|
Ashchykol Depression
The Ashchykol Depression ( kk, Ащыкөл ойпаты; rus, Ащыкольская впадина), is a depression in the Turkistan and Kyzylorda regions, Kazakhstan.Google Earth The village of Taykonyr, Suzak District, Turkistan Region is located in the depression. The Ashchykol zone includes a Important Bird Area. Geography The Ashchykol Depression lies between the lowest reaches of the Sarysu in the west and the mouth of the Chu river in the east. It extends roughly from east to west for a length of less than to the southwest of the Betpak-Dala desert and north of the northwestern end of the Karatau Range. It is a largely flat endorheic basin filled with mixed sand and clay deposits, as well as sandy alluvial sediments. There are numerous intermittent salt lakes and solonchaks. The main lakes are Akzhaikyn and Ashchykol. In wet years the Chu river may reach lake Akzhaikyn at the eastern end and the Sarysu river may end in the Telikol lake to the west. The la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentinel-2
Sentinel-2 is an Earth observation mission from the Copernicus Programme that systematically acquires optical imagery at high spatial resolution (10 m to 60 m) over land and coastal waters. The mission is currently a constellation with two satellites, Sentinel-2A and Sentinel-2B; a third satellite, Sentinel-2C, is currently undergoing testing in preparation for launch in 2024. The mission supports a broad range of services and applications such as agricultural monitoring, emergencies management, land cover classification or water quality. Sentinel-2 has been developed and is being operated by the European Space Agency, and the satellites were manufactured by a consortium led by Airbus Defence and Space in Friedrichshafen. Overview The Sentinel-2 mission has the following key characteristics: * Multispectral image, Multi-spectral data with 13 bands in the Visible spectrum, visible, Infrared#Regions within the infrared, near infrared, and Infrared#Regions within the infrared, sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Kazakhstan
The geology of Kazakhstan includes extensive basement rocks from the Precambrian and widespread Paleozoic rocks, as well as sediments formed in rift basins during the Mesozoic. Geologic history, stratigraphy and tectonics Archean rocks of the Zerenda Group, including schist, diamond-bearing gneiss, eclogite and marble are found in the Kokchetav Massif in the Kazakh Uplands. However, geologists have disagreed on dating with some indicating dates in the Middle Cambrian or Archean through Paleoproterozoic. Early Proterozoic rocks are better defined and include phyllite, schist, quartzite, porphyroids, porphyritoids, marble and jaspellite, intruded by 1.8 billion year old granite gneiss and 1.7 billion year old granosyenite. The Paleoproterozoic sequence is 14 kilometers thick. In the Jeltau Mountains, the basement is made up gneiss, schist, marble, amphibolite and eclogite. Migmatized gneiss, amphibolite and quartzite are found in the Mugodzhar area. Precambrian rocks a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
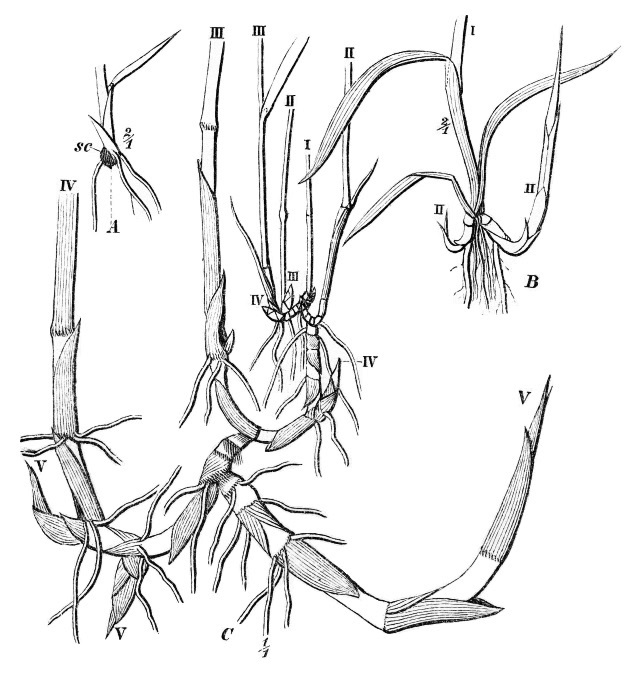
Salsola
''Salsola'' is a genus of the subfamily Salsoloideae in the family Amaranthaceae. The genus ''sensu stricto'' is distributed in central and southwestern Asia, North Africa, and the Mediterranean. A common name of various members of this genus and related genera is saltwort, for their salt tolerance. The genus name ''Salsola'' is from the Latin ''salsus'', meaning "salty". Description The species of ''Salsola'' are mostly subshrubs, shrubs, small trees, and rarely annuals. The leaves are mostly alternate, rarely opposite, simple, and entire. The bisexual flowers have five tepals and five stamens. The pistil ends in two stigmata. The fruit is spherical with a spiral embryo and no perisperm. Systematics The genus name ''Salsola'' was first published in 1753 by Linnaeus in ''Species Plantarum''. The type species is ''Salsola soda'' L. The genus ''Salsola'' belongs to the tribe Salsoleae ''s.s.'' of the subfamily Salsoloideae in the family Amaranthaceae. The genus was recircums ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeluropus
''Aeluropus'' is a genus of Eurasian and African plants in the grass family, found primarily in desert regions. ; Species * ''Aeluropus badghyzii'' Tzvelev - Turkmenistan * '' Aeluropus laciniatus'' Khodash. - Iran * '' Aeluropus lagopoides'' (L.) Thwaites - Mediterranean, Sahara, and Asia from Mauritania + Sicily to Kazakhstan + Nicobar Islands * '' Aeluropus littoralis'' (Gouan) Parl. - Mediterranean + Asia from Spain + Morocco to China * ''Aeluropus macrostachyus'' Hack. - Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan * ''Aeluropus pilosus'' (X.L.Yang) S.L.Chen & X.L.Yang - Xinjiang ; formerly included see '' Dactylis Odyssea'' * ''Aeluropus arabicus - Odyssea mucronata'' * ''Aeluropus mucronatus - Odyssea mucronata'' * ''Aeluropus pungens'' (Vahl) Boiss 1884 not K.Koch 1848 - ''Odyssea mucronata'' * ''Aeluropus smithii - Dactylis smithii'' See also * List of Poaceae genera The true grasses (Poaceae) are one of the largest plant families, with around 12,000 species and roughly 800 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winterfat
''Krascheninnikovia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the subfamily Chenopodioideae of the family Amaranthaceae known as winterfat, so-called because it is a nutritious livestock forage. They are known from Eurasia and western North America. These are hairy perennials or small shrubs which may be monoecious or dioecious. They bear spike inflorescences of woolly flowers. Description The species of ''Krascheninnikovia'' are erect subshrubs or shrubs. The plants are densely covered with dendroid stellate hairs and additionally with simple, unbranched hairs. The alternate leaves stand solitary or grouped in fascicles, and can be petiolate or nearly sessile. The flat, non-fleshy leaf blades are linear to narrowly lanceolate to ovate, with entire margins, and truncate, cuneate, rounded, or subcordate base. The flowers are unisexual, the plants can be monoecious or dioecious. Male flowers form an interrupted spike or subcapitate inflorescence of glomeruled, ebracteate flowers. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemisia (plant)
''Artemisia'' () is a large, diverse genus of plants with between 200 and 400 species belonging to the daisy family Asteraceae. Common names for various species in the genus include mugwort, wormwood, and sagebrush. ''Artemisia'' comprises hardy herbaceous plants and shrubs, which are known for the powerful chemical constituents in their essential oils. ''Artemisia'' species grow in temperate climates of both hemispheres, usually in dry or semiarid habitats. Notable species include '' A. vulgaris'' (common mugwort), '' A. tridentata'' (big sagebrush), '' A. annua'' (sagewort), '' A. absinthium'' (wormwood), ''A. dracunculus'' (tarragon), and '' A. abrotanum'' (southernwood). The leaves of many species are covered with white hairs. Most species have strong aromas and bitter tastes from terpenoids and sesquiterpene lactones, which discourage herbivory, and may have had a selective advantage. The small flowers are wind-pollinated. ''Artemisia'' species are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedges
The Cyperaceae are a family of graminoid (grass-like), monocotyledonous flowering plants known as sedges. The family is large, with some 5,500 known species described in about 90 genera, the largest being the "true sedges" genus ''Carex'' with over 2,000 species. These species are widely distributed, with the centers of diversity for the group occurring in tropical Asia and tropical South America. While sedges may be found growing in almost all environments, many are associated with wetlands, or with poor soils. Ecological communities dominated by sedges are known as sedgelands or sedge meadows. Some species superficially resemble the closely related rushes and the more distantly related grasses. Features distinguishing members of the sedge family from grasses or rushes are stems with triangular cross-sections (with occasional exceptions, a notable example being the tule which has a round cross-section) and leaves that are spirally arranged in three ranks. In comparison, gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmites
''Phragmites'' () is a genus of four species of large perennial reed grasses found in wetlands throughout temperate and tropical regions of the world. Taxonomy The World Checklist of Selected Plant Families, maintained by Kew Garden in London, accepts the following four species: * '' Phragmites australis'' ( Cav.) Trin. ex Steud. – cosmopolitan * '' Phragmites japonicus'' Steud. – Japan, Korea, Ryukyu Islands, Russian Far East * '' Phragmites karka'' ( Retz.) Trin. ex Steud. – tropical Africa, southern Asia, Australia, some Pacific Islands, invasive in New Zealand * '' Phragmites mauritianus'' Kunth – central + southern Africa, Madagascar, Mauritius The cosmopolitan common reed has the generally accepted botanical name ''Phragmites australis''. (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud. About 130 other synonyms have been proposed. Examples include ''Phragmites communis'' Trin., ''Arundo phragmites'' L., and ''Phragmites vulgaris'' (Lam.) Crép. (illegitimate name). Wildlife in r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almaty
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to 1936 as an autonomous republic as part of the Soviet Union, then from 1936 to 1991 as a union republic and finally from 1991 as an independent state to 1997 when the government relocated the capital to Akmola (renamed Astana in 1998, Nur-Sultan in 2019, and back to Astana in 2022). Almaty is still the major commercial, financial, and cultural centre of Kazakhstan, as well as its most populous and most cosmopolitan city. The city is located in the mountainous area of southern Kazakhstan near the border with Kyrgyzstan in the foothills of the Trans-Ili Alatau at an elevation of 700–900 m (2,300–3,000 feet), where the Large and Small Almatinka rivers run into the plain. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
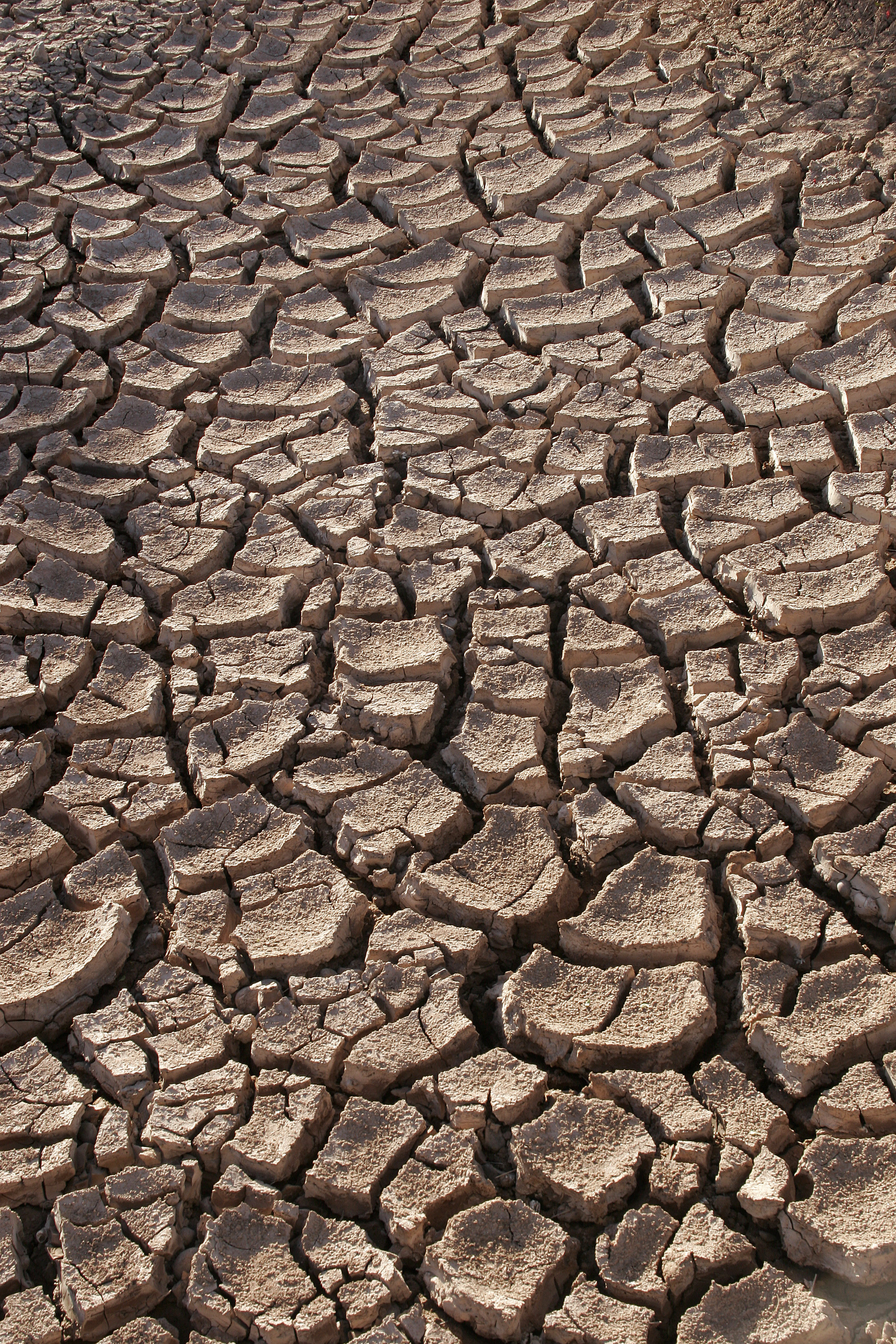
Takir (soil)
Takir (takyr) (russian: такыр, originally from Kazakh or another Turkic language) meaning "smooth, even, or bare", is a type of relief occurring in the deserts of Central Asia, similar to a salt flat in the southwestern United States. A takyr is usually formed in a shallow depressed area with a heavy clay soil, which is submerged by water after seasonal rains. After the water evaporates, a dried crust with fissures forms on the surface. The crust is often colonized by filamentous cyanobacteria. In the southwestern U.S. "takyrs" are known as "playas" or "salt flats", in Arab countries as "sabkha". See also *Daryalyktakyr The Daryalyktakyr Plain ( kk, Дариялықтақыр; rus, равнина Дарьялыктакыр), is an alluvial plain in the Kyzylorda Region, Kazakhstan.Google Earth The plain stretches across Zhalagash, Syrdarya and Shieli district ... References * Jayne Belnap, Otto Ludwig Lange. "Biological Soil Crusts: Structure, Function, and M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daryalyktakyr
The Daryalyktakyr Plain ( kk, Дариялықтақыр; rus, равнина Дарьялыктакыр), is an alluvial plain in the Kyzylorda Region, Kazakhstan.Google Earth The plain stretches across Zhalagash, Syrdarya and Shieli districts of Kyzylorda Region. A gas pipeline was built across the plain in 2012. The Shieli-Telikol Canal runs from north to south at the eastern edge. Geography The Daryalyktakyr lies north of the lower reaches of the Syr Darya and corresponds to an ancient channel where the river flowed. It extends roughly from WNW to ESE for a length of between the area to the north of Zhosaly town in the west and the Telikol lakes in the east. It is a large, elongated takir zone to the north of the current river channel covered with a top layer of alluvial sediments of mixed sand and clay. There are some solonetz and solonchak areas, as well as some small lakes and swamps at the southern edge. The Karaozek river, a right tributary of the Syr Darya, fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |