|
Azraq 18
Azraq 18 is an Epipalaeolithic archaeological site in the Azraq oasis, eastern Jordan. First recorded in a survey by Andrew Garrard and Nicholas Stanley-Price in 1975, and excavated by Garrard in 1985, it is one of many sites of prehistoric occupation around the perennial springs that feed the oasis. Of these, Azraq 18 is the only one associated with the Late Epipalaeolithic Natufian culture, which is dated to between around 15,000 to 11,500 years ago. Although the people of the Natufian culture were nomadic hunter-gatherers, Azraq 18 shows signs of repeated visits and use for long periods of time. The excavations revealed the remains of structures, heavy ground stone tools, finely-worked bone and microlithic stone tools, and a large volume of plant and animal remains. The animal remains included wild cattle and duck, indicating that the site was probably in or near to a wetland area. Notably, a collective burial of three adults and four children was discovered at the site; on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azraq Wetland Reserve, May 2017
Azraq ( ar, الأزرق meaning "blue") is a small town in Zarqa Governorate in central-eastern Jordan, east of Amman. The population of Azraq was 9,021 in 2004. The Muwaffaq Salti Air Base is located in Azraq. History Prehistory Archaeological evidence indicates that Azraq has been occupied for hundreds of thousands of years, with the oldest known remains dating to the Lower Palaeolithic, around 500–300,000 years ago. The spring-fed oasis provided a more or less constant source of water throughout this period, and probably acted as a refugium for humans and other animals at times when the surrounding area dried out. The oasis itself changed as the climate fluctuated: at times a permanent lake, a marsh, or a seasonal playa. During the Epipalaeolithic period the oasis was also an important focus of settlement. Later history Azraq has long been an important settlement in a remote and now-arid desert area of Jordan. The strategic value of the town and its castle ( Qasr A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovini
The Tribe (biology), tribe Bovini, or wild cattle, are medium to massive Bovinae, bovines that are native to North America, Eurasia, and Africa. These include the enigmatic, antelope-like saola, the African and Asiatic Bubalina, buffalos, and a clade that consists of bison and the wild cattle of the genus ''Bos''. Not only are they the largest members of the subfamily Bovinae, they are the largest species of their family Bovidae. The largest species is the gaur (''Bos gaurus''), weighing up to . Bovins and humans have had a long and complex relationship. Five of seven species have been successfully domesticated, with one species (cattle) being the most successful member of their lineage. Domesticated shortly after the Last Glacial Period, last ice age, Op. cit. in there are at least 1.4 billion cattle in the world. Domestic bovins have been selectively bred for beef, dairy products and leather, and serve as working animals. However, many species of wild cattle are threatened by e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1975 Archaeological Discoveries
It was also declared the ''International Women's Year'' by the United Nations and the European Architectural Heritage Year by the Council of Europe. Events January * January 1 - Watergate scandal (United States): John N. Mitchell, H. R. Haldeman and John Ehrlichman are found guilty of the Watergate cover-up. * January 2 ** The Federal Rules of Evidence are approved by the United States Congress. ** Bangladesh revolutionary leader Siraj Sikder is killed by police while in custody. ** A bomb blast at Samastipur, Bihar, India, fatally wounds Lalit Narayan Mishra, Minister of Railways. * January 5 – Tasman Bridge disaster: The Tasman Bridge in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, is struck by the bulk ore carrier , killing 12 people. * January 7 – OPEC agrees to raise crude oil prices by 10%. * January 10–February 9 – The flight of ''Soyuz 17'' with the crew of Georgy Grechko and Aleksei Gubarev aboard the ''Salyut 4'' space station. * January 15 – Alvor Agreement: Portugal an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ʿAin Mallaha
ʿAin Mallaha ( ar, عين ملاحة) or Eynan ( he, עינן) was an Epipalaeolithic settlement belonging to the Natufian culture, built and settled circa 10,000–8,000 BCE. The settlement is an example of hunter-gatherer sedentism, a crucial step in the transition from foraging to farming. ʿAin Mallaha has one of the earliest known archaeological evidence of dog domestication. The village This site is located in the Hula Valley of northern Israel, north of the Sea of Galilee, and is in an area surrounded by hills and located by an ancient lake, Lake Huleh. At the time of its Natufian inhabitance, the area was heavily forested in oak, almond, and pistachio trees. Evidence of settlement at Mallaha or ʿAin Mallaha dates back to the Mesolithic period at circa 10,000 BCE.Schmandt-Besserat, 2009, p47/ref> The first permanent village settlement of pre-agricultural times in Israel, Kathleen Kenyon describes the material remains found there as Natufian.Kenyon, 1985, p. 20.Kipf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic Skull Cult
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Grave
A mass grave is a grave containing multiple human corpses, which may or may not be identified prior to burial. The United Nations has defined a criminal mass grave as a burial site containing three or more victims of execution, although an exact definition is not unanimously agreed upon. Mass graves are usually created after many people die or are killed, and there is a desire to bury the corpses quickly for sanitation concerns. Although mass graves can be used during major conflicts such as war and crime, in modern times they may be used after a famine, epidemic, or natural disaster. In disasters, mass graves are used for infection and disease control. In such cases, there is often a breakdown of the social infrastructure that would enable proper identification and disposal of individual bodies. History Mass or communal burial was a common practice before the development of a dependable crematory chamber by Ludovico Brunetti in 1873. In ancient Rome waste and dead bodies of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The primary factor that distinguishes wetlands from terrestrial land forms or Body of water, water bodies is the characteristic vegetation of aquatic plants, adapted to the unique anoxic hydric soils. Wetlands are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as home to a wide range of plant and animal species. Methods for assessing wetland functions, wetland ecological health, and general wetland condition have been developed for many regions of the world. These methods have contributed to wetland conservation partly by raising public awareness of the functions some wetlands provide. Wetlands occur naturally on every continent. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or seawater, saltwater. The main w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form taxon; they do not represent a monophyletic group (the group of all descendants of a single common ancestral species), since swans and geese are not considered ducks. Ducks are mostly aquatic birds, and may be found in both fresh water and sea water. Ducks are sometimes confused with several types of unrelated water birds with similar forms, such as loons or divers, grebes, gallinules and coots. Etymology The word ''duck'' comes from Old English 'diver', a derivative of the verb 'to duck, bend down low as if to get under something, or dive', because of the way many species in the dabbling duck group feed by upending; compare with Dutch and German 'to dive'. This word replaced Old English / 'duck', possibly to avoid confusion with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
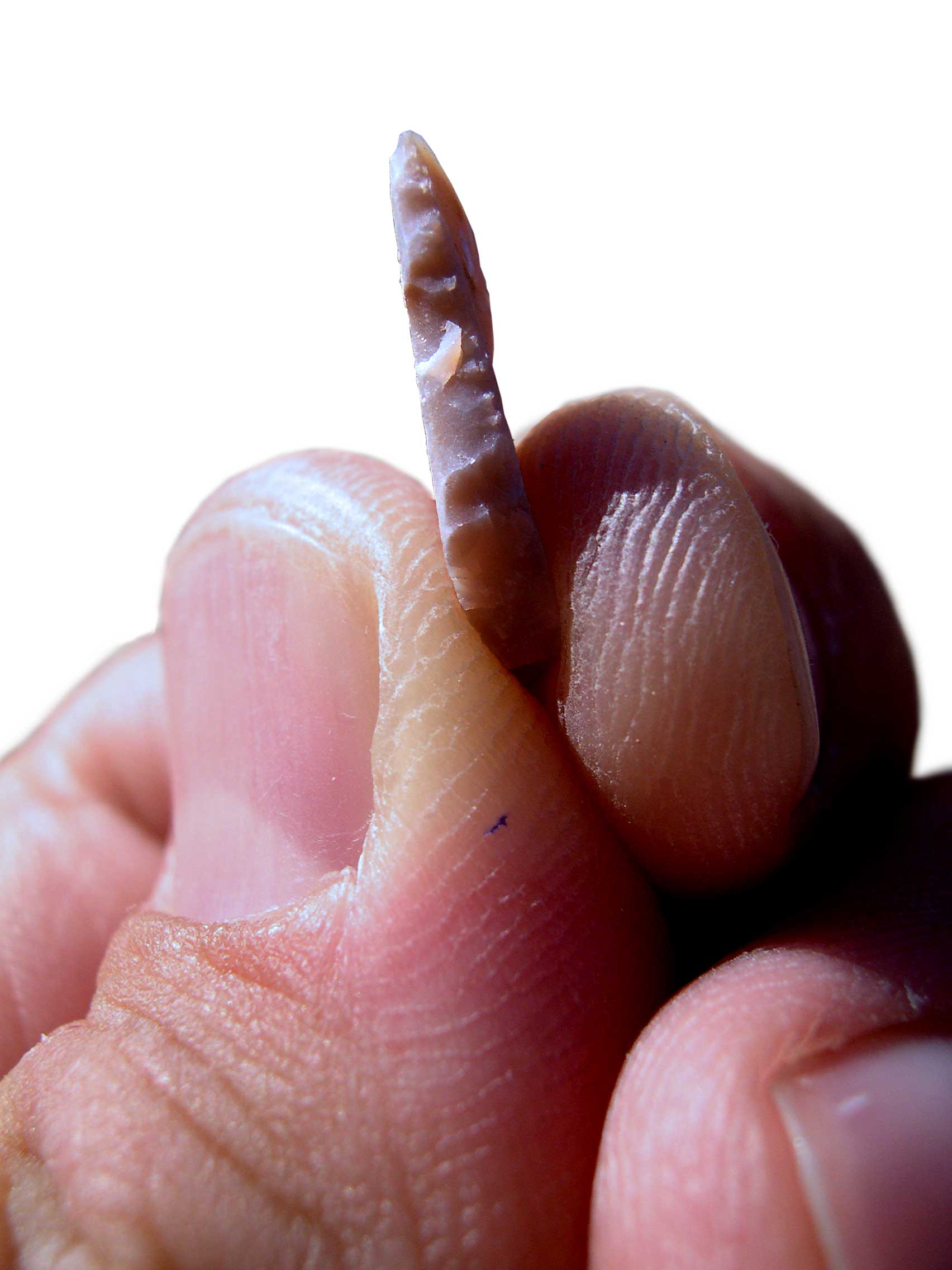
Microlith
A microlith is a small Rock (geology), stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 35,000 to 3,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. The microliths were used in spear points and arrowheads. Microliths are produced from either a small blade (Microblade technology, microblade) or a larger blade-like piece of flint by abrupt or truncated retouch (lithics), retouching, which leaves a very typical piece of waste, called a microburin. The microliths themselves are sufficiently worked so as to be distinguishable from workshop waste or accidents. Two families of microliths are usually defined: laminar and geometric. An assemblage of microliths can be used to date an archeological site. Laminar microliths are slightly larger, and are associated with the end of the Upper Paleolithic and the beginning of the Epipaleolithic era; geometric microliths are characteristic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
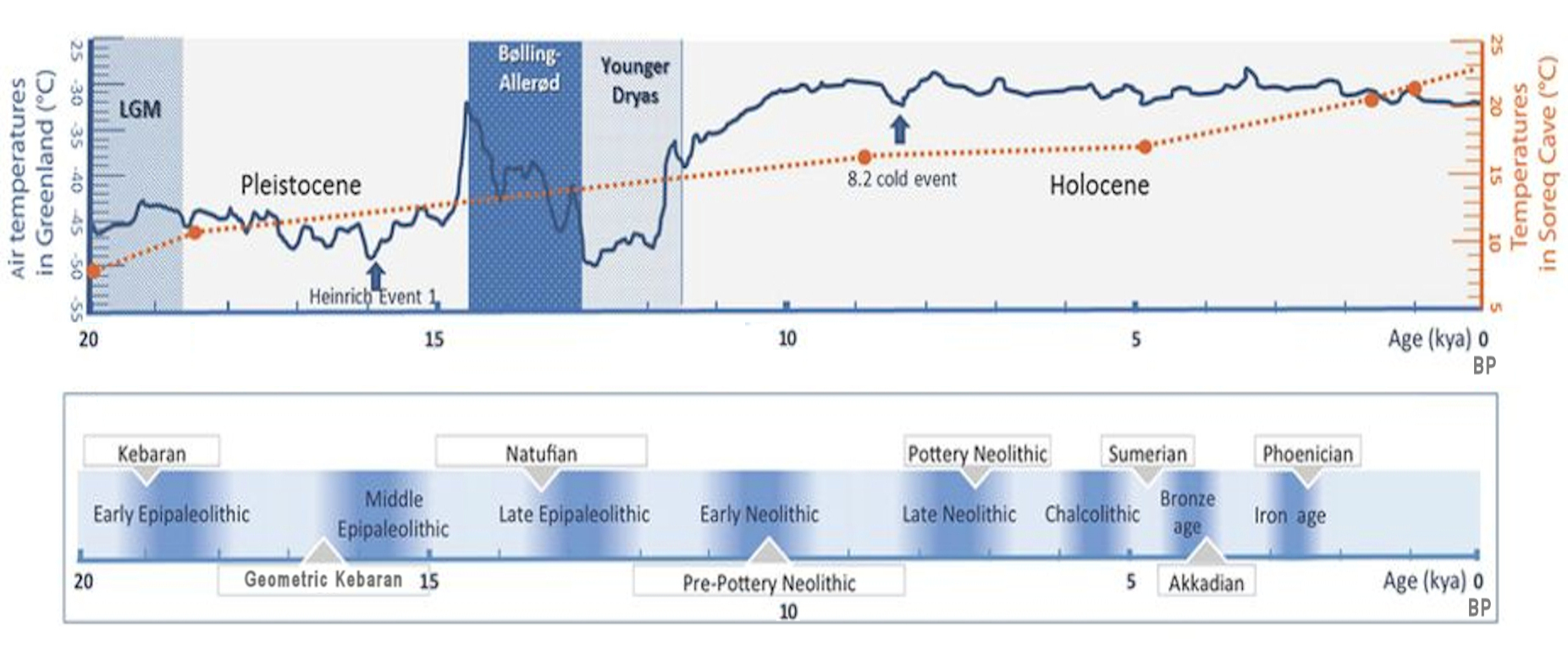
Epipalaeolithic Near East
The Epipalaeolithic Near East designates the Epipalaeolithic ("Final Old Stone Age", also known as Mesolithic) in the prehistory of the Near East. It is the period after the Upper Palaeolithic and before the Neolithic, between approximately 20,000 and 10,000 years Before Present (BP). The people of the Epipalaeolithic were nomadic hunter-gatherers who generally lived in small, seasonal camps rather than permanent villages. They made sophisticated stone tools using microliths—small, finely-produced blades that were hafted in wooden implements. These are the primary artifacts by which archaeologists recognise and classify Epipalaeolithic sites. The start of the Epipalaeolithic is defined by the appearance of microliths. Although this is an arbitrary boundary, the Epipalaeolithic does differ significantly from the preceding Upper Palaeolithic. Epipalaeolithic sites are more numerous, better preserved, and can be accurately radiocarbon dated. The period coincides with the gradual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |