|
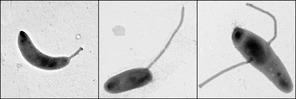
Asticcacaulis Biprosthecum
''Asticcacaulis biprosthecum'' is a stalked bacterial species phylogenetically closely related to the species ''Caulobacter crescentus ''Caulobacter crescentus'' is a Gram-negative, oligotrophic bacterium widely distributed in fresh water lakes and streams. The taxon is more properly known as ''Caulobacter vibrioides'' (Henrici and Johnson 1935). ''C. crescentus'' is an impo ...''. However, instead of a single polar organelle called the stalk, ''Asticcacaulis biprosthecum'' possesses two stalks that are laterally positioned along the cylindrical cell body. The ecological significance of this arrangement is unknown. References Caulobacterales Bacteria described in 1964 {{Alphaproteobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonadota
Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria) is a major phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. The renaming of phyla in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature. The phylum Proteobacteria includes a wide variety of pathogenic genera, such as '' Escherichia'', '' Salmonella'', '' Vibrio'', '' Yersinia'', '' Legionella'', and many others.Slonczewski JL, Foster JW, Foster E. Microbiology: An Evolving Science 5th Ed. WW Norton & Company; 2020. Others are free-living (non parasitic) and include many of the bacteria responsible for nitrogen fixation. Carl Woese established this grouping in 1987, calling it informally the "purple bacteria and their relatives". Because of the great diversity of forms found in this group, it was later informally named Proteobacteria, after Proteus, a Greek god of the sea capable of assuming many different shapes (not after the Proteobacteria genus ''Proteus''). In 2021 the In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphaproteobacteria
Alphaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota (formerly Proteobacteria). The Magnetococcales and Mariprofundales are considered basal or sister to the Alphaproteobacteria. The Alphaproteobacteria are highly diverse and possess few commonalities, but nevertheless share a common ancestor. Like all ''Proteobacteria'', its members are gram-negative and some of its intracellular parasitic members lack peptidoglycan and are consequently gram variable. Characteristics The Alphaproteobacteria are a diverse taxon and comprises several phototrophic genera, several genera metabolising C1-compounds (''e.g.'', ''Methylobacterium'' spp.), symbionts of plants (''e.g.'', '' Rhizobium'' spp.), endosymbionts of arthropods (''Wolbachia'') and intracellular pathogens (''e.g. Rickettsia''). Moreover, the class is sister to the protomitochondrion, the bacterium that was engulfed by the eukaryotic ancestor and gave rise to the mitochondria, which are organelles in eukaryoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caulobacteraceae
Caulobacteraceae is a family of Pseudomonadota within the alpha subgroup.Garrity, George M.; Brenner, Don J.; Krieg, Noel R.; Staley, James T. (eds.) (2005). Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Volume Two: The Proteobacteria, Part C: The Alpha-, Beta-, Delta-, and Epsilonproteobacteria. New York, New York: Springer. . Like all Pseudomonadota, the Caulobacteraceae are gram-negative. Caulobacteraceae includes the genera ''Asticcacaulis'', ''Brevundimonas'', ''Phenylobacterium'' and ''Caulobacter''. The typespecies ''Caulobacter'' gives its name also to the recently proposed subclass, the ''Caulobacteridae'', which includes the orders ''Caulobacterales'', '' Parvularculales'', ''Hyphomicrobiales'', ''Rhodobacterales'', ''Rhodospirillales'', '' Sneathiellales'', '' Sphingomonadales'', ''Kiloniellales The Rhodospirillales are an order of Pseudomonadota. Notable Families The ''Acetobacteraceae'' comprise the acetic acid bacteria, which are heterotrophic and produce acetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asticcacaulis
The ''Asticcacaulis'' are a genus of bacteria. Etymology The name ''Asticcacaulis'' derives from: Greek prefix ''a'', not; New Latin noun ''sticca'', stick; Latin masculine gender noun ''caulis'', stalk; Latin masculine gender In linguistics, grammatical gender system is a specific form of noun class system, where nouns are assigned with gender categories that are often not related to their real-world qualities. In languages with grammatical gender, most or all nouns ... noun ''Asticcacaulis'', stalk that does not stick. References Caulobacterales Bacteria genera {{Alphaproteobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caulobacter Crescentus
''Caulobacter crescentus'' is a Gram-negative, oligotrophic bacterium widely distributed in fresh water lakes and streams. The taxon is more properly known as ''Caulobacter vibrioides'' (Henrici and Johnson 1935). ''C. crescentus'' is an important model organism for studying the regulation of the cell cycle, asymmetric cell division, and cellular differentiation. ''Caulobacter'' daughter cells have two very different forms. One daughter is a mobile "swarmer" cell that has a single flagellum at one cell pole that provides swimming motility for chemotaxis. The other daughter, called the "stalked" cell, has a tubular stalk structure protruding from one pole that has an adhesive holdfast material on its end, with which the stalked cell can adhere to surfaces. Swarmer cells differentiate into stalked cells after a short period of motility. Chromosome replication and cell division only occurs in the stalked cell stage. ''C. crescentus'' derives its name from its crescent sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caulobacterales
''Caulobacterales'' is an order of gram-negative pseudomonadota Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria) is a major phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. The renaming of phyla in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature. The ... within the alpha subgroup.Garrity, George M.; Brenner, Don J.; Krieg, Noel R.; Staley, James T. (eds.) (2005). Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Volume Two: The Proteobacteria, Part C: The Alpha-, Beta-, Delta-, and Epsilonproteobacteria. New York, New York: Springer. . References Alphaproteobacteria Caulobacterales {{alphaproteobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |