|
Ashford Power Station
Ashford Power Station refers to any of three, engine-driven, electricity generating stations located in Ashford, Kent. Two of the stations, A and B, have been demolished, and one is an operational 21 MW peaking plant. Ashford A Ashford A power station (also known as Ashford Electricity Works) was located in Victoria Road, Ashford. It was adjacent to, and south of, the London to Dover railway, 575 metres north west of Ashford International railway station. The power station was built in 1923 to provide electricity to the town of Ashford. It was initially owned and operated by ''Ashford Urban District Council''. The plant consisted of Ruston vertical oil engines coupled to three 300 kW and one 700 kW English Electric alternators. There was also one Davey-Paxman 8-cylinder oil engine coupled to a 450 kW English Electric alternator. The total electricity generating capacity was 2.05 MW. The alternators generated electricity at 6.6 kV, Alternating Current, 3-phase, 50 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Electricity Authority
The British Electricity Authority (BEA) was established as the central British electricity authority in 1948 under the nationalisation of Great Britain's electricity supply industry enacted by the Electricity Act 1947. The BEA was responsible for the generation, transmission and sale of electricity to area electricity boards, and the development and maintenance of an efficient, coordinated and economical system of electricity supply. History The authority took over the operations of over 600 small public supply power companies, municipal authority electricity departments and the Central Electricity Board to form the BEA, which comprised a central authority and 14 area boards. Its scope did not include control of the North of Scotland Hydro-Electric Board, which had been founded in 1943 and remained independent of the BEA. The appointment of chairmen and members of the BEA and the area boards were made in August 1947 and the BEA was formally established on 15 August 1947. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
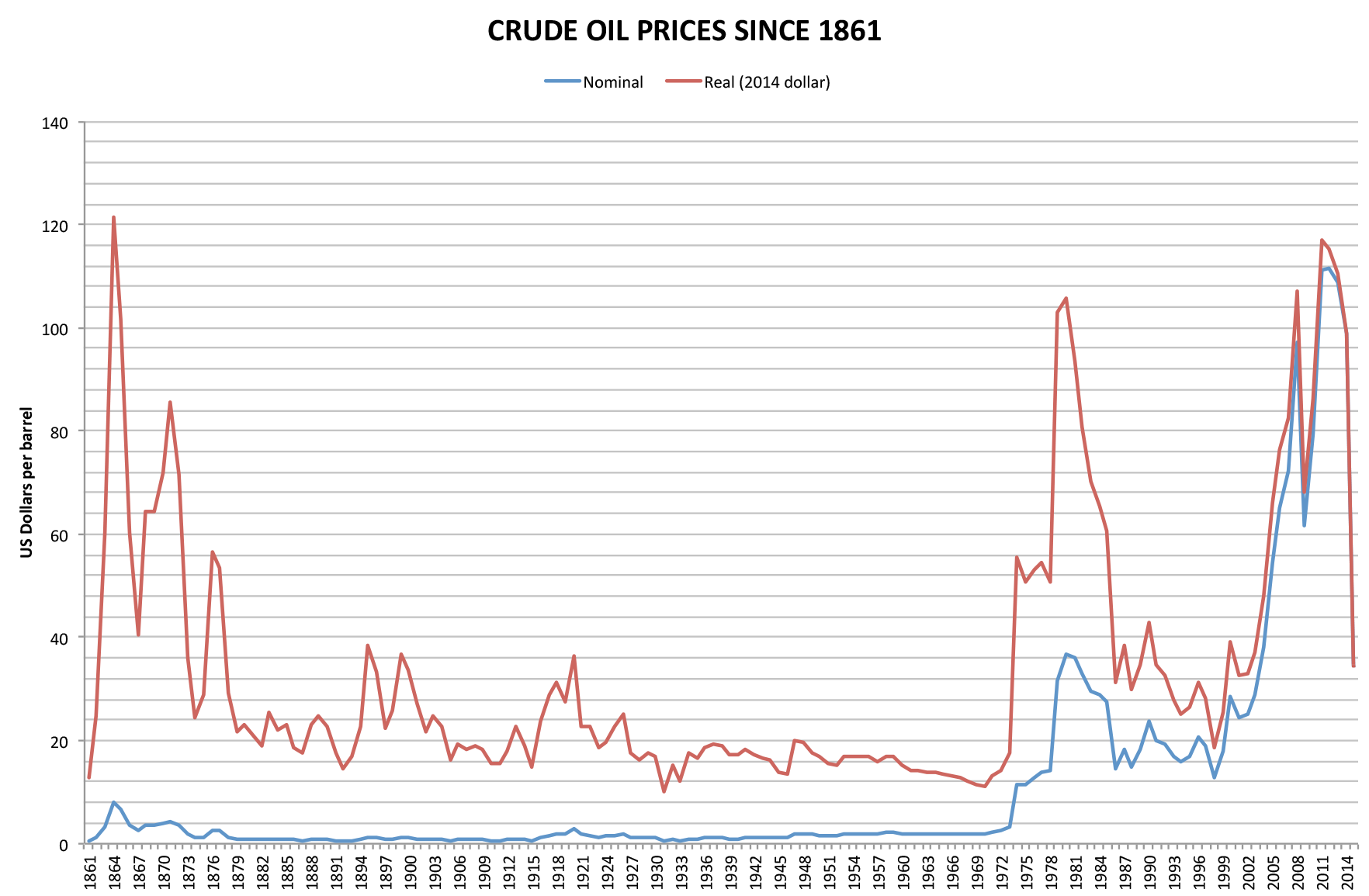
Diesel Fuel
Diesel fuel , also called diesel oil, is any liquid fuel specifically designed for use in a diesel engine, a type of internal combustion engine in which fuel ignition takes place without a spark as a result of compression of the inlet air and then injection of fuel. Therefore, diesel fuel needs good compression ignition characteristics. The most common type of diesel fuel is a specific fractional distillate of petroleum fuel oil, but alternatives that are not derived from petroleum, such as biodiesel, biomass to liquid (BTL) or gas to liquid (GTL) diesel are increasingly being developed and adopted. To distinguish these types, petroleum-derived diesel is sometimes called petrodiesel in some academic circles. In many countries, diesel fuel is standardised. For example, in the European Union, the standard for diesel fuel is EN 590. Diesel fuel has many colloquial names; most commonly, it is simply referred to as ''diesel''. In the United Kingdom, diesel fuel for on-road use is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Power Stations In England
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demolished Power Stations In The United Kingdom
Demolition (also known as razing, cartage, and wrecking) is the science and engineering in safely and efficiently tearing down of buildings and other artificial structures. Demolition contrasts with deconstruction, which involves taking a building apart while carefully preserving valuable elements for reuse purposes. For small buildings, such as houses, that are only two or three stories high, demolition is a rather simple process. The building is pulled down either manually or mechanically using large hydraulic equipment: elevated work platforms, cranes, excavators or bulldozers. Larger buildings may require the use of a wrecking ball, a heavy weight on a cable that is swung by a crane into the side of the buildings. Wrecking balls are especially effective against masonry, but are less easily controlled and often less efficient than other methods. Newer methods may use rotational hydraulic shears and silenced rock-breakers attached to excavators to cut or break through wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Grid (Great Britain)
In the electricity sector in the United Kingdom, the National Grid is the high-voltage electric power transmission network serving Great Britain, connecting power stations and major substations and ensuring that electricity generated anywhere on it can be used to satisfy demand elsewhere. The network covers the great majority of Great Britain and several of the surrounding islands. It does not cover Northern Ireland, which is part of a single electricity market with the Republic of Ireland. The GB grid is connected as a wide area synchronous grid nominally running at 50 hertz. There are also undersea interconnections to other grids in the Isle of Man, Northern Ireland, the Republic of Ireland, France, Belgium, the Netherlands and Norway. On the breakup of the Central Electricity Generating Board in 1990, the ownership and operation of the National Grid in England and Wales passed to National Grid Company plc, later to become National Grid Transco, and now National Grid plc. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, and helium are also usually present. Natural gas is colorless and odorless, so odorizers such as mercaptan (which smells like sulfur or rotten eggs) are commonly added to natural gas supplies for safety so that leaks can be readily detected. Natural gas is a fossil fuel and non-renewable resource that is formed when layers of organic matter (primarily marine microorganisms) decompose under anaerobic conditions and are subjected to intense heat and pressure underground over millions of years. The energy that the decayed organisms originally obtained from the sun via photosynthesis is stored as chemical energy within the molecules of methane and other hydrocarbons. Natural gas can be burned fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energy, digital industry, additive manufacturing and venture capital and finance, but has since divested from several areas, now primarily consisting of the first four segments. In 2020, GE ranked among the Fortune 500 as the 33rd largest firm in the United States by gross revenue. In 2011, GE ranked among the Fortune 20 as the 14th most profitable company, but later very severely underperformed the market (by about 75%) as its profitability collapsed. Two employees of GE – Irving Langmuir (1932) and Ivar Giaever (1973) – have been awarded the Nobel Prize. On November 9, 2021, the company announced it would divide itself into three investment-grade public companies. On July 18, 2022, GE unveiled the brand names of the companies it will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peaking Power Plant
Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the power supplied commands a much higher price per kilowatt hour than base load power. Peak load power plants are dispatched in combination with base load power plants, which supply a dependable and consistent amount of electricity, to meet the minimum demand. Although historically peaking power plants were frequently used in conjunction with coal baseload plants, peaking plants are now used less commonly. Combined cycle gas turbine plants have two or more cycles, the first of which is very similar to a peaking plant, with the second running on the waste heat of the first. That type of plant is often capable of rapidly starting up, albeit at reduced efficiency, and then over some hours transitioning to a more efficient baseload generation mode. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1973 Oil Crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War. The initial nations targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and the United States, though the embargo also later extended to Portugal, Rhodesia and South Africa. By the end of the embargo in March 1974, the price of oil had risen nearly 300%, from US to nearly globally; US prices were significantly higher. The embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long-term effects on global politics and the global economy. It was later called the "first oil shock", followed by the 1979 oil crisis, termed the "second oil shock". Background Arab-Israeli conflict Ever since the recreation of the State of Israel in 1948 there has been Arab–Israeli conflict in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Inquiry
A tribunal of inquiry is an official review of events or actions ordered by a government body. In many common law countries, such as the United Kingdom, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, Australia and Canada, such a public inquiry differs from a royal commission in that a public inquiry accepts evidence and conducts its hearings in a more public forum and focuses on a more specific occurrence. Interested members of the public and organisations may make (written) evidential submissions, as is the case with most inquiries, and also listen to oral evidence given by other parties. Typical events for a public inquiry are those that cause multiple deaths, such as public transport crashes or mass murders. In addition, in the United Kingdom, UK, the Planning Inspectorate, an agency of the Department for Communities and Local Government, routinely holds public inquiries into a range of major and lesser land use developments, including highways and other transport proposals. Advocacy groups and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilowatt Hour
A kilowatt-hour (unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common billing unit for electrical energy delivered to consumers by electric utilities. Definition The kilowatt-hour is a composite unit of energy equal to one kilowatt (kW) sustained for (multiplied by) one hour. Expressed in the standard unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI), the joule (symbol J), it is equal to 3,600 kilojoules or 3.6 MJ."Half-high dots or spaces are used to express a derived unit formed from two or more other units by multiplication.", Barry N. Taylor. (2001 ed.''The International System of Units.'' (Special publication 330). Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology. 20. Unit representations A widely used representation of the kilowatt-hour is "kWh", derived from its compone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooling Tower
A cooling tower is a device that rejects waste heat to the atmosphere through the cooling of a coolant stream, usually a water stream to a lower temperature. Cooling towers may either use the evaporation of water to remove process heat and cool the working fluid to near the wet-bulb air temperature or, in the case of ''dry cooling towers'', rely solely on air to cool the working fluid to near the dry-bulb air temperature using radiators. Common applications include cooling the circulating water used in oil refineries, petrochemical and other chemical plants, thermal power stations, nuclear power stations and HVAC systems for cooling buildings. The classification is based on the type of air induction into the tower: the main types of cooling towers are natural draft and induced draft cooling towers. Cooling towers vary in size from small roof-top units to very large hyperboloid structures (as in the adjacent image) that can be up to tall and in diameter, or rectangu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |