|
Avenue At Middelharnis
''The Avenue at Middelharnis'' is a Dutch Golden Age painting of 1689 by Meindert Hobbema, now in the National Gallery, London. It is in oil on canvas and measures . It shows a road leading to the village of Middelharnis on the island of Goeree-Overflakkee in the Meuse ( nl, Maas) delta in South Holland, the Netherlands. The painting has long been one of the best-known Dutch landscape paintings, and certainly Hobbema's best-known work, at least in the English-speaking world: "it is as if the artist had produced only a single picture" according to Christopher Lloyd. Cornelis Hofstede de Groot, the great specialist of a century ago, thought it "the finest picture, next to Rembrandt's '' Syndics'', which has been painted in Holland". According to Michael Levey, "it occupies a position in painting somewhat equivalent to that in poetry of '' Gray's Elegy'', and for Seymour Slive "it is the swan song of Holland's great period of landscape painting which fully deserves its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray's Elegy
''Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard'' is a poem by Thomas Gray, completed in 1750 and first published in 1751. The poem's origins are unknown, but it was partly inspired by Gray's thoughts following the death of the poet Richard West in 1742. Originally titled ''Stanzas Wrote in a Country Church-Yard'', the poem was completed when Gray was living near the Church of St Giles, Stoke Poges. It was sent to his friend Horace Walpole, who popularised the poem among London literary circles. Gray was eventually forced to publish the work on 15 February 1751 in order to preempt a magazine publisher from printing an unlicensed copy of the poem. The poem is an elegy in name but not in form; it employs a style similar to that of contemporary odes, but it embodies a meditation on death, and remembrance after death. The poem argues that the remembrance can be good and bad, and the narrator finds comfort in pondering the lives of the obscure rustics buried in the churchyard. The two version ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Van Ruisdael
Jacob Isaackszoon van Ruisdael (; 1629 – 10 March 1682) was a Dutch painter, draughtsman, and etcher. He is generally considered the pre-eminent landscape painter of the Dutch Golden Age, a period of great wealth and cultural achievement when Dutch painting became highly popular. Prolific and versatile, Ruisdael depicted a wide variety of landscape subjects. From 1646 he painted Dutch countryside scenes of remarkable quality for a young man. After a trip to Germany in 1650, his landscapes took on a more heroic character. In his late work, conducted when he lived and worked in Amsterdam, he added city panoramas and seascapes to his regular repertoire. In these, the sky often took up two-thirds of the canvas. In total he produced more than 150 Scandinavian views featuring waterfalls. Ruisdael's only registered pupil was Meindert Hobbema, one of several artists who painted figures in his landscapes. Hobbema's work has at times been confused with Ruisdael's. Ruisdael ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
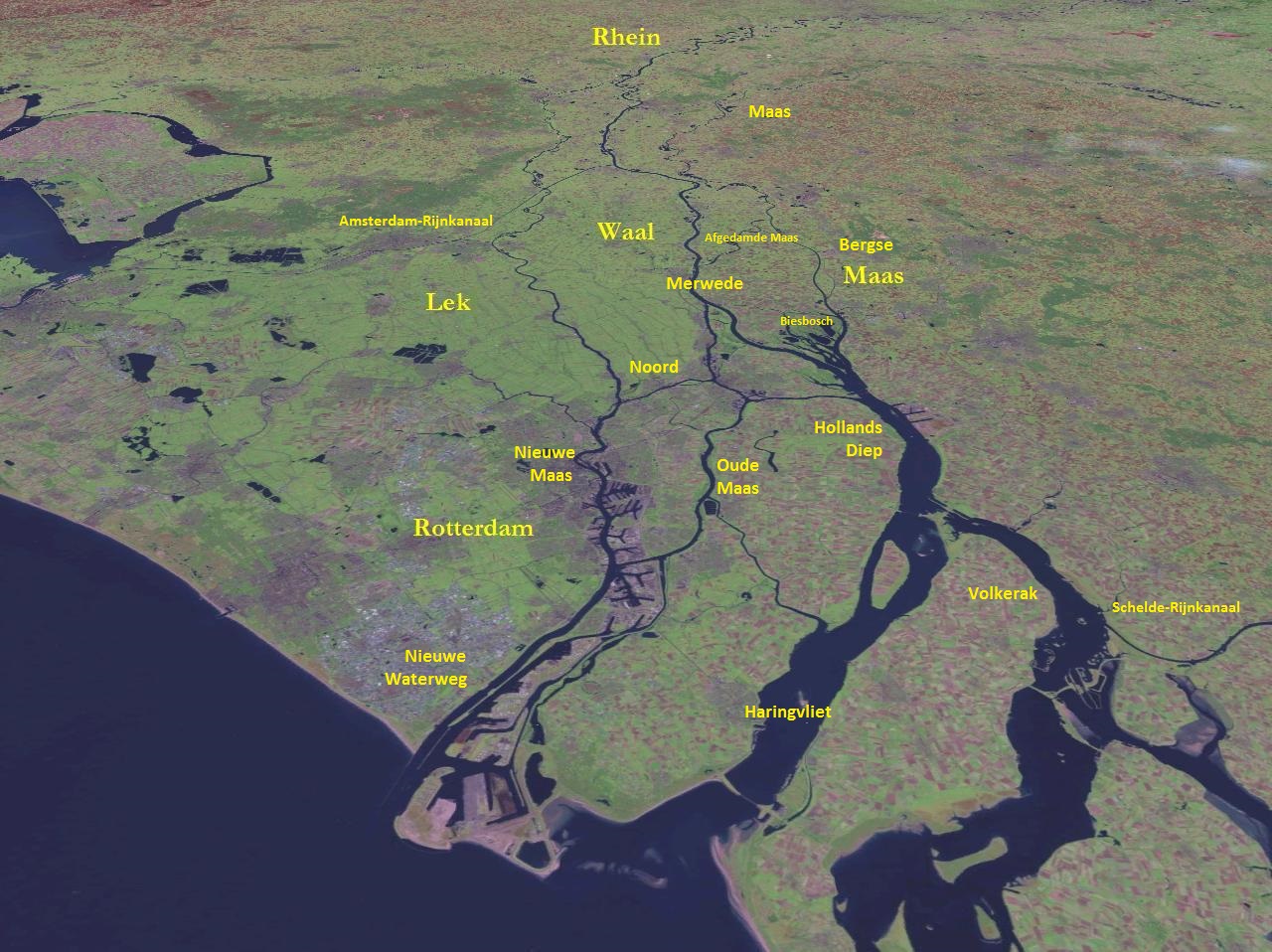
Meuse (river)
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a total length of . History From 1301 the upper Meuse roughly marked the western border of the Holy Roman Empire with the Kingdom of France, after Count Henry III of Bar had to receive the western part of the County of Bar (''Barrois mouvant'') as a French fief from the hands of King Philip IV. In 1408, a Burgundian army led by John the Fearless went to the aid of John III against the citizens of Liège, who were in open revolt. After the battle which saw the men from Liège defeated, John ordered the drowning in the Meuse of suspicious burghers and noblemen in Liège. The border remained stable until the annexation of the Three Bishoprics Metz, Toul and Verdun by King Henry II in 1552 and the occupation of the Duchy of Lorraine by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland , source1_coordinates= , source1_elevation = , source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein , source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland , source2_coordinates= , source2_elevation = , source_confluence = Reichenau , source_confluence_location = Tamins, Graubünden, Switzerland , source_confluence_coordinates= , source_confluence_elevation = , mouth = North Sea , mouth_location = Netherlands , mouth_coordinates = , mouth_elevation = , progression = , river_system = , basin_size = , tributaries_left = , tributaries_right = , custom_label = , custom_data = , extra = The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label= Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label= Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merwede
The Merwede () etymology uncertain, possibly derived from the ancient Dutch language, Dutch ''Merwe'' or ''Merowe'', a word meaning "wide water") is the name of several connected stretches of river in the Netherlands, between the cities of Woudrichem, Dordrecht and Papendrecht. The river is part of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and is mostly fed by the river Rhine. At first, a disconnected branch of the Meuse joins the Waal (river), Waal at Woudrichem to form the Boven Merwede (Upper Merwede). A few kilometers downstream it splits into the Beneden Merwede (Lower Merwede) on the right and the Nieuwe Merwede (New Merwede) on the left. All these rivers are tidal. The Nieuwe Merwede joins the Bergse Maas near Lage Zwaluwe to form the Hollands Diep estuary, and separates the Island of Dordrecht from the Biesbosch National Park. The Beneden Merwede splits into the Noord River and Oude Maas near Papendrecht. History In medieval times the name Merwede (or "Merwe" in Middle Dutch) was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voorne-Putten
Voorne-Putten is an island between the North Sea, the Brielse Meer and the rivers Oude Maas, Spui and Haringvliet in the province of South Holland. Voorne-Putten consists of the two former islands Voorne (the larger, western part) and Putten (the smaller, eastern part). It used to be separated by the river Bernisse which silted up and made the two islands one. It has 160,000 inhabitants (2008). Recently the riverbed has been dredged, and the two islands have been reformed. The North Sea coast of Voorne is a valuable nature reserve (sand dunes), even though the northern part of the area has lost much of its estuarine character with the building of the Maasvlakte, an extension of the Port of Rotterdam, in the 1960s.M.J. van der Maarel & E. Adriani, 1968. Voorne in de Branding: een beschouwing over de natuurwetenschappelijke betekenis van het kustgebied van Voorne in verband met mogelijke technische werken in dit gebied. Stichting Wetenschappelijk Duinonderzoek The rest of the is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haringvliet
The Haringvliet is a large inlet of the North Sea, in the province of South Holland in the Netherlands. It is an important estuary of the Rhine-Meuse delta. Near Numansdorp, the Hollands Diep splits into the Haringvliet and the Volkerak estuaries. It is closed off near Goedereede from the North Sea by the Haringvlietdam, which provides a road connection between the island of Voorne to the north and the island of Goeree-Overflakkee to the south. The dam with its sluices was built as part of the Delta Works sea barrier protection works. The Haringvliet estuary contains the island of Tiengemeten, which is separated from the river island of Hoeksche Waard by the Vuile Gat strait. History The Haringvliet was formed as a result of the extensive flooding event of 1216, which breached the dunes of Voorne and created a deep saltwater inlet. During a second flooding event, the St. Elizabeth floods of 1421, this inlet connected to the Merwede and became an important estuary of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital of the Netherlands is Amsterdam, The Hague has been described as the country's de facto capital. The Hague is also the capital of the province of South Holland, and the city hosts both the International Court of Justice and the International Criminal Court. With a population of over half a million, it is the third-largest city in the Netherlands, after Amsterdam and Rotterdam. The Hague is the core municipality of the Greater The Hague urban area, which comprises the city itself and its suburban municipalities, containing over 800,000 people, making it the third-largest urban area in the Netherlands, again after the urban areas of Amsterdam and Rotterdam. The Rotterdam–The Hague metropolitan area, with a population of approximately 2.6&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
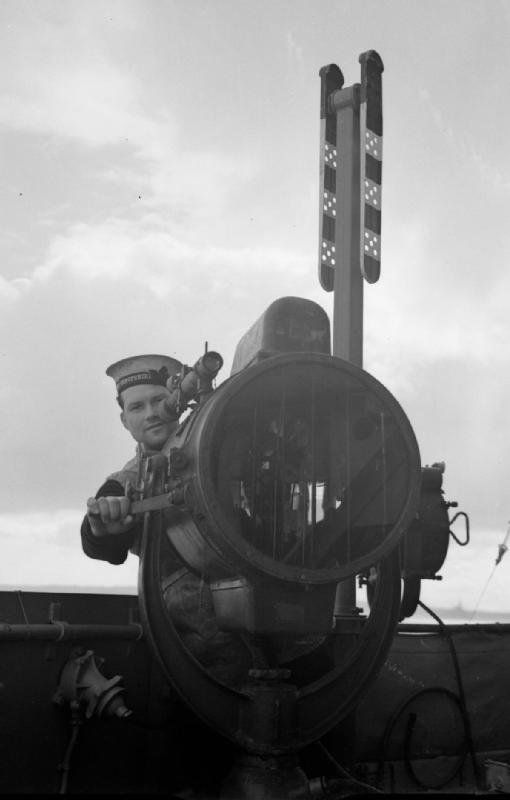
Semaphore
Semaphore (; ) is the use of an apparatus to create a visual signal transmitted over distance. A semaphore can be performed with devices including: fire, lights, flags, sunlight, and moving arms. Semaphores can be used for telegraphy when arranged in visually connected networks, or for traffic signalling such as in railway systems, or traffic lights in cities. Fire The Phryctoriae were a semaphore system used in Ancient Greece for the transmission of specific prearranged messages. Towers were built on selected mountaintops, so that one tower, the ''phryctoria'', would be visible to the next tower, usually twenty-miles distant. Flames were lit on one tower, then the next tower would light a flame in succession. The Byzantine beacon system was a semaphore developed in the 9th century during the Arab–Byzantine wars. The Byzantine Empire used a system of beacons to transmit messages from the border with the Abbasid Caliphate across Asia Minor to the Byzantine capital, Const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)