|
Atmospheric Dynamo
The Atmospheric dynamo is a pattern of electrical currents that are set up in the Earth's ionosphere by multiple effects, mostly the Sun's solar wind, but also the tides of the Moon and Sun. The currents flow in circuits between the poles and the equator, but they are not well understood. See also * Dynamo "Dynamo Electric Machine" (end view, partly section, ) A dynamo is an electrical generator that creates direct current using a commutator. Dynamos were the first electrical generators capable of delivering power for industry, and the foundat ... * Solar dynamo References Atmospheric electricity Ionosphere Space plasmas {{Astrophysics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Current
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Various common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of an electric charge, which can be either positive or negative, produces an electric field. The movement of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. When a charge is placed in a location with a non-zero electric field, a force will act on it. The magnitude of this force is given by Coulomb's law. If the charge moves, the electric field would be doing work on the electric charge. Thus we can speak of electric potential at a certain point in space, which is equal to the work done by an external agent in carrying a unit of posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. History of discovery As early as 1839, the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss postulated that an electrically conducting region of the atmosphere could account for observed variations of Earth's magnetic field. Sixty years later, Guglielmo Marconi received the first trans-Atlantic radio signal on December 12, 1901, in St. John's, Newfoundland (now in Canada) using a kite-supported antenna for reception. The transmitting station in Poldhu, Cornwall, used a spark-gap transmitter to produce a signal with a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
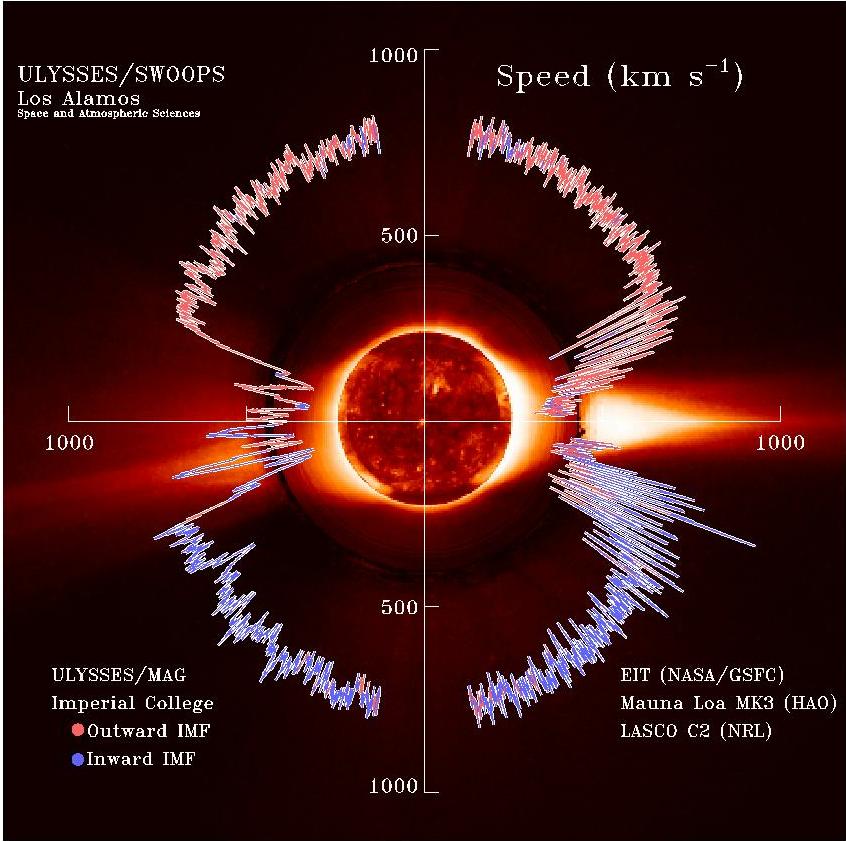
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of materials found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei such as C, N, O, Ne, Mg, Si, S, and Fe. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as P, Ti, Cr, 54Fe and 56Fe, and 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface. At a dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or "tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see '' Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude tides a day—is a third regular category. Tides va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographical Pole
A geographical pole or geographic pole is either of the two points on Earth where its axis of rotation intersects its surface. The North Pole lies in the Arctic Ocean while the South Pole is in Antarctica. North and South poles are also defined for other planets or satellites in the Solar System, with a North pole being on the same side of the invariable plane as Earth's North pole. Relative to Earth's surface, the geographic poles move by a few metres over periods of a few years. This is a combination of Chandler wobble, a free oscillation with a period of about 433 days; an annual motion responding to seasonal movements of air and water masses; and an irregular drift towards the 80th west meridian. As cartography requires exact and unchanging coordinates, the averaged locations of geographical poles are taken as fixed ''cartographic poles'' and become the points where the body's great circles of longitude intersect. See also * Earth's rotation * Polar motion * Pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also be used for any other celestial body that is roughly spherical. In spatial (3D) geometry, as applied in astronomy, the equator of a rotating spheroid (such as a planet) is the parallel (circle of latitude) at which latitude is defined to be 0°. It is an imaginary line on the spheroid, equidistant from its poles, dividing it into northern and southern hemispheres. In other words, it is the intersection of the spheroid with the plane perpendicular to its axis of rotation and midway between its geographical poles. On and near the equator (on Earth), noontime sunlight appears almost directly overhead (no more than about 23° from the zenith) every day, year-round. Consequently, the equator has a rather stable daytime temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamo
"Dynamo Electric Machine" (end view, partly section, ) A dynamo is an electrical generator that creates direct current using a commutator. Dynamos were the first electrical generators capable of delivering power for industry, and the foundation upon which many other later electric-power conversion devices were based, including the electric motor, the alternating-current alternator, and the rotary converter. Today, the simpler alternator dominates large scale power generation, for efficiency, reliability and cost reasons. A dynamo has the disadvantages of a mechanical commutator. Also, converting alternating to direct current using rectifiers (such as vacuum tubes or more recently via solid state technology) is effective and usually economical. History Induction with permanent magnets The Faraday disk was the first electric generator. The horseshoe-shaped magnet ''(A)'' created a magnetic field through the disk ''(D)''. When the disk was turned, this induced an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Dynamo
The solar dynamo is a physical process that generates the Sun's magnetic field. It is explained with a variant of the dynamo theory. A naturally occurring electric generator in the Sun's interior produces electric currents and a magnetic field, following the laws of Ampère, Faraday and Ohm, as well as the laws of fluid dynamics, which together form the laws of magnetohydrodynamics. The detailed mechanism of the solar dynamo is not known and is the subject of current research. Mechanism A dynamo converts kinetic energy into electric-magnetic energy. An electrically conducting fluid with shear or more complicated motion, such as turbulence, can temporarily amplify a magnetic field through Lenz's law: fluid motion relative to a magnetic field induces electric currents in the fluid that distort the initial field. If the fluid motion is sufficiently complicated, it can sustain its own magnetic field, with advective fluid amplification essentially balancing diffusive or ohmic de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Electricity
Atmospheric electricity is the study of electrical charges in the Earth's atmosphere (or that of another planet). The movement of charge between the Earth's surface, the atmosphere, and the ionosphere is known as the global atmospheric electrical circuit. Atmospheric electricity is an interdisciplinary topic with a long history, involving concepts from electrostatics, atmospheric physics, meteorology and Earth science. Thunderstorms act as a giant battery in the atmosphere, charging up the electrosphere to about 400,000 volts with respect to the surface. This sets up an electric field throughout the atmosphere, which decreases with increase in altitude. Atmospheric ions created by cosmic rays and natural radioactivity move in the electric field, so a very small current flows through the atmosphere, even away from thunderstorms. Near the surface of the Earth, the magnitude of the field is on average around 100 V/m. Atmospheric electricity involves both thunderstorms, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. History of discovery As early as 1839, the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss postulated that an electrically conducting region of the atmosphere could account for observed variations of Earth's magnetic field. Sixty years later, Guglielmo Marconi received the first trans-Atlantic radio signal on December 12, 1901, in St. John's, Newfoundland (now in Canada) using a kite-supported antenna for reception. The transmitting station in Poldhu, Cornwall, used a spark-gap transmitter to produce a signal with a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
