|
ATP6V1G2
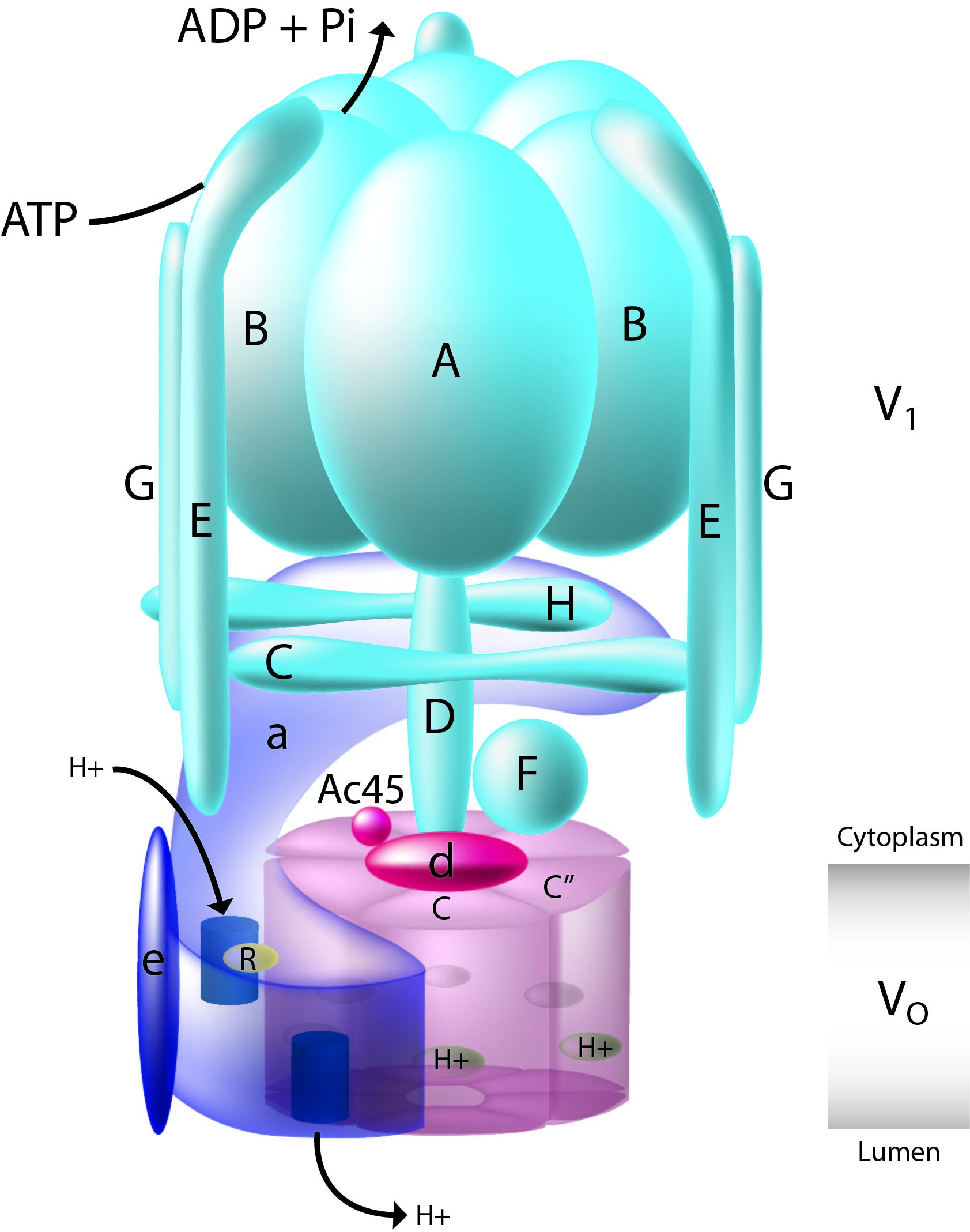
V-type proton ATPase subunit G 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ATP6V1G2'' gene. This gene encodes a component of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of intracellular compartments of eukaryotic cells. V-ATPase dependent acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and synaptic vesicle proton gradient generation. V-ATPase is composed of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. The V1 domain consists of three A and three B subunits, two G subunits plus the C, D, E, F, and H subunits. The V1 domain contains the ATP catalytic site. The V0 domain consists of five different subunits: a, c, c', c double prime, and d. Additional isoforms of many of the V1 and V0 subunit proteins are encoded by multiple genes, or alternatively spliced transcript variants. This encoded protein is one of three V1 domain G subunit proteins. This gene had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuolar ATPase
Vacuolar-type ATPase (V-ATPase) is a highly conserved evolutionarily ancient enzyme with remarkably diverse functions in eukaryotic organisms. V-ATPases acidify a wide array of intracellular organelles and pumps protons across the plasma membranes of numerous cell types. V-ATPases couple the energy of ATP hydrolysis to proton transport across intracellular and plasma membranes of eukaryotic cells. It is generally seen as the polar opposite of ATP synthase because ATP synthase is a proton channel that uses the energy from a proton gradient to produce ATP. V-ATPase however, is a proton pump that uses the energy from ATP hydrolysis to produce a proton gradient. The Archaea-type ATPase (A-ATPase) is a related group of ATPases found in archaea that often work as an ATP synthase. It forms a clade V/A-ATPase with V-ATPase. Most members of either group shuttle protons (), but a few members have evolved to use sodium ions () instead. Roles played by V-ATPases V-ATPases are foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton ATPase
In the field of enzymology, a proton ATPase is an enzyme that catalyzes the following chemical reaction: :ATP + + in \rightleftharpoons ADP + phosphate + out The 3 substrates of this enzyme are ATP, , and , whereas its 3 products are ADP, phosphate, and . Proton ATPases are divided into three groups as outlined below: P-type proton ATPase P-type ATPases form a covalent phosphorylated (hence the symbol ’P') intermediate as part of its reaction cycle. P-type ATPases undergo major conformational changes during the catalytic cycle. P-type ATPases are not evolutionary related to V- and F-type ATPases. Plasma membrane H+-ATPase P-type proton ATPase (or plasma membrane -ATPase) is found in the plasma membranes of eubacteria, archaea, protozoa, fungi and plants. Here it serves as a functional equivalent to the Na+/K+ ATPase of animal cells; i.e. it energizes the plasma membrane by forming an electrochemical gradient of protons (Na+ in animal cells), that in turn drives seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). Euka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Sorting
:''This article deals with protein targeting in eukaryotes unless specified otherwise.'' Protein targeting or protein sorting is the biological mechanism by which proteins are transported to their appropriate destinations within or outside the cell. Proteins can be targeted to the inner space of an organelle, different intracellular membranes, the plasma membrane, or to the exterior of the cell via secretion. Information contained in the protein itself directs this delivery process. Correct sorting is crucial for the cell; errors or dysfunction in sorting have been linked to multiple diseases. History In 1970, Günter Blobel conducted experiments on protein translocation across membranes. Blobel, then an assistant professor at Rockefeller University, built upon the work of his colleague George Palade. Palade had previously demonstrated that non-secreted proteins were translated by free ribosomes in the cytosol, while secreted proteins (and target proteins, in general) were tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zymogen
In biochemistry, a zymogen (), also called a proenzyme (), is an inactive precursor of an enzyme. A zymogen requires a biochemical change (such as a hydrolysis reaction revealing the active site, or changing the configuration to reveal the active site) for it to become an active enzyme. The biochemical change usually occurs in Golgi bodies, where a specific part of the precursor enzyme is cleaved in order to activate it. The inactivating piece which is cleaved off can be a peptide unit, or can be independently-folding domains comprising more than 100 residues. Although they limit the enzyme's ability, these N-terminal extensions of the enzyme or a “prosegment” often aid in the stabilization and folding of the enzyme they inhibit. The pancreas secretes zymogens partly to prevent the enzymes from digesting proteins in the cells in which they are synthesised. Enzymes like pepsin are created in the form of pepsinogen, an inactive zymogen. Pepsinogen is activated when chief ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. Endocytosis includes pinocytosis (cell drinking) and phagocytosis (cell eating). It is a form of active transport. History The term was proposed by De Duve in 1963. Phagocytosis was discovered by Élie Metchnikoff in 1882. Pathways Endocytosis pathways can be subdivided into four categories: namely, receptor-mediated endocytosis (also known as clathrin-mediated endocytosis), caveolae, pinocytosis, and phagocytosis Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is .... *Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is mediated by the production of smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Vesicle
In a neuron, synaptic vesicles (or neurotransmitter vesicles) store various neurotransmitters that are released at the synapse. The release is regulated by a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Vesicles are essential for propagating nerve impulses between neurons and are constantly recreated by the cell. The area in the axon that holds groups of vesicles is an axon terminal or "terminal bouton". Up to 130 vesicles can be released per bouton over a ten-minute period of stimulation at 0.2 Hz. In the visual cortex of the human brain, synaptic vesicles have an average diameter of 39.5 nanometers (nm) with a standard deviation of 5.1 nm. Structure Synaptic vesicles are relatively simple because only a limited number of proteins fit into a sphere of 40 nm diameter. Purified vesicles have a protein:phospholipid ratio of 1:3 with a lipid composition of 40% phosphatidylcholine, 32% phosphatidylethanolamine, 12% phosphatidylserine, 5% phosphatidylinositol, and 10% chole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton Gradient
An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consists of two parts, the chemical gradient, or difference in solute concentration across a membrane, and the electrical gradient, or difference in charge across a membrane. When there are unequal concentrations of an ion across a permeable membrane, the ion will move across the membrane from the area of higher concentration to the area of lower concentration through simple diffusion. Ions also carry an electric charge that forms an electric potential across a membrane. If there is an unequal distribution of charges across the membrane, then the difference in electric potential generates a force that drives ion diffusion until the charges are balanced on both sides of the membrane. Electrochemical gradients are essential to the operation of batteries and other electrochemical cells, photosynthesis and cellular respiration, and certain other bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |