|
ARHGEF10L
Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ARHGEF1'' gene. This protein is also called RhoGEF1 or p115-RhoGEF. Function Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1 is guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for the RhoA small GTPase protein. Rho is a small GTPase protein that is inactive when bound to the guanine nucleotide GDP. But when acted on by Rho GEF proteins such as RhoGEF1, this GDP is released and replaced by GTP, leading to the active state of Rho. In this active, GTP-bound conformation, Rho can bind to and activate specific effector proteins and enzymes to regulate cellular functions. In particular, active Rho is a major regulator of the cell actin cytoskeleton. RhoGEF1 is a member of a group of four RhoGEF proteins known to be activated by G protein coupled receptors coupled to the G12 and G13 heterotrimeric G proteins. The others are ARHGEF11 (also known as PDZ-RhoGEF), ARHGEF12 (also known as LARG) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARHGEF11
Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ARHGEF11'' gene. This protein is also called RhoGEF11 or PDZ-RhoGEF. Function Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 11 is guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for the RhoA small GTPase protein. Rho is a small GTPase protein that is inactive when bound to the guanine nucleotide GDP. But when acted on by Rho GEF proteins such as RhoGEF1, this GDP is released and replaced by GTP, leading to the active state of Rho. In this active, GTP-bound conformation, Rho can bind to and activate specific effector proteins and enzymes to regulate cellular functions. In particular, active Rho is a major regulator of the cell actin cytoskeleton. RhoGEF11 is a member of a group of four RhoGEF proteins known to be activated by G protein coupled receptors coupled to the G12 and G13 heterotrimeric G proteins. The others are ARHGEF1 (also known as p115-RhoGEF), ARHGEF12 (also known as LARG) and AKAP13 (al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
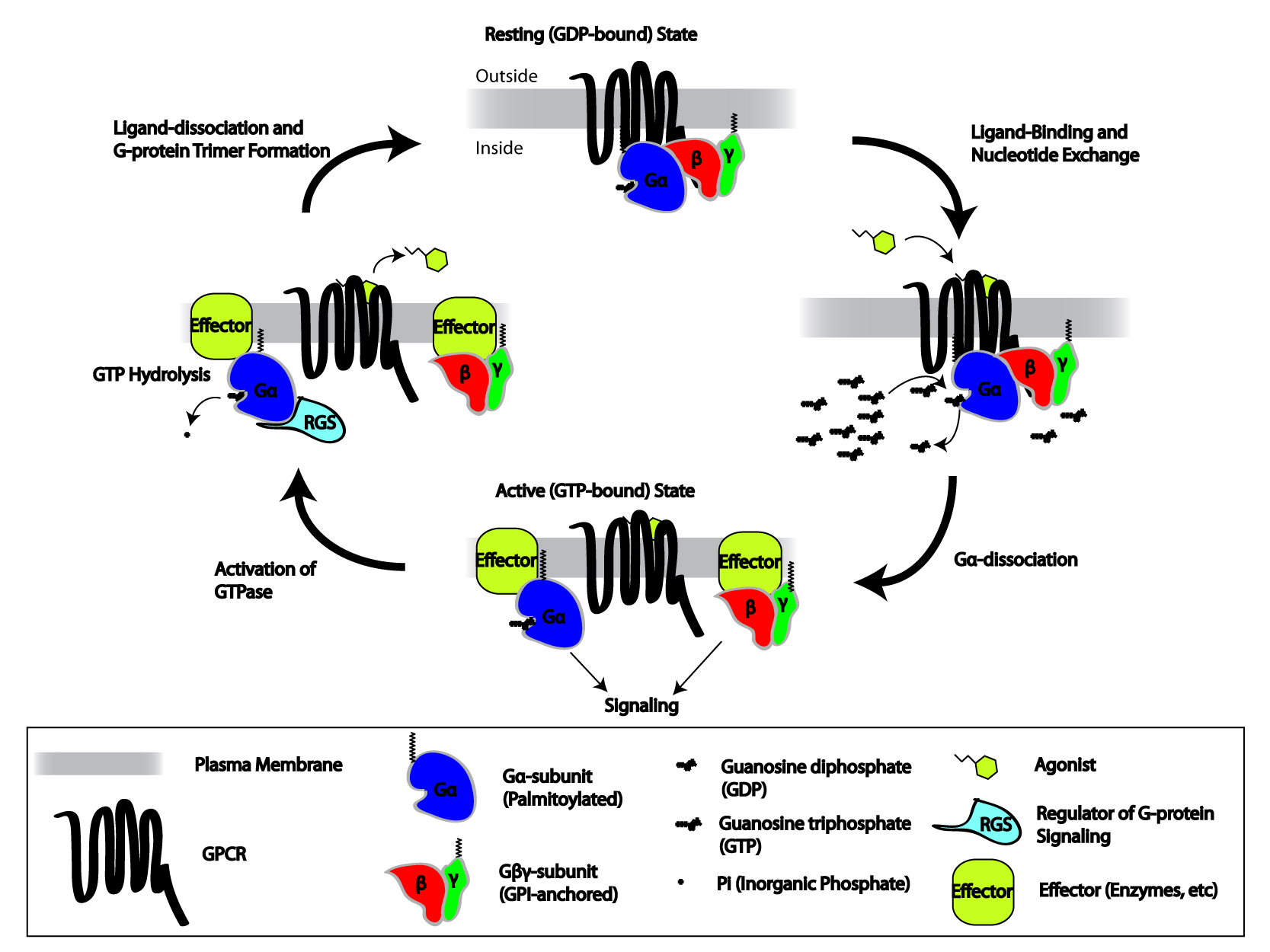
Heterotrimeric G Protein
Heterotrimeric G protein, also sometimes referred to as the ''"large" G proteins'' (as opposed to the subclass of smaller, monomeric small GTPases) are membrane-associated G proteins that form a Heteromer, heterotrimeric complex. The biggest non-structural difference between heterotrimeric and monomeric G protein is that heterotrimeric proteins bind to their cell-surface receptors, called G protein-coupled receptors, directly. These G proteins are made up of ''alpha'' (α), ''beta'' (β) and ''gamma'' (γ) Protein subunit, subunits. The alpha subunit is attached to either a GTP or GDP, which serves as an on-off switch for the activation of G-protein. When ligands bind a GPCR, the GPCR acquires GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor) ability, which activates the G-protein by exchanging the GDP on the ''alpha'' subunit to GTP. The binding of GTP to the ''alpha'' subunit results in a structural change and its dissociation from the rest of the G-protein. Generally, the ''alpha'' su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
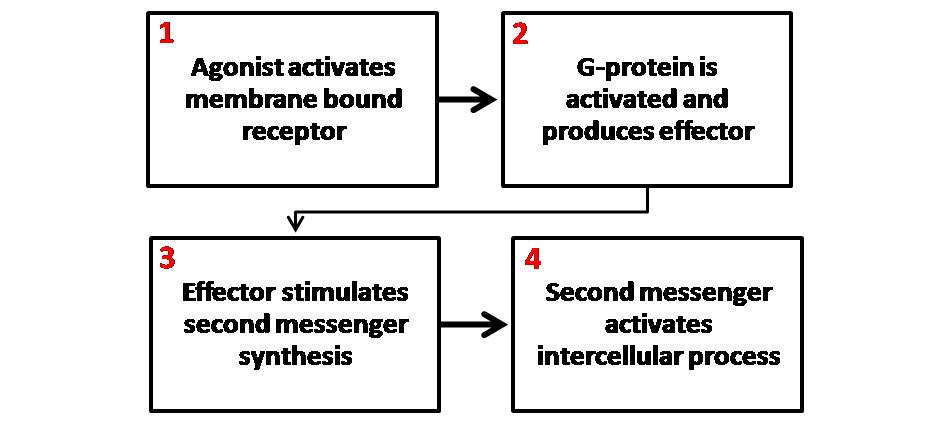
G Protein-coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) license. Ligands can bind either to extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site within transmembrane helices (Rhodopsin-like family). They are all activated by agonists although a spontaneous auto-activation of an empty receptor can also be observed. G protein-coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Messenger System
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form or cell signaling, encompassing both first messengers and second messengers, are classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, paracrine, and endocrine depending on the range of the signal.) Second messengers trigger physiological changes at cellular level such as proliferation, differentiation, migration, survival, apoptosis and depolarization. They are one of the triggers of intracellular signal transduction cascades. Examples of second messenger molecules include cyclic AMP, cyclic GMP, inositol triphosphate, diacylglycerol, and calcium. First messengers are extracellular factors, often hormones or neurotransmitters, such as epinephrine, growth hormone, and serotonin. Because peptide hormones and neurotransmitters typically are biochemically hydrophilic molecules, these first messenger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P110α
The phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase, catalytic subunit alpha (the HUGO-approved official symbol = PIK3CA; HGNC ID, HGNC:8975), also called p110α protein, is a class I PI 3-kinase catalytic subunit. The human p110α protein is encoded by the ''PIK3CA'' gene. Its role was uncovered by molecular pathological epidemiology (MPE). Function Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase (also called phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)) is composed of an 85 kDa regulatory subunit and a 110 kDa catalytic subunit. The protein encoded by this gene represents the catalytic subunit, which uses ATP to phosphorylate phosphatidylinositols (PtdIns), PtdIns4P and PtdIns(4,5)P2. The involvement of p110α in human cancer has been hypothesized since 1995. Support for this hypothesis came from genetic and functional studies, including the discovery of common activating PIK3CA missense mutations in common human tumors. It has been found to be oncogenic and is implicated in cervi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNA13
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GNA13'' gene. Interactions and functions The GNA13 gene encodes the G13 G protein alpha subunit. Together with GNA12, these two proteins comprise one of the four classes of heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunits. Heterotrimeric G proteins function in transducing hormone and neurotransmitter signals detected by cell surface G protein-coupled receptors to intracellular signaling pathways to modulate cell functions. G protein alpha subunits bind to guanine nucleotides and function in a regulatory cycle, and are active when bound to GTP but inactive and associated with the G beta-gamma complex when bound to GDP. Active GTP-bound G12 alpha subunit interacts with and activates ARHGEF1, ARHGEF11, and ARHGEF12. These ARHGEF proteins function as guanine nucleotide exchange factors for the Rho small GTPases to regulate the actin cytoskeleton. GNA13 has been shown to interact with AKA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNA12
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GNA12'' gene. Interactions and functions The GNA12 gene encodes the G12 G protein alpha subunit. Together with GNA13, these two proteins comprise one of the four classes of heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunits. Heterotrimeric G proteins function in transducing hormone and neurotransmitter signals detected by cell surface G protein-coupled receptors to intracellular signaling pathways to modulate cell functions. G protein alpha subunits bind to guanine nucleotides and function in a regulatory cycle, and are active when bound to GTP but inactive and associated with the G beta-gamma complex when bound to GDP. Active GTP-bound G12 alpha subunit interacts with and activates ARHGEF1, ARHGEF11, and ARHGEF12. These ARHGEF proteins function as guanine nucleotide exchange factors for the Rho small GTPases to regulate the actin cytoskeleton. GNA12 also interacts with PPP5C, HSP90, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD44
The CD44 antigen is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell–cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration. In humans, the CD44 antigen is encoded by the ''CD44'' gene on chromosome 11. CD44 has been referred to as HCAM (homing cell adhesion molecule), Pgp-1 (phagocytic glycoprotein-1), Hermes antigen, lymphocyte homing receptor, ECM-III, and HUTCH-1. Tissue distribution and isoforms CD44 is expressed in a large number of mammalian cell types. The standard isoform, designated CD44s, comprising exons 1–5 and 16–20 is expressed in most cell types. CD44 splice variants containing variable exons are designated CD44v. Some epithelial cells also express a larger isoform (CD44E), which includes exons v8–10. Function CD44 participates in a wide variety of cellular functions including lymphocyte activation, recirculation and homing, hematopoiesis, and tumor metastasis. CD44 is a receptor for hyaluronic acid and can also interact with other ligands, such as osteop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GTPase-activating Proteins
GTPase-activating proteins or GTPase-accelerating proteins (GAPs) are a family of regulatory proteins whose members can bind to activated G proteins and stimulate their GTPase activity, with the result of terminating the signaling event. GAPs are also known as RGS protein, or RGS proteins,Kimple, A.J. "Structural Determinants of G-protein α Subunit Selectivity by Regulator of G-protein Signaling 2 (RGS2)". ''The Journal of Biological Chemistry''. 284 (2009): 19402-19411. and these proteins are crucial in controlling the activity of G proteins. Regulation of G proteins is important because these proteins are involved in a variety of important cellular processes. The large G proteins, for example, are involved in transduction of signaling from the G protein-coupled receptor for a variety of signaling processes like hormonal signaling, and small G proteins are involved in processes like cellular trafficking and cell cycling. GAP's role in this function is to turn the G protein's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulator Of G Protein Signaling
Regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) are protein structural domains or the proteins that contain these domains, that function to activate the GTPase activity of heterotrimeric G-protein α-subunits. RGS proteins are multi-functional, GTPase-accelerating proteins that promote GTP hydrolysis by the α-subunit of heterotrimeric G proteins, thereby inactivating the G protein and rapidly switching off G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathways. Upon activation by receptors, G proteins exchange GDP for GTP, are released from the receptor, and dissociate into a free, active GTP-bound α-subunit and βγ-dimer, both of which activate downstream effectors. The response is terminated upon GTP hydrolysis by the α-subunit (), which can then re-bind the βγ-dimer ( ) and the receptor. RGS proteins markedly reduce the lifespan of GTP-bound α-subunits by stabilising the G protein transition state. Whereas receptors stimulate GTP binding, RGS proteins stimulate GTP hydrolysis. RGS pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |