|
Ascaltis Grisea
''Ascaltis grisea'' is a species of sea sponge in the family Leucascidae, first described as ''Leucosolenia grisea'' by Arthur Dendy Arthur Dendy (20 January 1865, in Manchester – 24 March 1925, in London) was an English zoologist known for his work on marine sponges and the terrestrial invertebrates of Victoria, Australia, notably including the "living fossil" '' Peripatus'' ... in 1891. It is known only from its type locality on the Houtman Albrolhos archipeligo in Western Australia. It is a marine sessile filter-feeder. References Clathrinida Animals described in 1924 Taxa named by Arthur Dendy Sponges of Australia Sponges described in 1924 {{calcarea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Dendy
Arthur Dendy (20 January 1865, in Manchester – 24 March 1925, in London) was an English zoologist known for his work on marine sponges and the terrestrial invertebrates of Victoria, Australia, notably including the "living fossil" '' Peripatus''. He was in turn professor of zoology in New Zealand, in South Africa and finally at King's College London. He was a Fellow of the Royal Society. Family life Dendy's parents were John Dendy, a silk fabric maker of Manchester, and Sarah Beard, daughter of John Relly Beard. His sisters included Mary Dendy and Helen Bosanquet. He married Ada Margaret Courtauld on 5 December 1888. They had four children, three daughters—including the artist Vera Ellen Poole (1890–1965)—and one son. Career He was educated in zoology at Owens College, Manchester, gaining his M.Sc. in 1887 and his D.Sc. in 1891. He worked on part of the report of the Challenger expedition (1872–1876), describing monaxonid sponges. In 1888 he moved to the Univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leslie M
Leslie may refer to: * Leslie (name), a name and list of people with the given name or surname, including fictional characters Families * Clan Leslie, a Scottish clan with the motto "grip fast" * Leslie (Russian nobility), a Russian noble family of Scottish origin Places Canada * Leslie, Saskatchewan * Leslie Street, a road in Toronto and York Region, Ontario ** Leslie (TTC), a subway station ** Leslie Street Spit, an artificial spit in Toronto United States * Leslie, Arkansas *Leslie, Georgia *Leslie, Michigan *Leslie, Missouri *Leslie, West Virginia * Leslie, Wisconsin *Leslie Township, Michigan *Leslie Township, Minnesota Elsewhere * Leslie Dam, a dam in Warwick, Queensland, Australia * Leslie, Mpumalanga, South Africa * Leslie, Aberdeenshire, Scotland, see List of listed buildings in Leslie, Aberdeenshire * Leslie, Fife, Scotland, UK Other uses * Leslie speaker system * Leslie Motor Car company * Leslie Controls, Inc. * Leslie (singer) (born 1985), French singer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
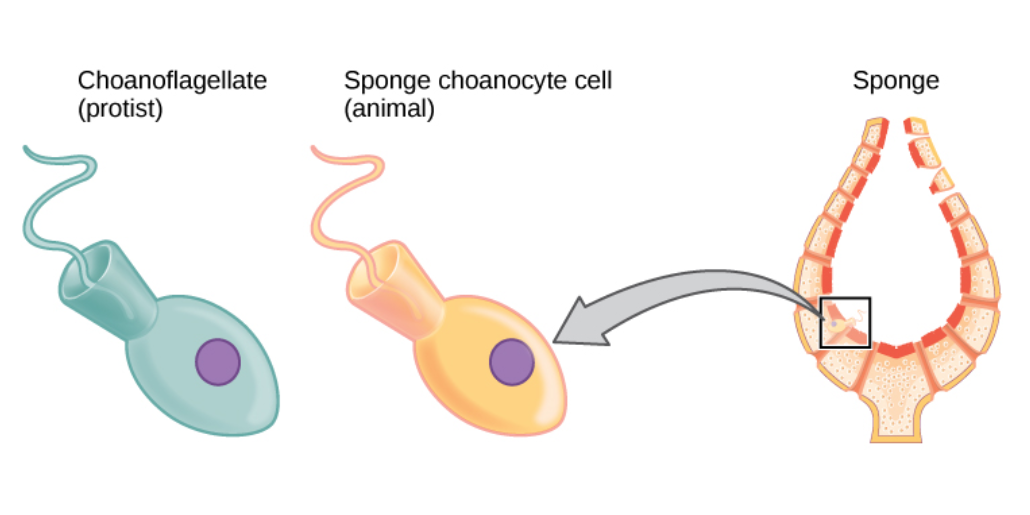
Sea Sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucascidae
Leucascidae is a family of calcareous sponges in the order Clathrinida The Clathrinida are an order of calcareous sponges found in marine environments. These sponges have an asconoid structure and lack a true dermal membrane or cortex. The spongocoel is lined with choanocytes Choanocytes (also known as "collar ce .... References Clathrinida Taxa named by Arthur Dendy {{calcarea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houtman Abrolhos
The Houtman Abrolhos (often called the Abrolhos Islands) is a chain of 122 islands and associated coral reefs, in the Indian Ocean off the west coast of Australia, about west of Geraldton, Western Australia. It is the southernmost true coral reef in the Indian Ocean, and one of the highest latitude reef systems in the world. It is one of the world's most important seabird breeding sites, and is the centre of Western Australia's largest single-species fishery, the western rock lobster fishery. It has a small seasonal population of fishermen, and a limited number of tourists are permitted for day trips, but most of the land area is off limits as conservation habitat. It is well known as the site of numerous shipwrecks, the most famous being the Dutch ships , which was wrecked in 1629, and , wrecked in 1727. The islands are an unincorporated area with no municipal government, subject to direct administration of the Government of Western Australia. In July 2019, the Houtman Abro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clathrinida
The Clathrinida are an order of calcareous sponges found in marine environments. These sponges have an asconoid structure and lack a true dermal membrane or cortex. The spongocoel is lined with choanocytes Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a t .... References Sponge orders {{calcarea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animals Described In 1924
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinoderms and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Arthur Dendy
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sponges Of Australia
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_photo_2.jpg)