|
Association Mapping
In genetics, association mapping, also known as "linkage disequilibrium mapping", is a method of mapping quantitative trait locus, quantitative trait loci (QTLs) that takes advantage of historic linkage disequilibrium to link phenotypes (observable characteristics) to genotypes (the genetic constitution of organisms), uncovering genetic associations. Theory Association mapping is based on the idea that traits that have entered a population only recently will still be linked to the surrounding genetic sequence of the original evolutionary ancestor, or in other words, will more often be found within a given haplotype, than outside of it. It is most often performed by scanning the entire genome for significant associations between a panel of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (which, in many cases are spotted onto glass slides to create "SNP genotyping, SNP chips") and a particular phenotype. These associations must then be independently verified in order to show that they either (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantitative Trait Locus
A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a locus (section of DNA) that correlates with variation of a quantitative trait in the phenotype of a population of organisms. QTLs are mapped by identifying which molecular markers (such as SNPs or AFLPs) correlate with an observed trait. This is often an early step in identifying the actual genes that cause the trait variation. Definition A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a region of DNA which is associated with a particular phenotypic trait, which varies in degree and which can be attributed to polygenic effects, i.e., the product of two or more genes, and their environment. . These QTLs are often found on different chromosomes. The number of QTLs which explain variation in the phenotypic trait indicates the genetic architecture of a trait. It may indicate that plant height is controlled by many genes of small effect, or by a few genes of large effect. Typically, QTLs underlie continuous traits (those traits which vary continuou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's weight divided by the square of the person's height—is over ; the range is defined as overweight. Some East Asian countries use lower values to calculate obesity. Obesity is a major cause of disability and is Obesity-associated morbidity, correlated with various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis. Obesity has individual, socioeconomic, and environmental causes. Some known causes are Western pattern diet, diet, low physical activity, automation, urbanization, quantitative trait locus, genetic susceptibility, medications, mental disorders, Economic policy, economic pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
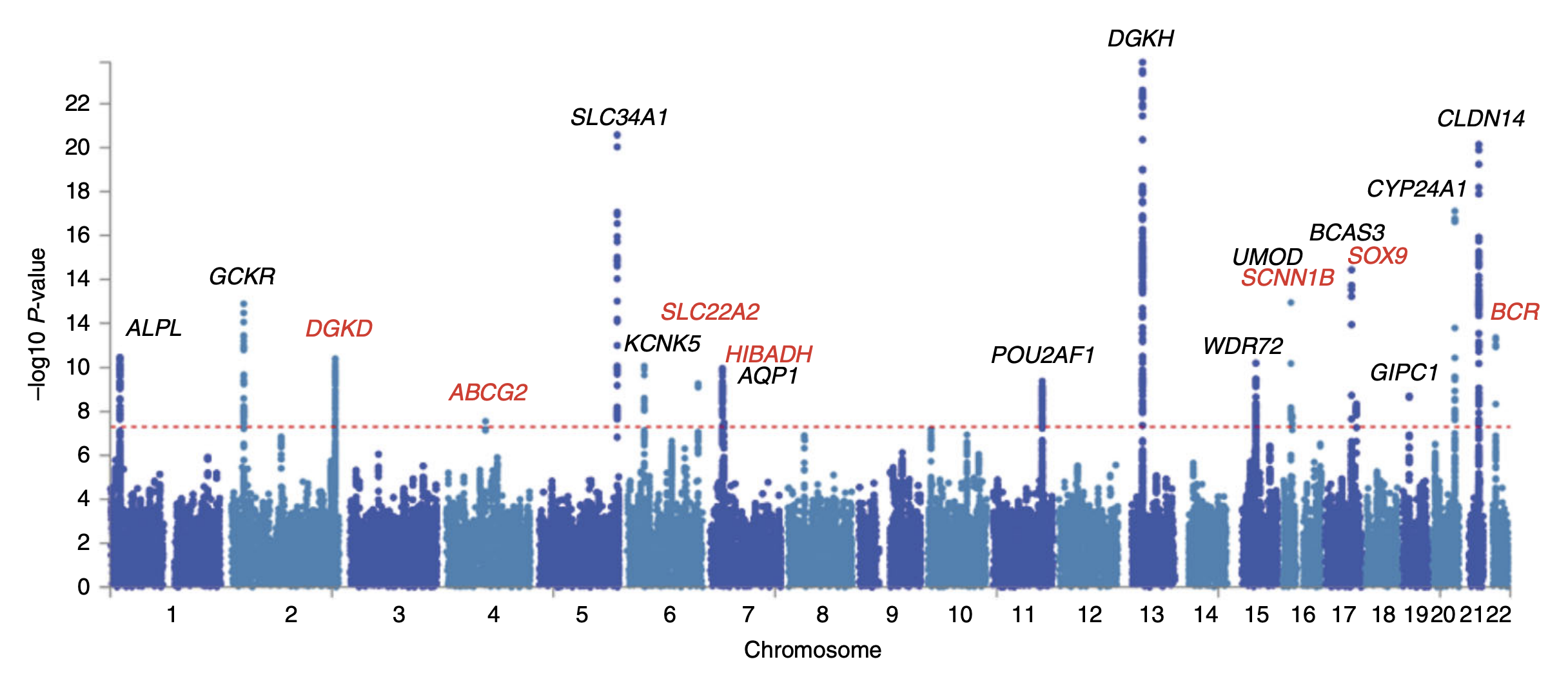
Genome-wide Association Study
In genomics, a genome-wide association study (GWA study, or GWAS), is an observational study of a genome-wide set of Single-nucleotide polymorphism, genetic variants in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait. GWA studies typically focus on associations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and traits like major human diseases, but can equally be applied to any other genetic variants and any other organisms. When applied to human data, GWA studies compare the DNA of participants having varying phenotypes for a particular trait or disease. These participants may be people with a disease (cases) and similar people without the disease (controls), or they may be people with different phenotypes for a particular trait, for example blood pressure. This approach is known as phenotype-first, in which the participants are classified first by their clinical manifestation(s), as opposed to Genotype-first approach, genotype-first. Each person gives a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association (ecology)
In phytosociology and community ecology an association is a type of community (ecology), ecological community with a predictable species composition and consistent physiognomy (structural appearance) which occurs in a particular habitat type. The term was first coined by Alexander von Humboldt and formalised by the International Botanical Congress in 1910. An association can be viewed as a real, integrated entity shaped either by species interactions or by similar habitat requirements, or it can be viewed as merely a common point along a continuum. The former view was championed by American ecologist Frederic Clements, who viewed the association as a whole that was more than the sum of its parts, and by Josias Braun-Blanquet, a Swiss-born phytosociologist. On the other end of the argument was American ecologist Henry Gleason, who saw these groupings of plant species as a coincidence produced by the "fluctuation and fortuitous immigration of plants, and an equally fluctuating and va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindawi (publisher)
Hindawi was a publisher of peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journals active in scientific, technical, and medical (STM) literature. It was founded in 1997 in Cairo, Egypt, and purchased in 2021 for $298 million by John Wiley & Sons, a large US-based publishing company. By 2022, Hindawi was publishing over 250 journals, including 64 journals indexed within the Science Citation Index Expanded, and 1 journal indexed within the Social Sciences Citation Index, with a total of 64 journals ranked with an impact factor. Since 2007, all of Hindawi's journals have been open access and published under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY). The quality of peer review at a number of Hindawi journals has been criticized. In 2010, Hindawi was classified as a possible predatory publisher by Jeffrey Beall, but was removed from the list following a successful appeal. Over the next years, the number of articles in Hindawi journals grew exponentially, the majority being published in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Journal Of Plant Genomics
This is a list of academic journal An academic journal (or scholarly journal or scientific journal) is a periodical publication in which Scholarly method, scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. They serve as permanent and transparent forums for the ...s published by Hindawi. A B C D E G H I J L M N O P Q R S T U V W References {{Reflist External linksList of journals published by Hindawi * Hindawi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linkage Disequilibrium
Linkage disequilibrium, often abbreviated to LD, is a term in population genetics referring to the association of genes, usually linked genes, in a population. It has become an important tool in medical genetics and other fields In defining LD, it is important first to distinguish the two very different concepts, linkage disequilibrium and linkage (genetic linkage). Linkage disequilibrium refers to the association of genes ''in a population.'' Linkage, on the other hand, tells us whether genes are on the same chromosome ''in an individual''. There is no necessary relationship between the two. Genes that are closely linked may or may not be associated in populations. Looking at parents and offspring, if genes at closely linked loci are together in the parent then they will usually be together in the offspring. But looking at individuals in a population with no known common ancestry, it is much more difficult to see any relationships. To give a concrete, although imaginary, example i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantitative Trait Locus
A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a locus (section of DNA) that correlates with variation of a quantitative trait in the phenotype of a population of organisms. QTLs are mapped by identifying which molecular markers (such as SNPs or AFLPs) correlate with an observed trait. This is often an early step in identifying the actual genes that cause the trait variation. Definition A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a region of DNA which is associated with a particular phenotypic trait, which varies in degree and which can be attributed to polygenic effects, i.e., the product of two or more genes, and their environment. . These QTLs are often found on different chromosomes. The number of QTLs which explain variation in the phenotypic trait indicates the genetic architecture of a trait. It may indicate that plant height is controlled by many genes of small effect, or by a few genes of large effect. Typically, QTLs underlie continuous traits (those traits which vary continuou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Based QTL Mapping
Quantitative trait loci mapping or QTL mapping is the process of identifying genomic regions that potentially contain genes responsible for important economic, health or environmental characters. Mapping QTLs is an important activity that plant breeders and geneticists routinely use to associate potential causal genes with phenotypes of interest. Family-based QTL mapping is a variant of QTL mapping where multiple-families are used. Pedigree in humans and wheat Pedigree information include information about ancestry. Keeping pedigree records is a centuries-old tradition. Pedigrees can also be verified using gene-marker data. In plants The method has been discussed in the context of plant breeding populations. Pedigree records are kept by plants breeders and pedigree-based selection is popular in several plant species. Plant pedigrees are different from that of humans, particularly as plant are hermaphroditic – an individual can be male or female and mating can be performed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nested Association Mapping
Nested association mapping (NAM) is a technique designed by the labs of Edward BucklerJames Holland anfor identifying and dissecting the genetic architecture of complex traits in corn (''Zea mays''). It is important to note that nested association mapping (unlike association mapping) is a specific technique that cannot be performed outside of a specifically designed population such as the Maize NAM population, the details of which are described below. Theory behind NAM NAM was created as a means of combining the advantages and eliminating the disadvantages of two traditional methods for identifying quantitative trait loci: linkage analysis and association mapping. Linkage analysis depends upon recent genetic recombination between two different plant lines (as the result of a genetic cross) to identify general regions of interest, with the advantage of requiring few genetic markers to ensure genome wide coverage and high statistical power per allele. Linkage analysis, however, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWAS
GWAS may refer to: *Genome-wide association study, study of mutations' correlations with disease or other phenotypic expressions *''gwas'', a Welsh term for a valet * Great Western Ambulance Service, the ambulance service serving Somerset, Gloucestershire and Wiltshire Wiltshire (; abbreviated to Wilts) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It borders Gloucestershire to the north, Oxfordshire to the north-east, Berkshire to the east, Hampshire to the south-east, Dorset to the south, and Somerset to .... *An online gaming abbreviation for "Game was a success". {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the average life expectancy following diagnosis is three to twelve years. The causes of Alzheimer's disease remain poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an allele of apolipoprotein E. Other risk factors include a history of head injury, clinical depression, and high blood pressure. The progression of the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |