|
Ascandra Corallicola
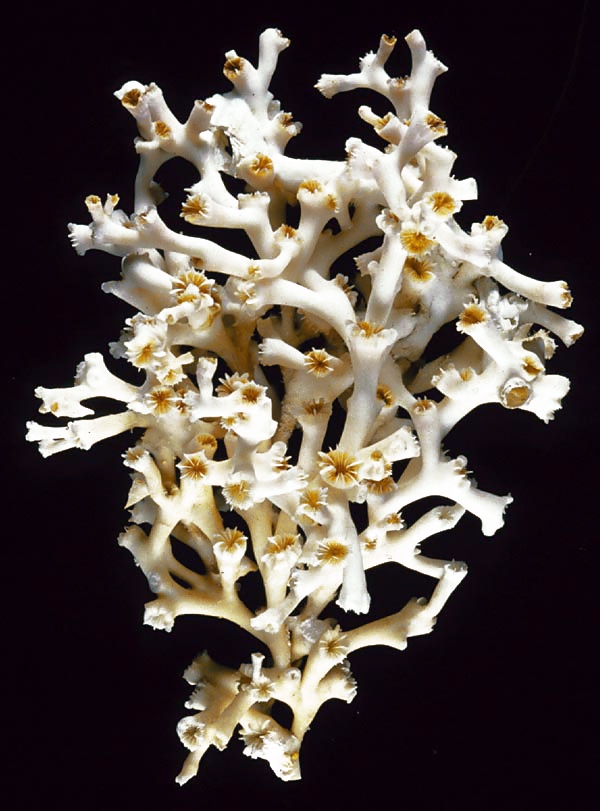
''Ascandra corallicola'' is a species of calcareous sponge in the family Leucaltidae. It is known from the coastal waters in northeast Atlantic at depths between , and on the Reykjanes Ridge as deep as . It occurs solely on dead parts of the corals ''Lophelia pertusa'' and '' Solenosmilia variabilis'', to which its specific name Specific name may refer to: * in Database management systems, a system-assigned name that is unique within a particular database In taxonomy, either of these two meanings, each with its own set of rules: * Specific name (botany), the two-part (bino ... ''corallicola'' refers to. References corallicola Fauna of the Atlantic Ocean Animals described in 2006 {{calcarea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcareous Sponge
The calcareous sponges of class Calcarea are members of the animal phylum Porifera, the cellular sponges. They are characterized by spicules made of calcium carbonate in the form of calcite or aragonite. While the spicules in most species have three points, in some species they have either two or four points. Biology All sponges in this class are strictly marine, and, while they are distributed worldwide, most are found in shallow tropical waters. Like nearly all other sponges, they are sedentary filter feeders. All three sponge body plans are represented within class Calcarea : asconoid, syconoid, and leuconoid. Typically, calcareous sponges are small, measuring less than in height, and drab in colour. However, a few brightly coloured species are also known. Calcareous sponges vary from radially symmetrical vase-shaped body types to colonies made up of a meshwork of thin tubes, or irregular massive forms. The skeleton has either a mesh or honeycomb structure. Classifica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucaltidae
Leucaltidae is a family of calcareous sponges in the order Clathrinida The Clathrinida are an order of calcareous sponges found in marine environments. These sponges have an asconoid structure and lack a true dermal membrane or cortex. The spongocoel is lined with choanocytes Choanocytes (also known as "collar ce .... References Clathrinida Taxa named by Arthur Dendy {{calcarea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reykjanes Ridge
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge (a divergent or constructive plate boundary) located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, and part of the longest mountain range in the world. In the North Atlantic, the ridge separates the North American from the Eurasian Plate and the African Plate, north and south of the Azores Triple Junction respectively. In the South Atlantic, it separates the African and South American plates. The ridge extends from a junction with the Gakkel Ridge (Mid-Arctic Ridge) northeast of Greenland southward to the Bouvet Triple Junction in the South Atlantic. Although the Mid-Atlantic Ridge is mostly an underwater feature, portions of it have enough elevation to extend above sea level, for example in Iceland. The ridge has an average spreading rate of about per year. Discovery A ridge under the northern Atlantic Ocean was first inferred by Matthew Fontaine Maury in 1853, based on soundings by the USS ''Dolphin''. The existence of the ridge and its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophelia Pertusa
''Lophelia pertusa'', the only species in the genus ''Lophelia'', is a cold-water coral that grows in the deep waters throughout the North Atlantic ocean, as well as parts of the Caribbean Sea and Alboran Sea. Although ''L. pertusa'' reefs are home to a diverse community, the species is extremely slow growing and may be harmed by destructive fishing practices, or oil exploration and extraction. Biology ''Lophelia pertusa'' is a reef building, deep water coral, but it does not contain zooxanthellae, the symbiotic algae which lives inside most tropical reef building corals. ''Lophelia'' lives at a temperature range from about and at depths between and over , but most commonly at depths of , where there is no sunlight. As a coral, it represents a colonial organism, which consists of many individuals. New polyps live and build upon the calcium carbonate skeletal remains of previous generations. Living coral ranges in colour from white to orange-red; each polyp has up to 16 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solenosmilia Variabilis
''Solenosmilia variabilis'' is a species of colonial coral in the family Caryophylliidae. It is a deep water, azooxanthellate coral with a semi-cosmopolitan distribution. Description ''Solenosmilia variabilis'' grows into small bushy colonies, the dichotomous branches often joining. It grows from an encrusting base on which there are a few corallites. The branches are thick near the base of the colony but more slender above; sometimes upper branches are just in diameter. The coenosteum can be smooth and white, granular, glossy and pale grey, or ridged with eight to ten transverse costae. The corallites are up to in diameter, with the septa grouped in sixes, arranged in three or more cycles. Growth of the colony is by intratentacular budding. Distribution ''S. variabilis'' has a semi-cosmopolitan distribution. It is widespread in both the Atlantic and Indian Oceans and has a circumpolar distribution in the Southern Ocean. Locations where it has been found include off South Af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascandra
''Ascandra'' is a genus of calcareous sponges of the family Leucaltidae and are found in oceans around the world. Species As of 2019, 15 valid species of ''Ascandra'' are recognized: * '' Ascandra ascandroides'' (Borojevic, 1971) * '' Ascandra atlantica'' (Thacker, 1908) * '' Ascandra biscayae'' (Borojevic & Boury-Esnault, 1987) * '' Ascandra brandtae'' (Rapp, Göcke, Tendal & Janussen, 2013) * '' Ascandra contorta'' (Bowerbank, 1866) * '' Ascandra corallicola'' (Rapp, 2006) * '' Ascandra crewsi'' Van Soest & De Voogd, 2015 * ''Ascandra densa ''Ascandra densa'' is a species of calcareous sponge The calcareous sponges of class Calcarea are members of the animal phylum Porifera, the cellular sponges. They are characterized by spicules made of calcium carbonate in the form of calc ...'' Haeckel, 1872 * '' Ascandra falcata'' Haeckel, 1872 * '' Ascandra izuensis'' (Tanita, 1942) * '' Ascandra kakaban'' Van Soest & De Voogd, 2015 * '' Ascandra loculosa'' (Dendy, 1891) * '' Asc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of The Atlantic Ocean
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is ''funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoologists and paleontologists use ''fauna'' to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics. Etymology ''Fauna'' comes from the name Fauna, a Roman goddess of earth and fertility, the Roman god Faunus, and the related forest spirits called Fauns. All three words are cognates of the name of the Greek god Pan, and ''panis'' is the Greek equivalent of fauna. ''Fauna'' is also the word for a book that catalogues the animals in such a manner. The term was first used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |