|
Asioi
The Asii, Osii, Ossii, Asoi, Asioi, Asini or Aseni were an ancient Indo-European people of Central Asia, during the 2nd and 1st centuries BCE. Known only from Classical Greek and Roman sources, they were one of the peoples held to be responsible for the downfall of the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom. In Greek Mythology they were the children of Iapetus and Asia. Modern scholars have attempted to identify the Asii with other peoples known from European and Chinese sources including the: Yuezhi, Tocharians, Issedones/Wusun and/or Alans. Historical sources The classical European sources relating to the Asii are brief. They sometimes survive only as quotations in other ancient sources, with textual variations that have led to widely varying translations and interpretations. During the 4th and 3rd Centuries BCE, Megasthenes, who lived in Arachosia and was an ambassador to the Mauryan court in Pataliputra, refers in his work ''Indika'' to three tribes with similar and possibly related names, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tushara Kingdom
The kingdom of Tushara according to Ancient Indian literature, such as the epic ''Mahabharata'' was a land located beyond north-west India. In the ''Mahabharata'', its inhabitants, known as the Tusharas, are depicted as ''mlechchas'' ("barbarians") and fierce warriors. Modern scholars generally see Tushara as synonymous with the historical "Tukhara", also known as Tokhara or Tokharistan – another name for Bactria. This area was the stronghold of the Kushan Empire, which dominated India between the 1st and 3rd centuries CE. Tukhara The historical Tukhara appears to be synonymous with the land known by Ancient Chinese scholars as ''Daxia'', from the 3rd century BCE onwards. Its inhabitants were known later to Ancient Greek scholars as the ''Tokharoi'' and to the Ancient Romans as ''Tochari''. Modern scholars appear to have conflated the ''Tukhara'' with the so-called Tocharians – an Indo-European people who lived in the Tarim Basin, in present-day Xinjiang, China, until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat at the hands of the Xiongnu in 176 BC, the Yuezhi split into two groups migrating in different directions: the Greater Yuezhi (''Dà Yuèzhī'' 大月氏) and Lesser Yuezhi (''Xiǎo Yuèzhī'' 小月氏). This started a complex domino effect that radiated in all directions and, in the process, set the course of history for much of Asia for centuries to come. The Greater Yuezhi initially migrated northwest into the Ili River, Ili Valley (on the modern borders of China and Kazakhstan), where they reportedly displaced elements of the Sakas. They were driven from the Ili Valley by the Wusun and migrated southward to Sogdia and later settled in Bactria. The Greater Yuezhi have consequently often been identified with peoples mentioned in classica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
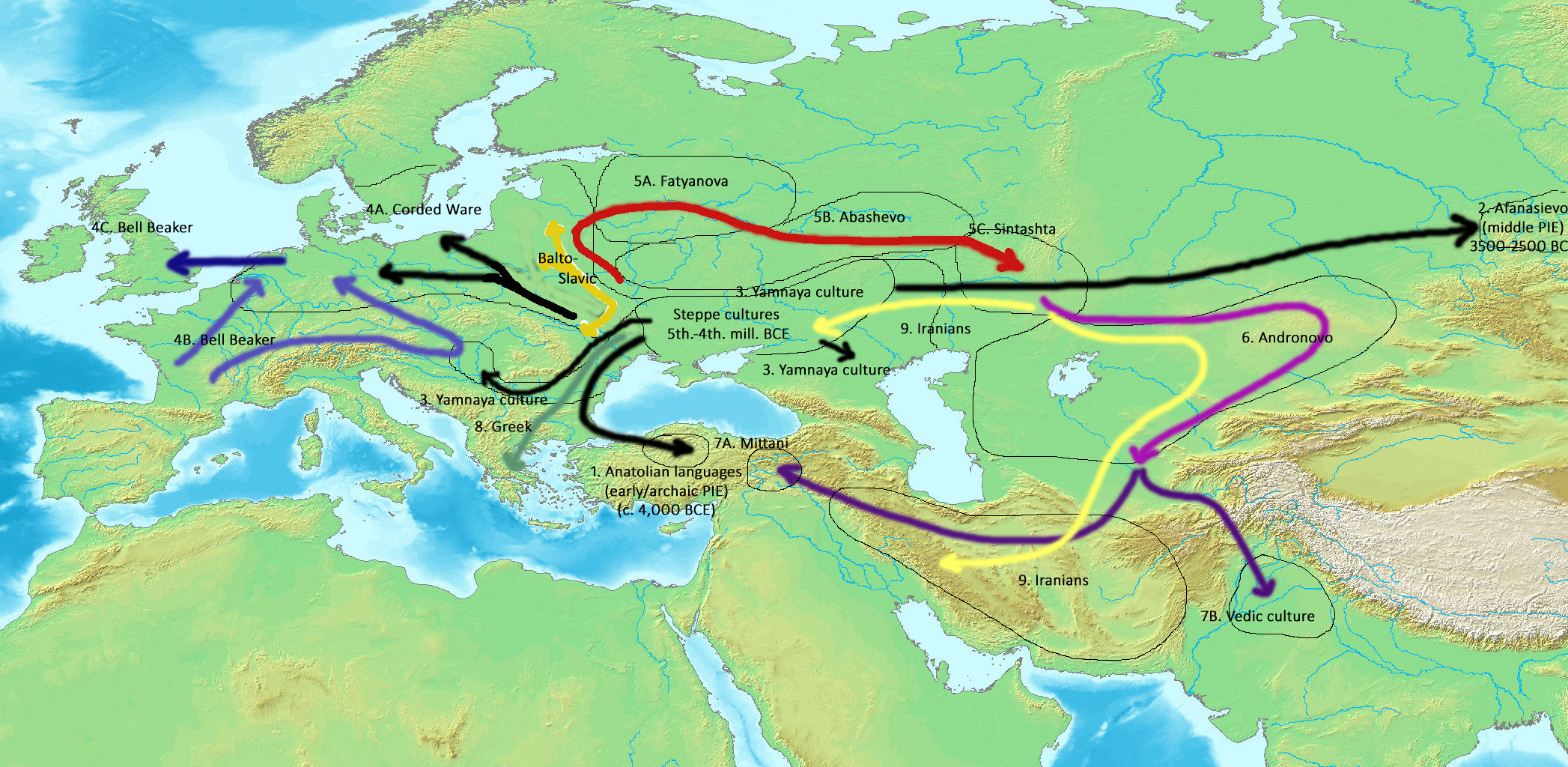
Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction. Knowledge of them comes chiefly from that linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics. The Proto-Indo-Europeans likely lived during the late Neolithic, or roughly the 4th millennium BC. Mainstream scholarship places them in the Pontic–Caspian steppe zone in Eurasia (present-day Ukraine and southern Russia). Some archaeologists would extend the time depth of PIE to the middle Neolithic (5500 to 4500 BC) or even the early Neolithic (7500 to 5500 BC) and suggest alternative location hypotheses. By the early second millennium BC, descendants of the Proto-Indo-Europeans had reached far and wide across Eurasia, including Anatolia (Hittites), the Aegean (the linguistic ancestors of Mycenaean Greece), the north of Europe (Corded War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
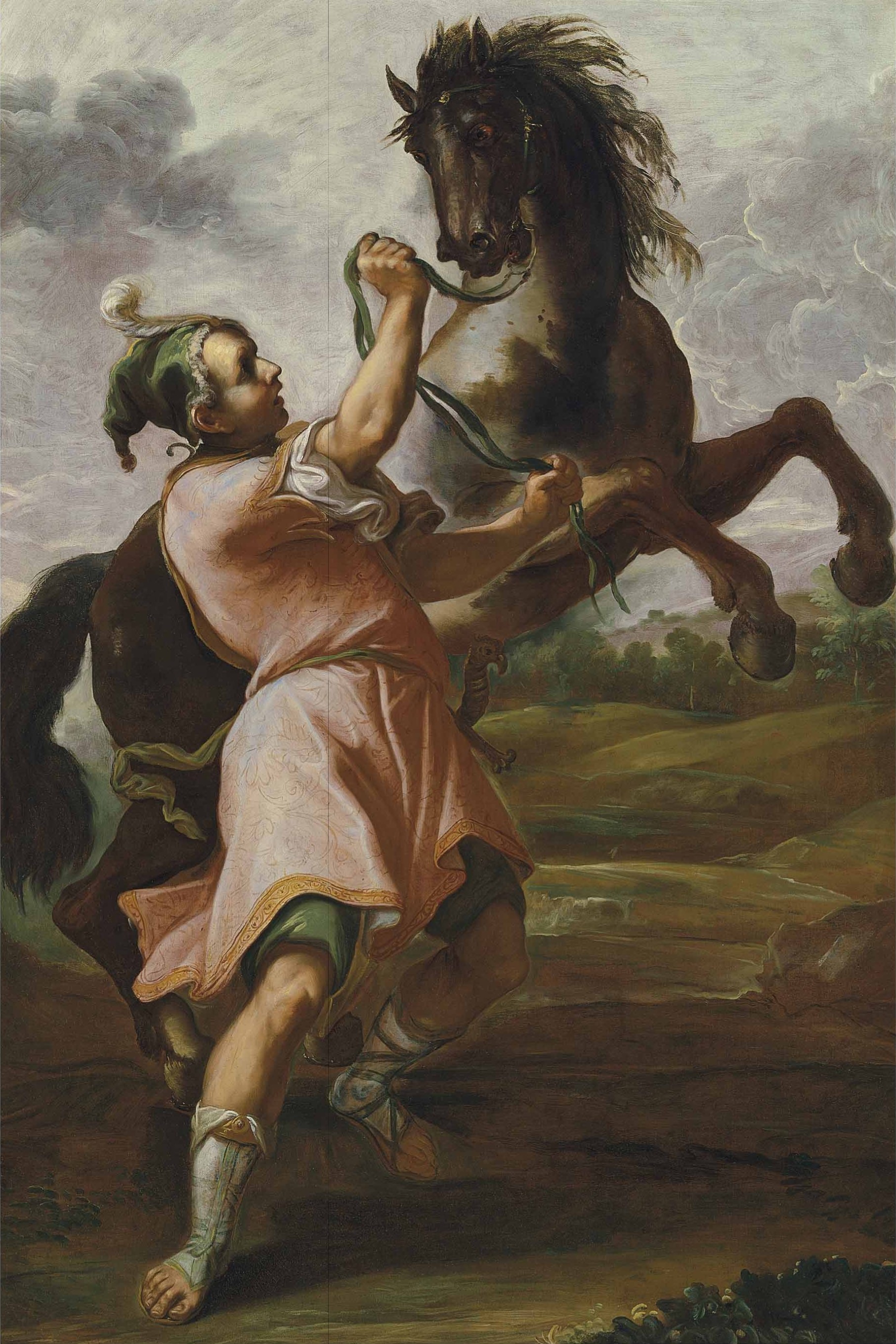
Bucephalus
Bucephalus or Bucephalas (; grc, Βουκεφάλας, ; – June 326 BC) was the horse of Alexander the Great, and one of the most famous horses of classical antiquity. Ancient historical accounts state that Bucephalus' breed was that of the "best Thessaly, Thessalian strain", and that he died in what is now Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab, Pakistan, after the Battle of the Hydaspes in 326 BC. The horse was reportedly buried at Jalalpur Sharif, a small town situated a short distance to the southwest of Jhelum. Another account states that Bucephalus is buried in Phalia, a town located near the city of Mandi Bahauddin, which was named after him (Alexandria Bucephalous). Bucephalus was named after Bucephalus (brand), a branding mark depicting an ox's head on his haunch. Taming of Bucephalus A massive creature with a massive head, Bucephalus is described as having a black coat with a large white star on his brow. He is also supposed to have had a "Horse markings#Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian People
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. The ancient Persians were originally an ancient Iranian people who had migrated to the region of Persis (corresponding to the modern-day Iranian province of Fars) by the 9th century BCE. Together with their compatriot allies, they established and ruled some of the world's most powerful empires that are well-recognized for their massive cultural, political, and social influence, which covered much of the territory and population of the ancient world.. Throughout history, the Persian people have contributed greatly to art and science. Persian literature is one of the world's most prominent literary traditions. In contemporary terminology, people from Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan who natively speak the Persian language are know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jhelum
Jhelum ( Punjabi and ur, ) is a city on the east bank of the Jhelum River, which is located in the district of Jhelum in the north of Punjab province, Pakistan. It is the 44th largest city of Pakistan by population. Jhelum is known for providing many soldiers to the British Army before independence, and later to the Pakistan armed forces – due to which it is also known as ''City of Soldiers'' or ''Land of Martyrs and Warriors''. Jhelum is a few miles upstream from the site of the ancient Battle of the Hydaspes between the armies of Alexander and King Porus. Possibly Jhelum City was the capital of Porus' Kingdom, Paurava. A city called Bucephala was founded nearby to commemorate the death of Alexander's horse, Bucephalus. Other notable sites nearby include the 16th-century Rohtas Fort, the Tilla Jogian complex of ancient temples, and the 16th-century Grand Trunk Road which passes through the city. According to the 2017 census of Pakistan, the population of Jhelum was 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of modern-day territory of, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Uzbekistan, and northern India, at least as far as Saketa and Sarnath near Varanasi (Benares), where inscriptions have been found dating to the era of the Kushan Emperor Kanishka the Great. The Kushans were most probably one of five branches of the Yuezhi confederation, an Indo-European nomadic people of possible Tocharian origin, who migrated from northwestern China (Xinjiang and Gansu) and settled in ancient Bactria. The founder of the dynasty, Kujula Kadphises, followed Greek religious ideas and iconography after the Greco-Bactrian tradition, and being a follower of Shaivism. The Kushans in general were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirata
The Kirāta ( sa, किरात) is a generic term in Sanskrit literature for people who had territory in the mountains, particularly in the Himalayas and Northeast India and who are believed to have been Sino-Tibetan in origin. The meaning of 'Kirata' referred by scholars as people with the lion's character, or mountain dwellers. Historical mention and mythology The ''Kirata''s often mentioned along with Cinas (Chinese), and slightly different from the Nishadas, are first mentioned in the Yajurveda (''Shukla'' XXX.16; ''Krisha'' III.4,12,1), and in the Atharvaveda (X.4,14). According to Suniti Kumar Chatterji, the name ''Kirata'' seems to be used for any non-Aryan hill-folk, however Manu's Dharmashastra (X.44) calls them "degraded Kshatriyas", which Chatterji infers to be a term for people who were advanced in military or civilization to some degree and not complete barbarians. It is speculated that the term is a Sanskritization of a Tibeto-Burman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ''Naturalis Historia'' (''Natural History''), which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. His nephew, Pliny the Younger, wrote of him in a letter to the historian Tacitus: Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume work ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus and Suetonius. Tacitus—who many scholars agree had never travelled in Germania—used ''Bella Germani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see things at great distance as if they were nearby was also called "Strabo". (; el, Στράβων ''Strábōn''; 64 or 63 BC 24 AD) was a Greek geographer, philosopher, and historian who lived in Asia Minor during the transitional period of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. Life Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus (in present-day Turkey) in around 64BC. His family had been involved in politics since at least the reign of Mithridates V. Strabo was related to Dorylaeus on his mother's side. Several other family members, including his paternal grandfather had served Mithridates VI during the Mithridatic Wars. As the war drew to a close, Strabo's grandfather had turned several Pontic fortress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justin (historian)
Justin ( la, Marcus Junianus Justinus Frontinus; century) was a Latin writer who lived under the Roman Empire. Life Almost nothing is known of Justin's personal history, his name appearing only in the title of his work. He must have lived after Gnaeus Pompeius Trogus, whose work he excerpted, and his references to the Romans and Parthians' having divided the world between themselves would have been anachronistic after the rise of the Sassanians in the third century. His Latin appears to be consistent with the style of the second century. Ronald Syme, however, argues for a date around AD 390, immediately before the compilation of the Augustan History, and dismisses anachronisms and the archaic style as unimportant, as he asserts readers would have understood Justin's phrasing to represent Trogus' time, and not his own. Works Justin was the author of an epitome of Trogus' expansive ''Liber Historiarum Philippicarum'', or ''Philippic Histories'', a history of the kings of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trogus
Gnaeus Pompeius Trogus also anglicized as was a Gallo-Roman historian from the Celtic Vocontii tribe in Narbonese Gaul who lived during the reign of the emperor Augustus. He was nearly contemporary with Livy. Life Pompeius Trogus's grandfather served under Pompey in his war against Sertorius. Owing to Pompey's influence, he was able to obtain Roman citizenship and his family adopted their patron's praenomen and nomen Gnaeus Pompeius. Trogus's father served under Julius Caesar as his secretary and interpreter. Trogus himself seems to have been a polymath. Works Following Aristotle and Theophrastus, Pompeius Trogus wrote books on the natural history of animals and plants. His principal work, however, was his 44-volume ''Philippic Histories and the Origin of the Whole World and the Places of the Earth'' ('' Historiae Philippicae et Totius Mundi Origines et Terrae Situs''), now lost, which, according to its surviving epitome, had as its principal theme the Macedonian Empire f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |