|
Astrakhan Governorate
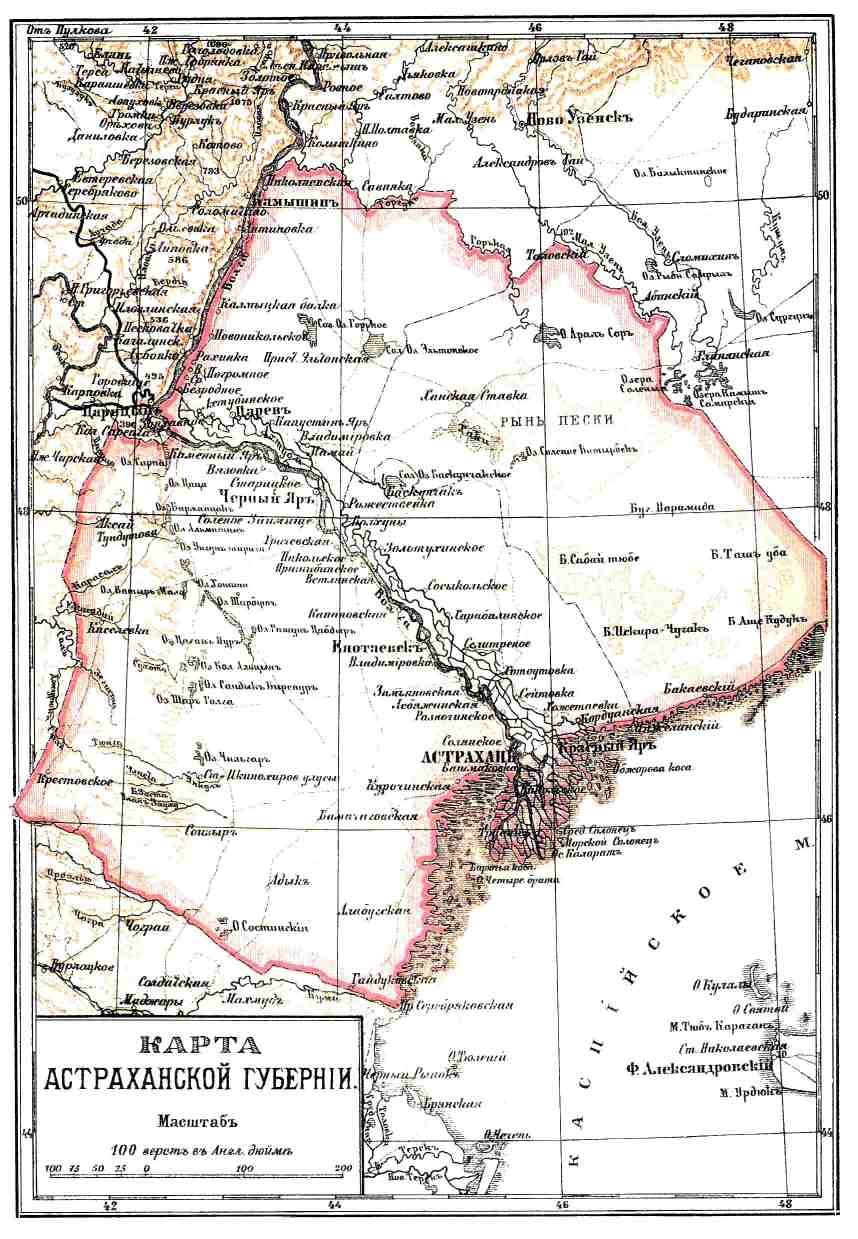
The Astrakhan Governorate () was an Imperial, Republican, and Soviet Russian administrative division (), which existed from 1717 – 1929. Created from separating the southwestern part of the Kazan Governorate, by Peter I's Reform in 1717. And abolished by the Bolshevik's administrative reform in 1928, where the governorate became part of Lower Volga Oblast (later Lower Volga Krai). The administrative center of the governorate is Astrakhan. Geography Geographical position The Astrakhan Governorate was located in the southeast of the European part of the Russian Empire, between 45° and 51° north latitude and 43° and 51° east longitude. The greatest length of the governorate from north to south is up to , and the greatest width from west to east was . Location of the Governorate concerning modern administrative boundaries On the territory of the former Astrakhan Governorate (within the borders of 1914), currently, the Astrakhan Oblast and the Republic of Kalmykia, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governorate (Russia)
A governorate, gubernia, province, or government ( rus, губе́рния, p=ɡʊˈbʲɛrnʲɪjə, also romanized ; uk, губернія, huberniia), was a major and principal administrative subdivision of the Russian Empire. After the empire was ended by revolution, they remained as subdivisions in Belarus, the Russian republic, Ukraine, and in the Soviet Union from its formation until 1929. The term is also translated as ''government'', ''governorate'', or ''province''. A governorate was ruled by a governor (, ''gubernator''), a word borrowed from Latin , in turn from Greek . Selected governorates were united under an assigned governor general such as the Grand Duchy of Finland, Congress Poland, Russian Turkestan and others. There also were military governors such as Kronstadt, Vladivostok, and others. Aside from governorates, other types of divisions were oblasts (region) and okrugs (district). First reform This subdivision type was created by the edict (ukase) of Peter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dagestan
Dagestan ( ; rus, Дагеста́н, , dəɡʲɪˈstan, links=yes), officially the Republic of Dagestan (russian: Респу́блика Дагеста́н, Respúblika Dagestán, links=no), is a republic of Russia situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe, along the Caspian Sea. It is located north of the Greater Caucasus, and is a part of the North Caucasian Federal District. The republic is the southernmost tip of Russia, sharing land borders with the countries of Azerbaijan and Georgia to the south and southwest, the Russian republics of Chechnya and Kalmykia to the west and north, and with Stavropol Krai to the northwest. Makhachkala is the republic's capital and largest city; other major cities are Derbent, Kizlyar, Izberbash, Kaspiysk and Buynaksk. Dagestan covers an area of , with a population of over 3.1 million, consisting of over 30 ethnic groups and 81 nationalities. With 14 official languages, and 12 ethnic groups each constituting more than 1% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volgograd
Volgograd ( rus, Волгогра́д, a=ru-Volgograd.ogg, p=vəɫɡɐˈɡrat), geographical renaming, formerly Tsaritsyn (russian: Цари́цын, Tsarítsyn, label=none; ) (1589–1925), and Stalingrad (russian: Сталингра́д, Stalingrád, label=none; ) (1925–1961), is the largest city and the administrative centre of Volgograd Oblast, Russia. The city lies on the western bank of the Volga, covering an area of , with a population of slightly over 1 million residents. Volgograd is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, sixteenth-largest city by population size in Russia, the second-largest city of the Southern Federal District, and the Volga#Biggest cities on the shores of the Volga, fourth-largest city on the Volga. The city was founded as the fortress of ''Tsaritsyn'' in 1589. By the nineteenth century, Tsaritsyn had become an important river-port and commercial centre, leading to its population to grow rapidly. In November 1917, at the start of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga Delta
The Volga Delta is the largest river delta in Europe, and occurs where Europe's largest river system, the Volga River, drains into the Caspian Sea in Russia's Astrakhan Oblast, north-east of the republic of Kalmykia. The delta is located in the Caspian Depression—the far eastern part of the delta lies in Kazakhstan. The delta drains into the Caspian approximately downstream from the city of Astrakhan. The Volga Delta has grown significantly in the 20th century because of changes in the level of the Caspian Sea. In 1880, the delta had an area of . Today the Volga Delta covers an area of and is approximately across. It has a classical "delta pattern". The delta lies in the arid climate zone, characterized by very little rainfall. The region receives less than one inch of rainfall in January and in July in normal years. Strong winds often sweep across the delta and form linear dunes. Along the front of the delta, one will find muddy sand shoals, mudflats, and coquina banks. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Strelbitsky
Ivan () is a Slavic male given name, connected with the variant of the Greek name (English: John) from Hebrew meaning 'God is gracious'. It is associated worldwide with Slavic countries. The earliest person known to bear the name was Bulgarian tsar Ivan Vladislav. It is very popular in Russia, Ukraine, Croatia, Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Slovenia, Bulgaria, Belarus, North Macedonia, and Montenegro and has also become more popular in Romance-speaking countries since the 20th century. Etymology Ivan is the common Slavic Latin spelling, while Cyrillic spelling is two-fold: in Bulgarian, Russian, Macedonian, Serbian and Montenegrin it is Иван, while in Belarusian and Ukrainian it is Іван. The Old Church Slavonic (or Old Cyrillic) spelling is . It is the Slavic relative of the Latin name , corresponding to English ''John''. This Slavic version of the name originates from New Testament Greek (''Iōánnēs'') rather than from the Latin . The Greek name is in tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bukey Horde
The Bukey Horde ( kk, , Бөкей Ордасы, ; russian: Букеевская Орда, ), also known as the Inner Horde or Interior Horde was an autonomous Khanate of Kazakhs located north of the Caspian Sea in between the Ural and Volga Rivers, but never reaching these rivers. The khanate officially existed from 1801 to 1845, when the position of khan was abolished and the area was fully absorbed into the administration of the Russian Empire. It was located in the western part of modern-day Kazakhstan. Its lands spread over about 71,000 square kilometers. History Background The population consisted primarily from 5 thousand families of Junior Juz. In the mid-19th century, the population grew to 200 thousand people. It was named after sultan Bokei Nuralyuly. In 1756 the Russians attempted to ban the Kazakhs from crossing the Ural River, partly to help the Bashkirs. This was difficult to enforce, given Russia's limited resources in the area. There were numerous illegal c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalmyk Steppe
Kalmuk Steppe, or Kalmyk Steppe is a steppe with a land area of approximately 100,000 km², bordering the northwest Caspian Sea, bounded by the Volga on the northeast, the Manych on the southwest, and the territory of the Don Cossacks on the northwest. The historic home to the Kalmuck or Kalmyks it is in the Federal subjects of Russia, Federal subject of Astrakhan Oblast in Russia. Before the appearance of the Kalmyks to this region, the area was long known as the Povoletsk steppe by the Russians. The western Kalmuck Steppe occupied by the Yergeni hills, is deeply trenched by ravines and rises 300 and occasionally 630 ft. above the sea. It is built up of Tertiary deposits, belonging to the Sarmatian division of the Miocene period and covered with bess and black earth, and its escarpments represent the old shore-line of the Caspian Sea, Caspian. No Caspian deposits are found on or within the Yergeni. These hills exhibit the usual black earth flora, and they have a settled population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsarev, Russia
Tsarev (russian: Царев) is a rural locality (a selo) and the administrative center of Tsarevskoye Rural Settlement, Leninsky District, Volgograd Oblast Volgograd Oblast (russian: Волгогра́дская о́бласть, ''Volgogradskaya oblast'') is a federal subject (an oblast) of Russia, located in the Volga region of Southern Russia. Its administrative center is Volgograd. The populat ..., Russia. The population was 1,521 as of 2010. There are 19 streets. Geography Tsarev is located on the left bank of the Akhtuba River, 19 km southeast of Leninsk (the district's administrative centre) by road. Saray is the nearest rural locality. References Rural localities in Leninsky District, Volgograd Oblast {{LeninskyVGG-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Though villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture, and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chernoyarsky Uyezd
Chernoyarsky (masculine), Chernoyarskaya (feminine), or Chernoyarskoye (neuter) may refer to: *Chernoyarsky District Chernoyarsky District (russian: Черноя́рский райо́н) is an administrativeLaw #67/2006-OZ and municipalLaw #43/2004-OZ district (raion), one of the eleven in Astrakhan Oblast, Russia. It is located in the north of the oblast. Th ..., a district of Astrakhan Oblast, Russia * Chernoyarsky (rural locality) (''Chernoyarskaya'', ''Chernoyarskoye''), name of several rural localities in Russia {{Geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yenotayevsky Uyezd
Yenotayevsky District (russian: Енота́евский райо́н) is an administrativeLaw #67/2006-OZ and municipalLaw #43/2004-OZ district (raion), one of the eleven in Astrakhan Oblast, Russia. It is located in the west of the oblast. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the rural locality (a '' selo'') of Yenotayevka Yenotayevka (russian: Енота́евка) is a rural locality (a selo) and the administrative center of Yenotayevsky District of Astrakhan Oblast, Russia Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spannin .... Population: 27,625 ( 2002 Census); The population of Yenotayevka accounts for 28.4% of the district's total population. References Notes Sources * * {{Use mdy dates, date=September 2012 Districts of Astrakhan Oblast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(1857).png)

