|
Asebeia
Asebeia (Ancient Greek: ἀσέβεια) was a criminal charge in ancient Greece for the "desecration and mockery of divine objects", for "irreverence towards the state gods" and disrespect towards parents and dead ancestors. It translates into English as impiety or godlessness. Most evidence for it comes from Athens. The antonym of asebeia is eusebeia ( εὐσέβεια), which can be translated as "piety". As piety was the generally desired and expected form of behaviour and mindset, being called and regarded impious (ἀσεβής) was already a form of punishment. Trials in Athens Every single citizen, including a third party, could bring this charge (''graphē asebeias'') to the Archon basileus. Instead of a single law or text defining the charge and proceedings to take place in case of asebeia, there is an array of texts in which it appears. Plutarch, Polybios, Demosthenes and Aristotle refer to it in their texts. The trials were publicly held at the ''Heliaia'' and were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
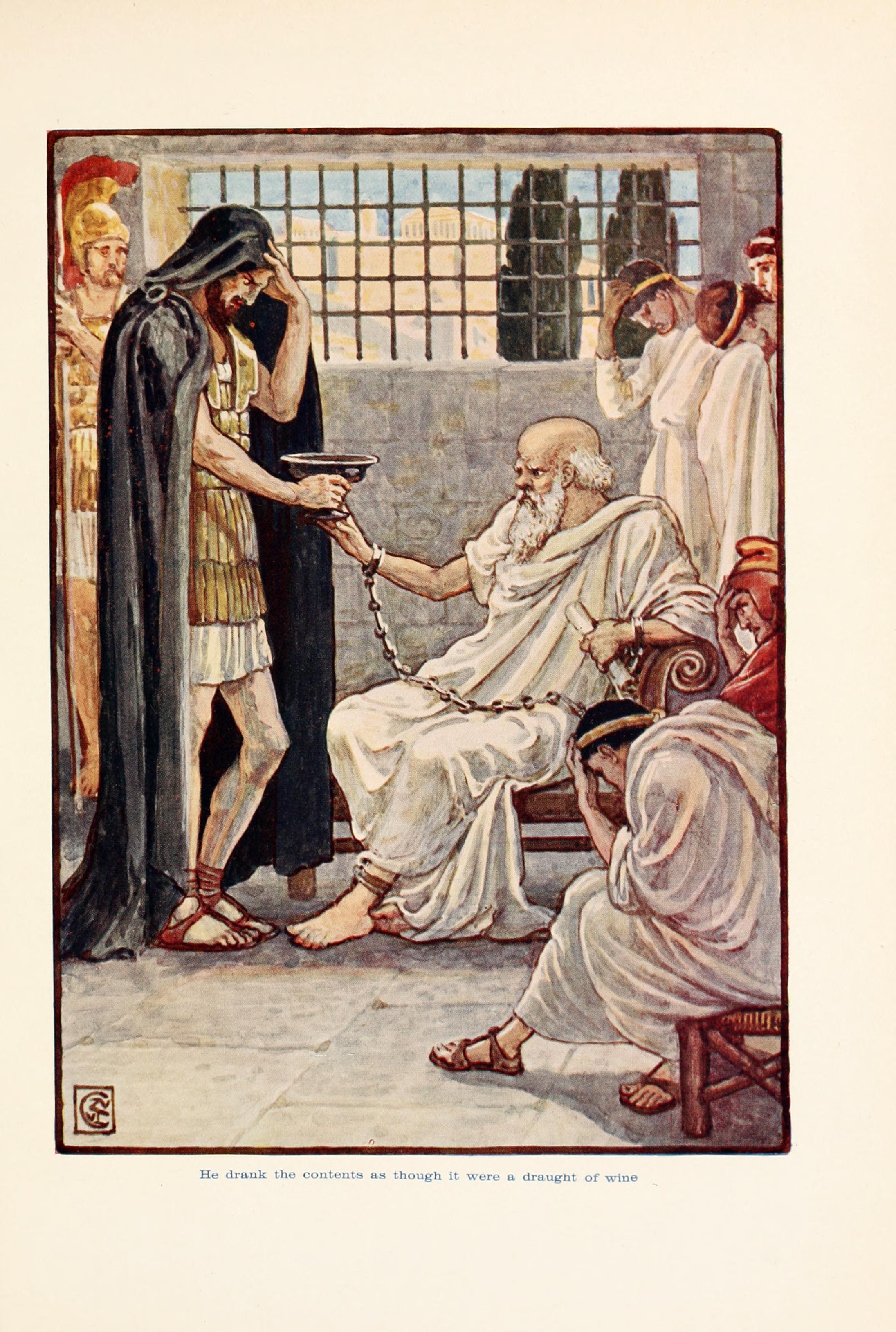
Socrates
Socrates (; ; –399 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no texts and is known mainly through the posthumous accounts of classical writers, particularly his students Plato and Xenophon. These accounts are written as dialogues, in which Socrates and his interlocutors examine a subject in the style of question and answer; they gave rise to the Socratic dialogue literary genre. Contradictory accounts of Socrates make a reconstruction of his philosophy nearly impossible, a situation known as the Socratic problem. Socrates was a polarizing figure in Athenian society. In 399 BC, he was accused of impiety and corrupting the youth. After a trial that lasted a day, he was sentenced to death. He spent his last day in prison, refusing offers to help him escape. Plato's dialogues are among the most co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andocides
Andocides (; grc-gre, Ἀνδοκίδης, ''Andokides''; c. 440 – c. 390 BC) was a logographer (speech writer) in Ancient Greece. He was one of the ten Attic orators included in the "Alexandrian Canon" compiled by Aristophanes of Byzantium and Aristarchus of Samothrace in the third century BC. Life Andocides was the son of Leogoras, and was born in Athens around 440 BC. He belonged to the ancient Eupatrid family of the Kerykes, who traced their lineage up to Odysseus and the god Hermes.Pseudo-Plutarch, ''Lives of the Ten Orators''Plutarch, ''Alcibiades'' 21 During his youth, Andocides seems to have been employed on various occasions as ambassador to Thessaly, Macedonia, Molossia, Thesprotia, Italy, and Sicily. And although he was frequently attacked for his political opinions, he maintained his ground until, in 415, he became involved in the charge brought against Alcibiades for having profaned the mysteries and mutilated the Herms on the eve of the departure of the Athenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodorus The Atheist
Theodorus the Atheist ( el, Θεόδωρος ὁ ἄθεος; c. 340 – c. 250 BCE), of Cyrene, was a Greek philosopher of the Cyrenaic school. He lived in both Greece and Alexandria, before ending his days in his native city of Cyrene. As a Cyrenaic philosopher, he taught that the goal of life was to obtain joy and avoid grief, and that the former resulted from knowledge, and the latter from ignorance. However, his principal claim to fame was his alleged atheism. He was usually designated by ancient writers ''ho atheos'' (), "the atheist." Life Theodorus was a disciple of Aristippus the Younger, grandson of the elder and more famous Aristippus. He heard the lectures of a number of philosophers beside Aristippus; such as Anniceris, and Dionysius the dialectician, Zeno of Citium, and Pyrrho. He was banished from Cyrene, but for what reason is not stated; and it is from the saying recorded of him on this occasion, "Men of Cyrene, you do ill in banishing me from Libya to Greec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trial Of Socrates
The trial of Socrates (399 BC) was held to determine the philosopher's guilt of two charges: ''asebeia'' (impiety) against the pantheon of Athens, and corruption of the youth of the city-state; the accusers cited two impious acts by Socrates: "failing to acknowledge the gods that the city acknowledges" and "introducing new deities". The death sentence of Socrates was the legal consequence of asking politico-philosophic questions of his students, which resulted in the two accusations of moral corruption and impiety. At trial, the majority of the ''dikasts'' (male-citizen jurors chosen by lot) voted to convict him of the two charges; then, consistent with common legal practice voted to determine his punishment and agreed to a sentence of death to be executed by Socrates's drinking a poisonous beverage of hemlock. Primary-source accounts of the trial and execution of Socrates are the '' Apology of Socrates'' by Plato and the '' Apology of Socrates to the Jury'' by Xenophon of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protagoras
Protagoras (; el, Πρωταγόρας; )Guthrie, p. 262–263. was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher and rhetorical theorist. He is numbered as one of the sophists by Plato. In his dialogue '' Protagoras'', Plato credits him with inventing the role of the professional sophist. Protagoras also is believed to have created a major controversy during ancient times through his statement that, "Man is the measure of all things," interpreted (possibly wrongly, since he disagreed) by Plato to mean that there is no objective truth; Protagoras seems to have meant that each person's own personal history, experiences and expectations, developed over their lifetime, determine their judgments, opinions, and statements regarding "truth" (which is the title of the book in which Protagoras made this statement). When a person makes a judgment about a certain thing—good or bad or beautiful or unjust—that person will differ from other people's judgments because their experience has been differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phryne
Phryne (; grc, Φρύνη, Phrū́nē, 371 BC – after 316 BC) was an ancient Greek hetaira (courtesan). From Thespiae in Boeotia, she was active in Athens, where she became one of the wealthiest women in Greece. She is best known for her trial for impiety, where she was defended by the orator Hypereides. According to legend, she was acquitted after baring her breasts to the jury, though the historical accuracy of this episode is doubtful. She also modeled for the artists Apelles and Praxiteles, and the Aphrodite of Knidos was based on her. Life Phryne was from Thespiae in Boeotia, though she seems to have spent most of her life in Athens. She was probably born around 371 BC, and was the daughter of Epicles. Both Plutarch and Athenaeus say that Phryne's real name was Mnesarete.Plutarch, ''Moralia'' "De Pythiae oraculis" 14 According to Plutarch she was called Phryne because she had a yellow complexion like a toad (in Greek: φρύνη); she also used the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ninos (priestess)
Ninos or Nino was an ancient Athenian woman who was executed at some point in the classical period. Her case is known through three mentions in speeches by Demosthenes – '' Against Boeotus I'' and ''II'', and ''On the False Embassy'' – and one in Josephus. The prosecution was apparently brought by a man named Menecles, who would go on to be prosecuted in turn by Ninos' son. The date of the prosecution is uncertain: ''Against Boeotus I'' was delivered in 348, which provides a terminus ante quem; Esther Eidinow suggests a date of between 362 and 358 BC. The case was apparently well known in the mid-fourth century, as Demosthenes refers to it in his speeches as if the jury are expected to be familiar with the case. According to Demosthenes, Ninos was a priestess, and was charged with bringing together '' thiasoi''. One scholiast on this passage says that her crime was mocking the Dionysian Mysteries; another says that she made love potions. It is unclear where the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
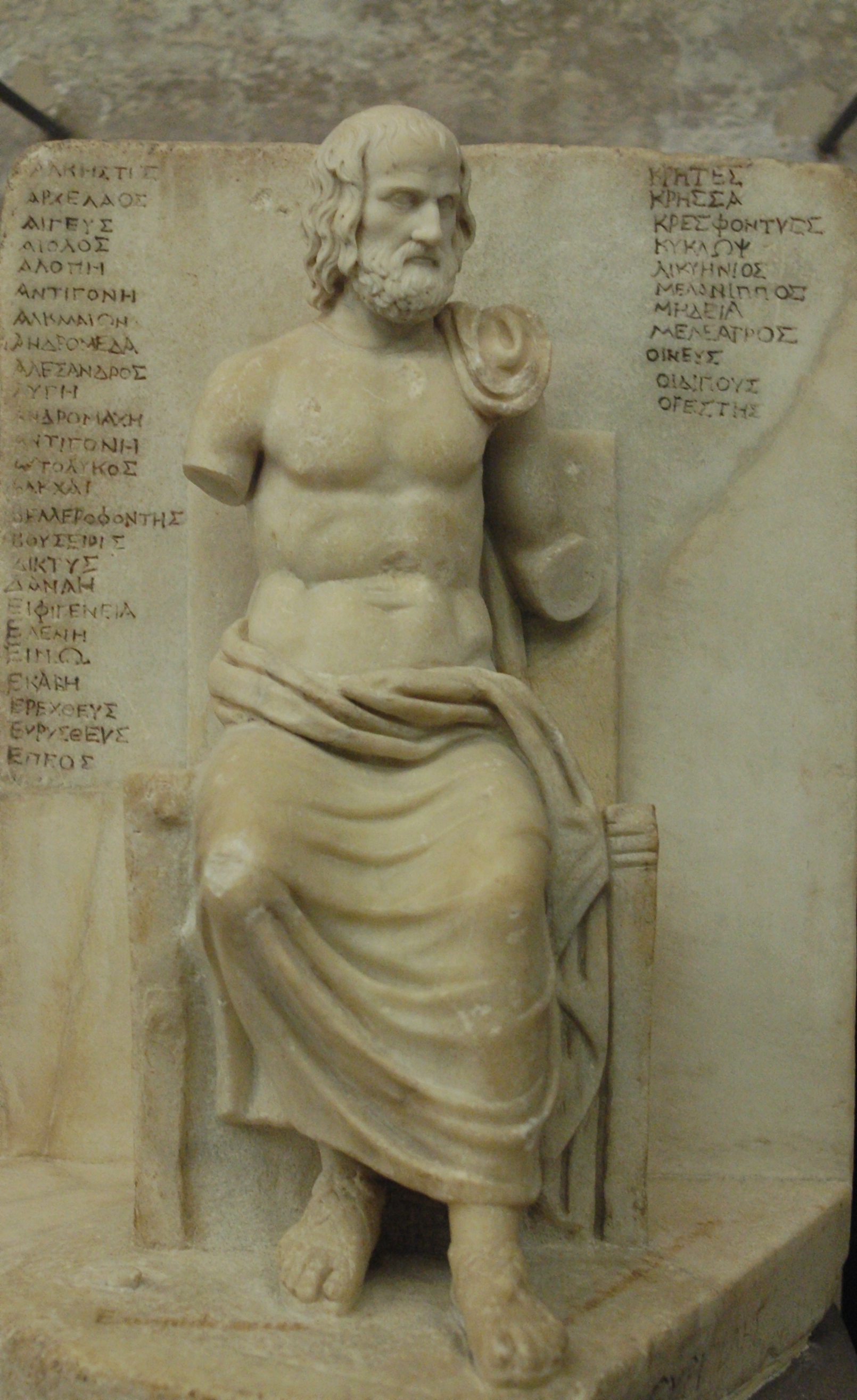
Euripides
Euripides (; grc, Εὐριπίδης, Eurīpídēs, ; ) was a tragedian Tragedy (from the grc-gre, τραγῳδία, ''tragōidia'', ''tragōidia'') is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful events that befall a main character. Traditionally, the intention of tragedy i ... of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars attributed ninety-five plays to him, but the ''Suda'' says it was ninety-two at most. Of these, eighteen or nineteen have survived more or less complete (''Rhesus (play), Rhesus'' is suspect). There are many fragments (some substantial) of most of his other plays. More of his plays have survived intact than those of Aeschylus and Sophocles together, partly because his popularity grew as theirs declinedMoses Hadas, ''Ten Plays by Euripides'', Bantam Classic (2006), Introduction, p. ixhe became, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diopeithes
{{short description, Athenian military leader Diopeithes (Greek: Διoπείθης; lived during the 4th century BC) was an Athenian general, probably father of the poet Menander, who was sent out to the Thracian Chersonese about 343 BC, at the head of a body of Athenian settlers or cleruchs. Disputes having arisen about their boundaries between these settlers and the Cardians, the latter were supported, but not with arms in the first instance, by king Philip II of Macedon (359–336 BC), who, when the Athenians remonstrated, proposed that their quarrel with Cardia should be referred to arbitration. This proposal being indignantly rejected, Philip sent troops to the assistance of the Cardians, and Diopeithes retaliated by ravaging the maritime district of Thrace, which was subject to the Macedonians, while Philip was absent in the interior of the same country on his expedition against Teres and Cersobleptes. Philip sent a letter of remonstrance to Athens, and Diopeithes was arraign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagoras Of Melos
Diagoras "the Atheist" of Melos ( el, Διαγόρας ὁ Μήλιος) was a Greek poet and sophist of the 5th century BC. Throughout antiquity, he was regarded as an atheist, but very little is known for certain about what he actually believed. Anecdotes about his life indicate that he spoke out against ancient Greek religion. He allegedly chopped up a wooden statue of Heracles and used it to roast his lentils and revealed the secrets of the Eleusinian Mysteries. The Athenians accused him of ''asebeia'' (impiety) and banished him from their city. He died in Corinth. Life Diagoras was the son of Telecleides or Teleclytus, and was born in the island of Melos, one of the Cyclades. According to the Suda, he was a disciple of Democritus after Democritus had paid 10,000 drachmas to free Diagoras from captivity following the cruel subjugation of Melos (416 BC); however no early sources mention an association with Democritus. The Suda also states that in his youth Diagoras had acquired ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demades
Demades ( el, Δημάδης, BC) was an Athenian orator and demagogue. Background and early life Demades was born into a poor family of ancient Paeania and was employed at one time as a common sailor, but he rose to a prominent position at Athens thanks to his eloquence as well as his unscrupulous character. He espoused the cause of Philip II of Macedon in the war against Olynthus, and was thus brought into bitter and lifelong enmity with Demosthenes, whom he at first supported. Relations with Macedon Demades fought against the Macedonians in the Battle of Chaeronea, and was taken prisoner. Having made a favourable impression upon Philip, he was released together with his fellow-captives, and was instrumental in bringing about a treaty of peace between Macedonia and Athens. Demades continued to be a favourite of Alexander, and, prompted by a bribe, saved Demosthenes and some other Athenian orators from his vengeance. It was also chiefly owing to him that Alexander, after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)