|
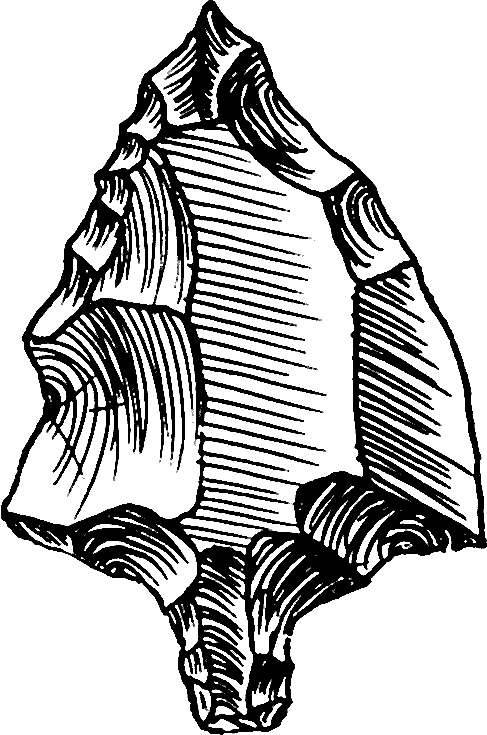
Aterian Culture
The Aterian is a Middle Stone Age (or Middle Paleolithic, Middle Palaeolithic) stone tool Archaeological industry, industry centered in North Africa, from Mauritania to Egypt, but also possibly found in Oman and the Thar Desert. The earliest Aterian dates to c. 150,000 years ago, at the site of Ifri n'Ammar in Morocco. However, most of the early dates cluster around the beginning of the Eemian, Last Interglacial, around 150,000 to 130,000 years ago, when the environment of North Africa began to ameliorate. The Aterian disappeared around 20,000 years ago. The Aterian is primarily distinguished through the presence of tanged or pedunculated tools, and is named after the type site of Bir el Ater, south of Tébessa. Bifacially-worked, leaf-shaped tools are also a common artifact (archaeology), artefact type in Aterian assemblages, and so are racloirs and Levallois technique, Levallois flakes and cores. Items of personal adornment (pierced and ochred Nassarius shell beads) are known fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in the west, to Egypt's Suez Canal. Varying sources limit it to the countries of Algeria, Libya, Morocco, and Tunisia, a region that was known by the French during colonial times as "''Afrique du Nord''" and is known by Arabs as the Maghreb ("West", ''The western part of Arab World''). The United Nations definition includes Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, Sudan, and the Western Sahara, the territory disputed between Morocco and the Sahrawi Republic. The African Union definition includes the Western Sahara and Mauritania but not Sudan. When used in the term Middle East and North Africa (MENA), it often refers only to the countries of the Maghreb. North Africa includes the Spanish cities of Ceuta and Melilla, and plazas de s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tébessa
Tébessa or Tebessa ( ar, تبسة ''Tibissa'', ''Tbessa'' or ''Tibesti''), the classical Theveste, is the capital city of Tébessa Province region of northeastern Algeria. It hosts several historical landmarks, the most important one being the wall that surrounds the city and its gates. The city is also known for its traditional Algerian carpets. Tébessa was home to over 190,000 people in 2007. Name Tebessa, written ' in French, was known to the ancient Greeks as () or (, 'Hundred Gates'). This was Latinized as ''Theveste''. History In antiquity, Theveste formed part of the Roman empire. After the establishment of the Roman Empire, the 3rd Augustan Legion was based in Theveste before being transferred to Lambaesis. Theveste later became a Roman colony, probably under Trajan in the early 2nd century. At the time of Trajan it was a flourishing city with around 30,000 inhabitants. The ruins surviving in present-day Tebessa are very rich in ancient monuments, among them b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eemian
The Eemian (also called the last interglacial, Sangamonian, Sangamonian Stage, Ipswichian, Mikulin, Kaydaky, penultimate,NOAA - Penultimate Interglacial Period http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/global-warming/penultimate-interglacial-period Valdivia or Riss-Würm) was the interglacial period which began about 130,000 years ago at the end of the Penultimate Glacial Period and ended about 115,000 years ago at the beginning of the Last Glacial Period. It corresponds to Marine Isotope Stage 5e. Although sometimes referred to as the "last interglacial" (in the "most recent previous" sense of "last"), it was the second-to-latest interglacial period of the current Ice Age, the most recent being the Holocene which extends to the present day (having followed the last glacial period). The prevailing Eemian climate was, on average, around 1 to 2 degrees Celsius (1.8 to 3.6 Fahrenheit) warmer than that of the Holocene. During the Eemian, the proportion of in the atmosphere was about 280 parts per mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ResearchGate
ResearchGate is a European commercial social networking site for scientists and researchers to share papers, ask and answer questions, and find collaborators. According to a 2014 study by ''Nature'' and a 2016 article in ''Times Higher Education'', it is the largest academic social network in terms of active users, although other services have more registered users, and a 2015–2016 survey suggests that almost as many academics have Google Scholar profiles. While reading articles does not require registration, people who wish to become site members need to have an email address at a recognized institution or to be manually confirmed as a published researcher in order to sign up for an account. Members of the site each have a user profile and can upload research output including papers, data, chapters, negative results, patents, research proposals, methods, presentations, and software source code. Users may also follow the activities of other users and engage in discussions with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt, while Alexandria, the second-largest city, is an important industrial and tourist hub at the Mediterranean coast. At approximately 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the 14th-most populated country in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country, tracing its heritage along the Nile Delta back to the 6th–4th millennia BCE. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture, ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية الموريتانية), is a sovereign country in West Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to the north and northwest, Algeria to the northeast, Mali to the east and southeast, and Senegal to the southwest. Mauritania is the 11th-largest country in Africa and the 28th-largest in the world, and 90% of its territory is situated in the Sahara. Most of its population of 4.4 million lives in the temperate south of the country, with roughly one-third concentrated in the capital and largest city, Nouakchott, located on the Atlantic coast. The country's name derives from the ancient Berber kingdom of Mauretania, located in North Africa within the ancient Maghreb. Berbers occupied what is now Mauritania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Industry
