|
Atari Transputer Workstation
The Atari Transputer Workstation (also known as ATW-800, or simply ATW) is a workstation class computer released by Atari Corporation in the late 1980s, based on the INMOS transputer. It was introduced in 1987 as the Abaq, but the name was changed before sales began. Sales were almost non-existent, and the product was canceled after only a few hundred units had been produced. History In 1986, Tim King left his job at MetaComCo, along with a few other employees, to start Perihelion Software in England. There they started development of a new parallel-processing operating system known as "HeliOS". At about the same time a colleague, Jack Lang, started Perihelion (later Perihelion Hardware) to create a new transputer based workstation that would run HeliOS. While at MetaComCo, much of the Perihelion Software team had worked with both Atari Corp. and Commodore International, producing ST BASIC for the former, and AmigaDOS for the latter. The principals still had contacts with bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atari Corporation
Atari Corporation was an American manufacturer of computers and video game consoles. It was founded by Jack Tramiel on May 17, 1984, as Tramel Technology, Ltd., but then took on the Atari name less than two months later when Warner Communications sold the home computing and game console assets of Atari, Inc. to Tramiel. Its chief products were the Atari ST, Atari XE, Atari 7800, Atari Lynx and Atari Jaguar. The company reverse merged with JTS Inc. in 1996, becoming a small division which itself closed after JTS sold all Atari assets to Hasbro Interactive in 1998. History The company was founded by Commodore International's founder Jack Tramiel soon after his resignation from Commodore in January 1984. Initially named Tramel Technology, Ltd., the company's goal was to design and sell a next-generation home computer. On July 1, 1984, TTL bought the Consumer Division assets of Atari, Inc. from Warner, and TTL was renamed Atari Corporation. Warner sold the division for $24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amiga 2000
The Amiga 2000, or A2000, is a personal computer released by Commodore in March 1987. It was introduced as a "big box" expandable variant of the Amiga 1000 but quickly redesigned to share most of its electronic components with the contemporary Amiga 500 for cost reduction. Expansion capabilities include two 3.5" drive bays (one of which is used by the included floppy drive) and one 5.25" bay that could be used by a 5.25" floppy drive (for IBM PC compatibility), a hard drive, or CD-ROM once they became available. The Amiga 2000 is the first Amiga model that allows expansion cards to be added internally. SCSI host adapters, memory cards, CPU cards, network cards, graphics cards, serial port cards, and PC compatibility cards were available, and multiple expansions can be used simultaneously without requiring an expansion cage like the Amiga 1000 does. Not only does the Amiga 2000 include five Zorro II card slots, the motherboard also has four PC ISA slots, two of which are in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics Processing Unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed to manipulate and alter memory to accelerate the creation of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display device. GPUs are used in embedded systems, mobile phones, personal computers, workstations, and game consoles. Modern GPUs are efficient at manipulating computer graphics and image processing. Their parallel structure makes them more efficient than general-purpose central processing units (CPUs) for algorithms that process large blocks of data in parallel. In a personal computer, a GPU can be present on a video card or embedded on the motherboard. In some CPUs, they are embedded on the CPU die. In the 1970s, the term "GPU" originally stood for ''graphics processor unit'' and described a programmable processing unit independently working from the CPU and responsible for graphics manipulation and output. Later, in 1994, Sony used the term (now standing for ''graphics processing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bit Blit
Bit blit (also written BITBLT, BIT BLT, BitBLT, Bit BLT, Bit Blt etc., which stands for ''bit block transfer'') is a data operation commonly used in computer graphics in which several bitmaps are combined into one using a '' boolean function''. The operation involves at least two bitmaps: a "source" (or "foreground") and a "destination" (or "background"), and possibly a third that is often called the "mask A mask is an object normally worn on the face, typically for protection, disguise, performance, or entertainment and often they have been employed for rituals and rights. Masks have been used since antiquity for both ceremonial and pra ...". The result may be written to a fourth bitmap, though often it replaces the destination. The pixels of each are combined bitwise according to the specified raster operation (ROP) and the result is then written to the destination. The ROP is essentially a Boolean logic, boolean formula. The most obvious ROP overwrites the destinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blitter
A blitter is a circuit, sometimes as a coprocessor or a logic block on a microprocessor, dedicated to the rapid movement and modification of data within a computer's memory. A blitter can copy large quantities of data from one memory area to another relatively quickly, and in parallel with the CPU, while freeing up the CPU's more complex capabilities for other operations. A typical use for a blitter is the movement of a bitmap, such as windows and fonts in a graphical user interface or images and backgrounds in a 2D video game. The name comes from the bit blit operation of the 1973 Xerox Alto, which stands for bit-block transfer. A blit operation is more than a memory copy, because it can involve data that's not byte aligned (hence the ''bit'' in ''bit blit''), handling transparent pixels (pixels which should not overwrite the destination), and various ways of combining the source and destination data. Blitters have largely been superseded by programmable graphics process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical User Interface
The GUI ( "UI" by itself is still usually pronounced . or ), graphical user interface, is a form of user interface that allows User (computing), users to Human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through graphical icon (computing), icons and audio indicator such as primary notation, instead of text-based user interface, text-based UIs, typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of CLIs (command-line interfaces), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard. The actions in a GUI are usually performed through Direct manipulation interface, direct manipulation of the graphical elements. Beyond computers, GUIs are used in many handheld mobile devices such as MP3 players, portable media players, gaming devices, smartphones and smaller household, office and Distributed control system, industrial controls. The term ''GUI'' tends not to be applied to other lower-display resolution User ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Window System
The X Window System (X11, or simply X) is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems. X provides the basic framework for a GUI environment: drawing and moving windows on the display device and interacting with a mouse and keyboard. X does not mandate the user interfacethis is handled by individual programs. As such, the visual styling of X-based environments varies greatly; different programs may present radically different interfaces. X originated as part of Project Athena at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1984. The X protocol has been at version 11 (hence "X11") since September 1987. The X.Org Foundation leads the X project, with the current reference implementation, X.Org Server, available as free and open-source software under the MIT License and similar permissive licenses. Purpose and abilities X is an architecture-independent system for remote graphical user interfaces and input device capabilities. Each person u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stack (data Structure)
In computer science, a stack is an abstract data type that serves as a collection of elements, with two main operations: * Push, which adds an element to the collection, and * Pop, which removes the most recently added element that was not yet removed. Additionally, a peek operation can, without modifying the stack, return the value of the last element added. Calling this structure a ''stack'' is by analogy to a set of physical items stacked one atop another, such as a stack of plates. The order in which an element added to or removed from a stack is described as last in, first out, referred to by the acronym LIFO. As with a stack of physical objects, this structure makes it easy to take an item off the top of the stack, but accessing a datum deeper in the stack may require taking off multiple other items first. Considered as a linear data structure, or more abstractly a sequential collection, the push and pop operations occur only at one end of the structure, referre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Management Unit
A memory management unit (MMU), sometimes called paged memory management unit (PMMU), is a computer hardware unit having all memory references passed through itself, primarily performing the translation of virtual memory addresses to physical addresses. An MMU effectively performs virtual memory management, handling at the same time memory protection, cache control, bus arbitration and, in simpler computer architectures (especially 8-bit systems), bank switching. Overview Modern MMUs typically divide the virtual address space (the range of addresses used by the processor) into pages, each having a size which is a power of 2, usually a few kilobytes, but they may be much larger. The bottom bits of the address (the offset within a page) are left unchanged. The upper address bits are the virtual page numbers. Page table entries Most MMUs use an in-memory table of items called a " page table", containing one " page table entry" (PTE) per page, to map virtual page numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley ( BSD), Microsoft ( Xenix), Sun Microsystems (SunOS/ Solaris), HP/ HPE (HP-UX), and IBM ( AIX). In the early 1990s, AT&T sold its rights in Unix to Novell, which then sold the UNIX trademark to The Open Group, an industry consortium founded in 1996. The Open Group allows the use of the mark for certified operating systems that comply with the Single UNIX Specification (SUS). Unix systems are characterized by a modular design that is sometimes called the " Unix philosophy". According to this p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instructions Per Second
Instructions per second (IPS) is a measure of a computer's processor speed. For complex instruction set computers (CISCs), different instructions take different amounts of time, so the value measured depends on the instruction mix; even for comparing processors in the same family the IPS measurement can be problematic. Many reported IPS values have represented "peak" execution rates on artificial instruction sequences with few branches and no cache contention, whereas realistic workloads typically lead to significantly lower IPS values. Memory hierarchy also greatly affects processor performance, an issue barely considered in IPS calculations. Because of these problems, synthetic benchmarks such as Dhrystone are now generally used to estimate computer performance in commonly used applications, and raw IPS has fallen into disuse. The term is commonly used in association with a metric prefix (k, M, G, T, P, or E) to form kilo instructions per second (kIPS), million instructio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
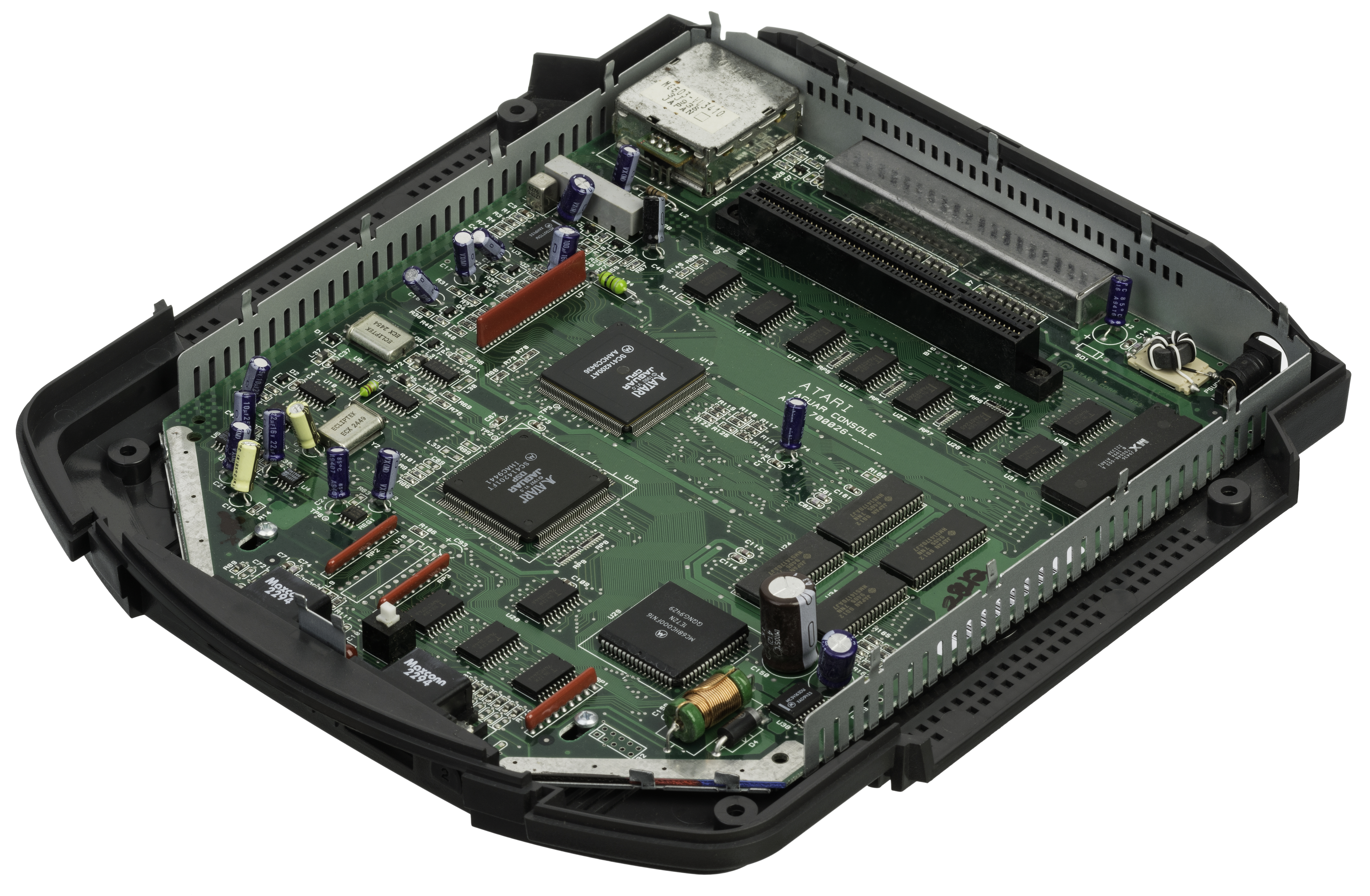
Atari Jaguar
The Atari Jaguar is a home video game console developed by Atari Corporation and released in North America in November 1993. Part of the fifth generation of video game consoles, it competed with the 16-bit Sega Genesis, the Super NES and the 32-bit 3DO Interactive Multiplayer that launched the same year. Powered by two custom 32-bit Tom and in addition to a Motorola 68000, Atari marketed it as the world's first 64-bit game system, emphasizing its 64-bit bus used by the blitter. The Jaguar launched with ''Cybermorph'' as the pack-in game, which received divisive reviews. The system's library ultimately comprised only 50 licensed games. Development of the Atari Jaguar started in the early 1990s by Flare Technology, which focused on the system after cancellation of the Atari Panther console. The multi-chip architecture, hardware bugs, and poor tools made writing games for the Jaguar difficult. Underwhelming sales further eroded the console's third-party support. Atari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |