|
Asher Arieli
Rabbi Asher Arieli (born 1957) is the senior lecturer at Yeshivas Mir in Israel. He is globally renowned for his lectures on Talmud and is widely recognized as a Gadol in his own right. He presently delivers the largest Talmudic lecture by attendance in the world with 1000 daily attendees. His primary, daily shiur begins at about 6:00pm and is streamed live aKol Haloshon. Family life Rabbi Asher Arieli is married to Rebbetzin Malka, the daughter of Hagaon Rabbi Nachum Partzovitz, the late Rosh Yeshiva of Mir. Rabbi Arieli is the son of Rabbi Chaim Yaakov Arieli, author of Be'er Yaakov (באר יעקב). Rabbi Chaim Yaakov Arieli was the son of Rabbi Yitzhak Arieli, author of Einaim L'Mishpat (עינים למשפט) and Mashgiach Ruchani of Mercaz HaRav. Rabbi Mordechai Ilan, the son-in-law of Rabbi Yitzhak Arieli is Reb Asher's paternal uncle. Reb Chaim Yaakov's wife is the sister of Rabbi Moishe Sternbuch, as are the wives of Rabbi Meshulam Dovid Soloveitchik and Dayan Chanoch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthodox Judaism
Orthodox Judaism is the collective term for the traditionalist and theologically conservative branches of contemporary Judaism. Theologically, it is chiefly defined by regarding the Torah, both Written and Oral, as revealed by God to Moses on Mount Sinai and faithfully transmitted ever since. Orthodox Judaism, therefore, advocates a strict observance of Jewish law, or ''halakha'', which is to be interpreted and determined exclusively according to traditional methods and in adherence to the continuum of received precedent through the ages. It regards the entire ''halakhic'' system as ultimately grounded in immutable revelation, and beyond external influence. Key practices are observing the Sabbath, eating kosher, and Torah study. Key doctrines include a future Messiah who will restore Jewish practice by building the temple in Jerusalem and gathering all the Jews to Israel, belief in a future bodily resurrection of the dead, divine reward and punishment for the righteous and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akiva Eiger
Rabbi Akiva Eiger (, also spelled Eger; , yi, עקיבא אייגער), or Akiva Güns (17611837) was an outstanding Talmudic scholar, influential halakhic decisor and foremost leader of European Jewry during the early 19th century. He was also a mohel. Life Eiger was born in Pressburg - Bratislava, Royal Hungary (modern-day Slovakia). He was a child prodigy and was educated first at the Mattersburg yeshiva and later by his uncle, Rabbi Wolf Eiger, (1756–1795) (b. ''5516'', d. ''6 Tishrei 5556''), at the Breslau (Wrocław) yeshiva, who later became rabbi of Biała and Leipnik. Out of respect for his uncle he changed his surname to Eiger. He therefore shared the full name Akiva Eiger with his maternal grandfather, the first Rabbi Akiva Eiger (17221758) (b. ''5482'', d. ''15 Elul 5518''), the author of ''Mishnas De'Rebbi Akiva'' who was rabbi of Zülz, Silesia from 1749 and Pressburg from 1756. He was the rabbi of Märkisch Friedland, West Prussia, from 1791 until 1815; t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haredi Rabbis In Israel
Haredi Judaism ( he, ', ; also spelled ''Charedi'' in English; plural ''Haredim'' or ''Charedim'') consists of groups within Orthodox Judaism that are characterized by their strict adherence to ''halakha'' (Jewish law) and traditions, in opposition to modern values and practices. Its members are usually referred to as ultra-Orthodox in English; however, the term "ultra-Orthodox" is considered pejorative by many of its adherents, who prefer terms like strictly Orthodox or Haredi. Haredi Jews regard themselves as the most religiously authentic group of Jews, although other Jewish religious movements, movements of Judaism disagree. Some scholars have suggested that Haredi Judaism is a reaction to societal changes, including Jewish emancipation, political emancipation, the ''Haskalah'' movement derived from the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment, Jewish assimilation, acculturation, Jewish secularism, secularization, religious reform in all its forms from mild to extreme, the rise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yechiel Spero
Yechiel ( he, יְחִיאֵל) is a Hebrew masculine given name meaning "May God live" or "God shall live". Several people in the Bible have this name. See Jehiel (biblical figure). Alternative spellings of Yechiel include Jehiel, Yehiel, Yechi'el, and Yiddish variants include Ichel, Ychel, Echiel, Cheil, and Chil may refer to: People *Yehiel Bar (born 1975), Israeli politician *Jehiel Brooks (1797–1886), American soldier and politician *Yehiel De-Nur (1909–2001), Israeli writer *Yehiel Dresner (1922–1947), Israeli paramilitary fighter *Yechiel Eckstein (1951–2019), American rabbi *Yechiel Fishel Eisenbach (1925–2008), Israeli rabbi *Jehiel R. Elyachar (1898–1989), American engineer *Yechiel Michel Epstein (1829–1908), Lithuanian rabbi *Yehiel Lasri (born 1957), Israeli politician and mayor *Yechiel Leiter (born 1959), Israeli political scientist and civic leader *Yechiel Lerer (1910–1943), Polish poet *Yehiel Rabinowitz (born 1939), French artist *Yechiel S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved throughout history as the main liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. Hebrew is the only Canaanite language still spoken today, and serves as the only truly successful example of a dead language that has been revived. It is also one of only two Northwest Semitic languages still in use, with the other being Aramaic. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' Lashon Hakodesh'' (, ) since an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a vernacular based on High German fused with many elements taken from Hebrew (notably Mishnaic) and to some extent Aramaic. Most varieties of Yiddish include elements of Slavic languages and the vocabulary contains traces of Romance languages.Aram Yardumian"A Tale of Two Hypotheses: Genetics and the Ethnogenesis of Ashkenazi Jewry".University of Pennsylvania. 2013. Yiddish is primarily written in the Hebrew alphabet. Prior to World War II, its worldwide peak was 11 million, with the number of speakers in the United States and Canada then totaling 150,000. Eighty-five percent of the approximately six million Jews who were murdered in the Holocaust were Yiddish speakers,Solomon Birnbaum, ''Grammatik der jiddischen Sprache'' (4., erg. Aufl., Hambu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kallah
Yarchei Kallah (Hebrew: "''months of the bride''") is the name of a teachers' convention that was held twice a year in Babylonian Academies, by the Jews then in captivity in Babylon, after the beginning of the amoraic period, in the two months Adar and Elul. The name refers to the Torah as bride to be studied in the months of farming inactivity after oil and wine harvest. Description For each year's convention of the Kallah, a treatise of the Mishnah was written forming the subject of explanation and discussion at the convention, according to Ta'anit 10b. cites opinions attributing authorship to either Jehudai Gaon (8th century) or to Eliezer ben Hyrcanus (c.100 CE) with later additions and redaction. The regular Kallah conventions concerned issues related to marriage, chastity, and moral purity. The subject matter was largely taken from the Babylonian Talmud. The importance of the Kallah Convention (referred to under another name) is extolled in the Midrash Tanḥuma: "Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agudat Yisrael
Agudat Yisrael ( he, אֲגוּדָּת יִשְׂרָאֵל, lit., ''Union of Israel'', also transliterated ''Agudath Israel'', or, in Yiddish, ''Agudas Yisroel'') is a Haredi Jewish political party in Israel. It began as a political party representing Haredi Jews in Poland, originating in the Agudath Israel movement in Upper Silesia. It later became the Party of many Haredim in Israel. It was the umbrella party for many, though not all, Haredi Jews in Israel until the 1980s, as it had been during the British Mandate of Palestine. Since the 1980s, it has become a predominantly Hasidic party, though it often combines with the Degel HaTorah non-Hasidic Ashkenazi Haredi party for elections and coalition-forming (although not with the Sephardi and Mizrahi Haredi party Shas). When so combined, they are known together as United Torah Judaism. History When political Zionism began to emerge in the 1890s, and recruit supporters in Europe and America, it was opposed by many Orthodox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siyum On Kesubos
A ''siyum'' ( he, סיום) ("completion"), in Judaism, occasionally spelled siyyum, is the completion of any established unit of Torah study. The most common units are a single volume of the Talmud, or of Mishnah, but there are other units of learning that may lead to a siyum. The typical structure of a siyum event includes a conclusion of the study, reading of the '' Hadran'' text, kaddish, and a celebratory meal. The custom to make a ''siyum'' is first mentioned in the Talmud: "Abaye said: grant me my reward, for when I see a young Torah scholar who has completed a tractate, I make a celebration for the rabbis." Type of study The typical siyum is on a single book of Talmud, or on the entirety of the Mishna. This is due to the Talmud being an explanation of the Mishna, with each tractate of the Mishnah being relatively short, but the Talmudical version of it occupying an entire book. (A single published book of Mishnah typically covers many Tractates.) Talmud and Mishnah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
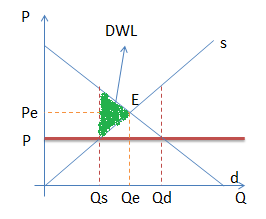
Rent Control
Rent regulation is a system of laws, administered by a court or a public authority, which aims to ensure the affordability of housing and tenancies on the rental market for dwellings. Generally, a system of rent regulation involves: *Price controls, limits on the rent that a landlord may charge, typically called rent control or rent stabilization *Eviction controls: codified standards by which a landlord may terminate a tenancy *Obligations on the landlord or tenant regarding adequate maintenance of the property *A system of oversight and enforcement by an independent regulator and ombudsman The loose term "rent control" covers a spectrum of regulation which can vary from setting the absolute amount of rent that can be charged, with no allowed increases, to placing different limits on the amount that rent can increase; these restrictions may continue between tenancies, or may be applied only within the duration of a tenancy. As of 2016, at least 14 of the 36 OECD countries have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |