|
Aubrey Valley
Aubrey Valley is a 35-mile (56 km) long valley located in southwest Coconino County, Arizona with the northwest border of Yavapai County. The valley is located at the southwest border of the Aubrey Cliffs; to the west and southwest, the Yampai Divide and the Seventyfour Plains form flatlands between four bordering mountain ranges at the northwest terminus of the Arizona transition zone. The Aubrey Cliffs form the east and northeast valley border, and are part of the escarpment at the southwest perimeter of the Coconino Plateau, southwest Colorado Plateau. The Aubrey Cliffs re-appear northwest of the valley's north end, at the southeast of Prospect Valley. The Toroweap Fault is buried near the center of Aubrey Valley, west of the cliffs, and continues northwest into Prospect Valley, and to the Colorado River, west Grand Canyon. The Hurricane Fault-(of the Hurricane Cliffs) begins there, and both faults continue, the Hurricane going northwest, the Toroweap northeast, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aubrey Cliffs
Aubrey Cliffs are a series of cliff escarpments located in Coconino County, in northwestern Arizona. Geology The Toroweap Fault, west of Aubrey Valley in the south, and of Prospect Valley in the northwest, formed the Aubrey Cliffs. The cliffs form part of the southwest perimeter of the Coconino Plateau. The Toroweap Fault separates from the Hurricane Fault-(Hurricane Cliffs), at the Colorado River, in the western Grand Canyon. Both faults continue northeast, and northwest into southern Utah. Geography The Aubrey Cliffs begin near Route 66 about five miles west of Seligman and run generally north to the Colorado River in the Grand Canyon (coordinates ranging from 35.35, -112.95 to 36.19, -113.02). The most prominent section is southern half, which overlooks the Aubrey Valley to the west and rises approximately above the valley floor to an elevation of about . It is located on the Big Boquillas Ranch, a checkerboard area of state trust land and fee land owned by the Navajo Nation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Fault
The Hurricane Fault is an intracrustal seismic fault that runs along the boundary between the Colorado Plateau block and the Basin and Range geologic province of western North America. It is a 250-km-long, north-south striking, high-angle, down-to-the-west normal fault, running from about Cedar City, Utah southward into northwestern Arizona. The fault is named for the community of Hurricane A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend .... The 1992 St. George earthquake (magnitude 5.8), which triggered a damaging landslide, has been attributed to the Hurricane Fault. References Structural geology Geology of Utah {{US-geology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valleys Of Arizona
A valley is an elongated low area often running between Hill, hills or Mountain, mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over a very long period. Some valleys are formed through erosion by glacier, glacial ice. These glaciers may remain present in valleys in high mountains or polar areas. At lower latitudes and altitudes, these glaciation, glacially formed valleys may have been created or enlarged during ice ages but now are ice-free and occupied by streams or rivers. In desert areas, valleys may be entirely dry or carry a watercourse only rarely. In karst, areas of limestone bedrock, dry valleys may also result from drainage now taking place cave, underground rather than at the surface. Rift valleys arise principally from tectonics, earth movements, rather than erosion. Many different types of valleys are described by geographers, using terms th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Yavapai County, Arizona
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are the fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Coconino County, Arizona
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peach Springs, Arizona
, native_name_lang = hu , settlement_type = Census-designated place , image_skyline = Peach Springs-John Osterman Shell Gas Station-1929.jpg , imagesize = , image_caption = John Osterman Shell gas station , image_seal = Peach Springs-The Great Seal of the Halapai Tribe.jpg , image_map = Mohave_County_Incorporated_and_Unincorporated_areas_Peach_Springs_highlighted.svg , mapsize = 250px , map_caption = Location in Mohave County and the state of Arizona , image_map1 = , mapsize1 = , map_caption1 = , pushpin_map = Arizona#USA , pushpin_label = Peach Springs , pushpin_label_position = left , pushpin_map_caption = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_type1 = State , subdivision_type2 = County , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_name1 = Arizona , s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Canyon Caverns
The Grand Canyon Caverns ( yuf-x-hav, Ŧathiil Ñwaʼa or , ), located just a few miles east of Peach Springs, Arizona, lie below ground level. They are among the largest dry caverns in the United States. Dry caverns compose only 3% of caverns in the world. Because of the lack of water, stalagmites and stalactites are rare in the caverns. During the Mississippian Period, 345 million years ago, the southwestern United States was covered by ocean. Skeletons of sea life settling to the depths, created a mud with a high percentage of calcium. This eventually hardened into the limestone bedrock seen in the caverns today. Over millions of years, the bedrock was pushed up to over above sea level. Approximately 35 million years ago, rainfall flowed into the rock, and eroded passages that lead to the Colorado River and what is now the Grand Canyon. Millions of years later, the evaporating water left calcium deposits on the walls and floors, creating the formations that can be viewe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seligman, Arizona
Seligman ( yuf-x-hav, Thavgyalyal) is a census-designated place (CDP) on the northern border of Yavapai County, in northwestern Arizona, United States. The population was 456 at the 2000 census. Geography Seligman is located at (35.328199, −112.874303), at in elevation, alongside the Big Chino Wash, in a northern section of Chino Valley. The wash is a major tributary of the Verde River. Seligman is a popular stopping point along Historic U.S. Route 66. According to the United States Census Bureau, the Seligman CDP has a total area of , all land. History The region was in the longtime homeland of the Havasupai people, who had a settlement in the present day Seligman area. The town site was on Beale's Wagon Road, and a stage stop on the Mojave Road Originally, Seligman was called "Prescott Junction" because it was the railroad stop on the Santa Fe mainline junction with the Prescott and Arizona Central Railway Company feeder line running to Prescott, in the Arizona Terr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arizona State Route 66
State Route 66 (SR 66) is a surface road in the U.S. state of Arizona in Mohave and Coconino Counties. In 1914, the road was designated "National Old Trails Highway" but in 1926 was re-designated as U.S. Route 66. In 1985, U.S. Route 66 was dropped from the highway system. Parts of the highway were either absorbed into I-40, turned over to the state (SR 66), or turned over to Yavapai County. Route description State Route 66 is a relic of the former U.S. Route 66 in Arizona and is the only part of old US 66 in Arizona to have state route markers. Its western terminus is near Kingman at exit 52 on Interstate 40 and its eastern terminus was near Seligman at exit 123 on Interstate 40. In 1990, the state turned over the easternmost of SR 66 (known as Crookton Rd) to Yavapai County for maintenance. State Route 66 tends downward toward the west, with the vegetation becoming more desert-like toward Kingman. The terrain changes at a slower pace than the more direct Interstate 40, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
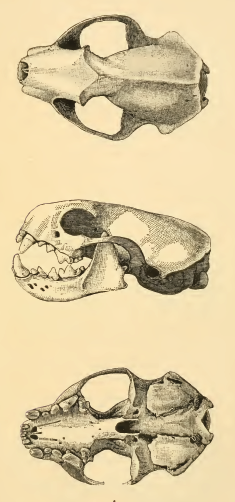
Black-footed Ferret
The black-footed ferret (''Mustela nigripes''), also known as the American polecatHeptner, V. G. (Vladimir Georgievich); Nasimovich, A. A; Bannikov, Andrei Grigorovich; Hoffmann, Robert S. (2001)''Mammals of the Soviet Union''Volume: v. 2, pt. 1b. Washington, D.C. : Smithsonian Institution Libraries and National Science Foundation. or prairie dog hunter, is a species of mustelid native to central North America. The black-footed ferret is roughly the size of a mink and is similar in appearance to the European polecat and the Asian steppe polecat. It is largely nocturnal and solitary, except when breeding or raising litters. Up to 90% of its diet is composed of prairie dogs. The species declined throughout the 20th century, primarily as a result of decreases in prairie dog populations and sylvatic plague. It was declared extinct in 1979, but a residual wild population was discovered in Meeteetse, Wyoming in 1981. A captive-breeding program launched by the United States Fish and W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstate 40 In Arizona
Interstate 40 (I-40) is an east–west Interstate Highway that has a section in the US state of Arizona, connecting sections in California and New Mexico. The Interstate is also referred to as the Purple Heart Trail to honor those wounded in combat who have received the Purple Heart. It enters Arizona from the west at a crossing of the Colorado River southwest of Kingman. It travels eastward across the northern portion of the state, connecting the cities of Kingman, Ash Fork, Williams, Flagstaff, Winslow, and Holbrook. I-40 continues into New Mexico, heading to Albuquerque. The highway has major junctions with U.S. Route 93 (US 93)—the main highway connecting Phoenix and Las Vegas, Nevada—in Kingman and again approximately to the east and I-17—the freeway linking Phoenix to northern Arizona) in Flagstaff. For the majority of its routing through Arizona, I-40 follows the historic alignment of US 66. The lone exception is a stretch between Kingma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to its west by Nevada. Utah also touches a corner of New Mexico in the southeast. Of the fifty U.S. states, Utah is the 13th-largest by area; with a population over three million, it is the 30th-most-populous and 11th-least-densely populated. Urban development is mostly concentrated in two areas: the Wasatch Front in the north-central part of the state, which is home to roughly two-thirds of the population and includes the capital city, Salt Lake City; and Washington County in the southwest, with more than 180,000 residents. Most of the western half of Utah lies in the Great Basin. Utah has been inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous groups such as the ancient Puebloans, Navajo and Ute. The Spanish were the first Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)