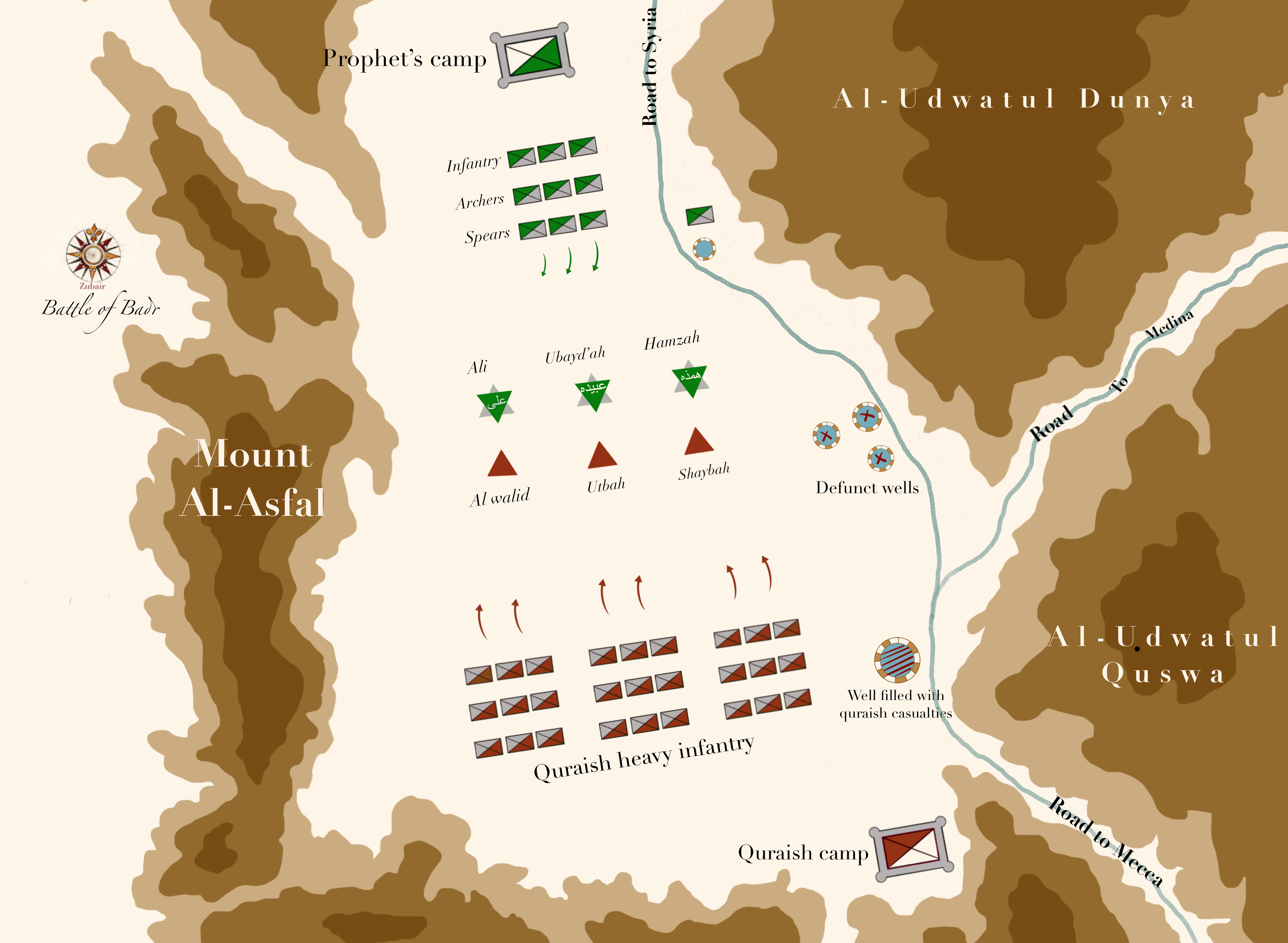
Battle Of Badr
The Battle of Badr ( ar, غَزْوَةُ بَدِرْ ), also referred to as The Day of the Criterion (, ) in the Quran, Qur'an and by Muslims, was fought on 13 March 624 CE (17 Ramadan (calendar month), Ramadan, 2 Anno Hegirae, AH), near the present-day city of Badr, Saudi Arabia, Badr, Madinah Province, Al Madinah Province in Saudi Arabia. Muhammad, commanding an army of his Companions of the Prophet, Sahaba, defeated an army of the Quraysh led by Amr ibn Hishām, better known as Abu Jahl. The battle marked the beginning of the six-year war between Muhammad and his tribe. Prior to the battle, the Muslims and the Meccans had fought several smaller skirmishes in late 623 and early 624. Muhammad took keen interest in capturing Meccan caravans after Hegira, his migration to Medina, seeing it as repayment for his people, the Muhajirun. A few days before the battle, when he learnt of a Makkan caravan returning from the Levant led by Abu Sufyan ibn Harb, Muhammad gathered a small E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Uhud
The Battle of Uhud ( ar, غَزْوَة أُحُد, ) was fought on Saturday, 23 March 625 AD (7 Shawwal, 3 AH), in the valley north of Mount Uhud.Watt (1974) p. 136. The Qurayshi Meccans, led by Abu Sufyan ibn Harb, commanded an army of 3,000 men toward Muhammad's stronghold in Medina. The battle was the only battle throughout the Muslim–Quraysh War in which the Muslims did not manage to defeat their enemy and it came just a year after the Battle of Badr. Abu Sufyan became the ''de facto'' leader of the Quraish after the death of Amr ibn Hishām at Badr nine months prior. Wanting to avenge the Meccan's losses at the Battle of Badr, he marched upon Medina from Makkah on 10 December 624 AD with a force three times stronger than that of the Meccans at Badr. Another reason for the battle was to protect the trade route of Abu Sufyan's caravans. The Battle of Uhud was the second military encounter between the Meccans and the Muslims and the first one in which the Muslims were on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Trench
The Battle of the Trench ( ar, غزوة الخندق, Ghazwat al-Khandaq), also known as the Battle of Khandaq ( ar, معركة الخندق, Ma’rakah al-Khandaq) and the Battle of the Confederates ( ar, غزوة الاحزاب, Ghazwat al-Ahzab), took place in the year 627; it was a 27-day-long defense by Muslims of Yathrib (now Medina) from Arab and Jewish tribes. The strength of the confederate armies is estimated at around 10,000 men with six hundred horses and some camels, while the Medinan defenders numbered 3,000. The largely outnumbered defenders of Medina, mainly Muslims led by the Islamic prophet Muhammad, dug a trench on the suggestion of Salman the Persian, which, together with Medina's natural fortifications, rendered the confederacy's cavalry (consisting of horses and camels) useless, locking the two sides in a stalemate. Hoping to make several attacks at once, the confederates persuaded the Muslim-allied Medinan Jews, Banu Qurayza, to attack the city from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anas Ibn Malik
Anas ibn Mālik ibn Naḍr al-Khazrajī al-Anṣārī ( ar, أنس بن مالك الخزرجي الأنصاري (c.612 – c.712 Finding the Truth in Judging the Companions, 1. 84-5; EI2, 1. 482 A. J. Wensinck J. Robson) was a well-known ''sahabi'' (companion) of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Biography Anas ibn Malik, a member of the Najjar clan of the Khazraj tribe of Yathrib, was born ten years before the Muhammad's Hijrah. After his father, Malik ibn Nadr, died a non-Muslim, his mother, Umm Sulaim, remarried to a new convert, Abu Talha ibn Thabit. Anas's half-brother from this marriage was Abdullah ibn Abi Talha.Biography of Rumaysa bint Milhan - Mother of Anas bin Malik at Compendium of Muslim Texts When Muhammad arrived in Medina in 62 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Abbas
ʿAbd Allāh ibn ʿAbbās ( ar, عَبْد ٱللَّٰه ٱبْن عَبَّاس; c. 619 – 687 CE), also known as Ibn ʿAbbās, was one of the cousins of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He is considered to be the greatest mufassir of the Qur'an. He was the son of Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib, an uncle of Muhammad, and a nephew of Maymunah bint al-Harith, who later became Muhammad's wife. During the early struggles for the caliphate he supported Ali, and was made governor of Basra. He withdrew to Mecca shortly afterwards. During the reign of Mu'awiya I he lived in Hejaz and often travelled to Damascus. After Mu'awiya I died in 680 CE he fled to at-Ta'if, where he died in around 687 CE. 'Abd Allah ibn Abbas was highly regarded for his knowledge of traditions and his critical interpretation of the Qur'an. From early on, he gathered information from other companions of Muhammad and gave classes and wrote commentaries. Biography Family He was the third son of a wealthy merchant, ‘A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)