:''Not to be confused with industrial archaeology, the archaeology of (modern) industrial sites.'' In the archaeology of the Stone Age, an industry or technocomplex is a typological classification of stone tools. An industry consists of a number of lithic assemblages, typically including a range of different types of tools, that are grouped together on the basis of shared technological or morphological characteristics. For example, the Acheulean industry includes hand-axes, cleavers, scrapers and other tools with different forms, but which were all manufactured by the symmetrical reduction of a bifacial core producing large flakes. Industries are usually named after a type site where these characteristics were first observed (e.g. the Mousterian industry is named after the site of Le Moustier). By contrast, Neolithic axeheads from the Langdale axe industry were recognised as a type well before the centre at Great Langdale was identified by finds of debitage and other re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Paleolithic in African archeology. The Middle Paleolithic broadly spanned from 300,000 to 30,000 years ago. There are considerable dating differences between regions. The Middle Paleolithic was succeeded by the Upper Paleolithic subdivision which first began between 50,000 and 40,000 years ago. Pettit and White date the Early Middle Paleolithic in Great Britain to about 325,000 to 180,000 years ago (late Marine Isotope Stage 9 to late Marine Isotope Stage 7), and the Late Middle Paleolithic as about 60,000 to 35,000 years ago. According to the theory of the recent African origin of modern humans, anatomically modern humans began migrating out of Africa during the Middle Stone Age/Middle Paleolithic around 125,000 years ago and began to replace e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Stone Age
The Middle Stone Age (or MSA) was a period of African prehistory between the Early Stone Age and the Late Stone Age. It is generally considered to have begun around 280,000 years ago and ended around 50–25,000 years ago. The beginnings of particular MSA stone tools have their origins as far back as 550–500,000 years ago and as such some researchers consider this to be the beginnings of the MSA. The MSA is often mistakenly understood to be synonymous with the Middle Paleolithic of Europe, especially due to their roughly contemporaneous time span, however, the Middle Paleolithic of Europe represents an entirely different hominin population, ''Homo neanderthalensis'', than the MSA of Africa, which did not have Neanderthal populations. Additionally, current archaeological research in Africa has yielded much evidence to suggest that modern human behavior and cognition was beginning to develop much earlier in Africa during the MSA than it was in Europe during the Middle Paleoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberomaurusian
The Iberomaurusian is a backed bladelet lithic industry found near the coasts of Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. It is also known from a single major site in Libya, the Haua Fteah, where the industry is locally known as the Eastern Oranian.The "Western Oranian" would refer to the Iberomaurusian in Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia, but this expression is seldom used. The Iberomaurusian seems to have appeared around the time of the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), somewhere between c. 25,000 and 23,000 cal BP. It would have lasted until the early Holocene c. 11,000 cal BP. The name of the Iberomaurusian means "of Iberia and Mauretania", the latter being a Latin name for Northwest Africa. Pallary (1909) coined this termPallary, P., 1909. Instructions pour la recherche préhistorique dans le Nord-Ouest de l'Afrique, Algiers. to describe assemblages from the site of La Mouillah in the belief that the industry extended over the strait of Gibraltar into the Iberian peninsula. This theory is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khormusan
Khormusan industry was a Paleolithic archeological industry in Egypt and Sudan dated at 42,000 to 18,000 BP. The Khormusan industry in Egypt began between 42,000 and 32,000 BP. Khormusans developed tools not only from stone but also from animal bones and hematite. They also developed small arrow heads resembling those of Native Americans, but no bows have been found. The end of the Khormusan industry came around 18,000 BP. with the appearance of other cultures in the region, including the Gemaian.Nicolas-Christophe Grimal. ''A History of Ancient Egypt''. p. 20. Blackwell (1994). It was succeeded by the Halfan culture The Halfan industry is one of the Late Epipalaeolithic industries of the Upper Nile Valley that seems to have appeared in northern Sudan c. 22.5-22.0 ka cal BP. It is one of the earliest known backed-bladelet industries in Northern Africa, d .... References Upper Paleolithic cultures of Africa Prehistory of the Middle East Lithics Industries (archaeo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |