|
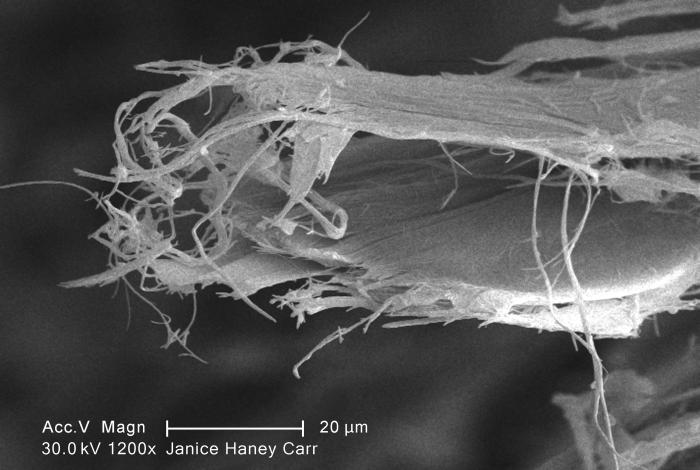
Asbestiform
Asbestiform is a crystal habit. It describes a mineral that grows in a fibrous aggregate of high tensile strength, flexible, long, and thin crystals that readily separate.Committee on Asbestos: Selected Health Effects, 2006, ''Asbestos: Selected Cancers,'' National Academies Press, The most common asbestiform mineral is chrysotile, commonly called "white asbestos", a magnesium phyllosilicate part of the serpentine group. Other asbestiform minerals include riebeckite, an amphibole whose fibrous form is known as crocidolite or "blue asbestos", and brown asbestos, a cummingtonite-grunerite solid solution series. The United States Environmental Protection Agency explains that, "In general, exposure may occur only when the asbestos-containing material is disturbed or damaged in some way to release particles and fibers into the air." "Mountain leather" is an old-fashioned term for flexible, sheet-like natural formations of asbestiform minerals which resemble leather. Asbestos-containi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asbestos
Asbestos () is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere by abrasion and other processes. Inhalation of asbestos fibres can lead to various dangerous lung conditions, including mesothelioma, asbestosis, and lung cancer, so it is now notorious as a serious health and safety hazard. Archaeological studies have found evidence of asbestos being used as far back as the Stone Age to strengthen ceramic pots, but large-scale mining began at the end of the 19th century when manufacturers and builders began using asbestos for its desirable physical properties. Asbestos is an excellent electrical insulator and is highly fire-resistant, so for much of the 20th century it was very commonly used across the world as a building material, until its adverse effects on human health were more widely acknowl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral Habits
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or are organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral, or may be an aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spacially segregated into disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riebeckite
Riebeckite is a sodium-rich member of the amphibole group of silicate minerals, chemical formula Na2(Fe2+3Fe3+2)Si8O22(OH)2. It forms a solid solution series with magnesioriebeckite. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system, usually as long prismatic crystals showing a diamond-shaped cross section, but also in fibrous, bladed, acicular, columnar, and radiating forms. Its Mohs hardness is 5.0–6.0, and its specific gravity is 3.0–3.4. Cleavage is perfect, two directions in the shape of a diamond; fracture is uneven, splintery. It is often translucent to nearly opaque. Name and discovery Riebeckite was first described in 1888 for an occurrence on Socotra Island, Aden Governorate, Yemen, and named for German explorer Emil Riebeck (1853–1885). The mineral is also known as crocidolite. Occurrence Riebeckite typically forms dark-blue elongated to fibrous crystals in highly alkali granites, syenites, rarely in felsic volcanics, granite pegmatites and schist. It occurs in banded i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinolite
Actinolite is an amphibole silicate mineral with the chemical formula . Etymology The name ''actinolite'' is derived from the Greek word ''aktis'' (), meaning "beam" or "ray", because of the mineral's fibrous nature. Mineralogy Actinolite is an intermediate member in a solid-solution series between magnesium-rich tremolite, , and iron-rich ferro-actinolite, . Mg and Fe ions can be freely exchanged in the crystal structure. Like tremolite, asbestiform actinolite is regulated as asbestos. Occurrence Actinolite is commonly found in metamorphic rocks, such as contact aureoles surrounding cooled intrusive igneous rocks. It also occurs as a product of metamorphism of magnesium-rich limestones. The old mineral name ''uralite'' is at times applied to an alteration product of primary pyroxene by a mixture composed largely of actinolite. The metamorphosed gabbro or diabase rock bodies, referred to as epidiorite, contain a considerable amount of this ''uralitic'' alteratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysotile
Chrysotile or white asbestos is the most commonly encountered form of asbestos, accounting for approximately 95% of the asbestos in the United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor (2007)29 C.F.R. 1910.1001 Appendix J. and a similar proportion in other countries.Institut national de recherche sur la sécurité (1997).Amiante." ''Fiches toxicologiques.'' n° 167. (in French) It is a soft, fibrous silicate mineral in the serpentine subgroup of phyllosilicates; as such, it is distinct from other asbestiform minerals in the amphibole group. Its idealized chemical formula is Mg( Si O)( OH). The material has physical properties which make it desirable for inclusion in building materials, but poses serious health risks when dispersed into air and inhaled. Polytypes Three polytypes of chrysotile are known. These are very difficult to distinguish in hand specimens, and polarized light microscopy must normally be used. Some older ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Habit
In mineralogy, crystal habit is the characteristic external shape of an individual crystal or crystal group. The habit of a crystal is dependent on its crystallographic form and growth conditions, which generally creates irregularities due to limited space in the crystallizing medium (commonly in rocks).Klein, Cornelis, 2007, ''Minerals and Rocks: Exercises in Crystal and Mineral Chemistry, Crystallography, X-ray Powder Diffraction, Mineral and Rock Identification, and Ore Mineralogy,'' Wiley, third edition, Wenk, Hans-Rudolph and Andrei Bulakh, 2004, ''Minerals: Their Constitution and Origin,'' Cambridge, first edition, Recognizing the habit can aid in mineral identification and description, as the crystal habit is an external representation of the internal ordered atomic arrangement. Most natural crystals, however, do not display ideal habits and are commonly malformed. Hence, it is also important to describe the quality of the shape of a mineral specimen: * Euhedral: a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpentine Group
Serpentine subgroup (part of the kaolinite-serpentine group in the category of phyllosilicates) are greenish, brownish, or spotted minerals commonly found in serpentinite. They are used as a source of magnesium and asbestos, and as decorative stone. The name comes from the greenish colour and smooth or scaly appearance from the Latin , meaning "serpent rock". Serpentine subgroup is a set of common rock-forming hydrous magnesium iron phyllosilicate () minerals, resulting from the metamorphism of the minerals that are contained in mafic to ultramafic rocks. They may contain minor amounts of other elements including chromium, manganese, cobalt or nickel. In mineralogy and gemology, serpentine may refer to any of the 20 varieties belonging to the serpentine subgroup. Owing to admixture, these varieties are not always easy to individualize, and distinctions are not usually made. There are three important mineral polymorphs of serpentine: antigorite, lizardite and chrysotile. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
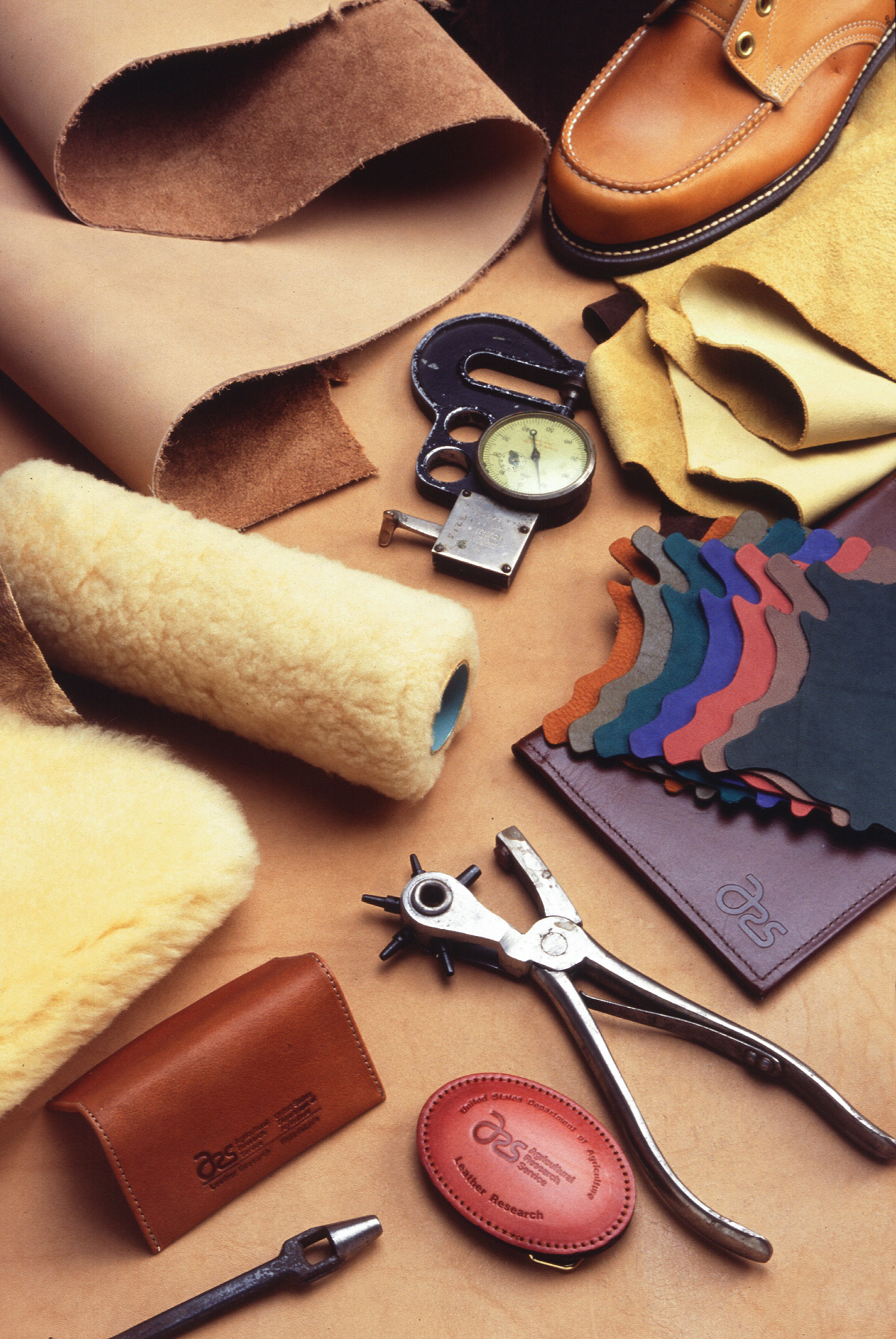
Leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, and aquatic animals such as seals and alligators. Leather can be used to make a variety of items, including clothing, footwear, handbags, furniture, tools and sports equipment, and lasts for decades. Leather making has been practiced for more than 7,000 years and the leading producers of leather today are China and India. Animal rights groups claim that modern commercial leather making and the consumption of its products is unethically killing animals. According to the life-cycle assessment (LCA) report for the United Nations Industrial Development Organization, 99% of the raw hides and skins used in the production of leather derive from animals raised for meat and/or dairy production. Critics of tanneries claim that they engage in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibole
Amphibole () is a group of inosilicate minerals, forming prism or needlelike crystals, composed of double chain tetrahedra, linked at the vertices and generally containing ions of iron and/or magnesium in their structures. Its IMA symbol is Amp. Amphiboles can be green, black, colorless, white, yellow, blue, or brown. The International Mineralogical Association currently classifies amphiboles as a mineral supergroup, within which are two groups and several subgroups. Mineralogy Amphiboles crystallize into two crystal systems, monoclinic and orthorhombic. In chemical composition and general characteristics they are similar to the pyroxenes. The chief differences from pyroxenes are that (i) amphiboles contain essential hydroxyl (OH) or halogen (F, Cl) and (ii) the basic structure is a double chain of tetrahedra (as opposed to the single chain structure of pyroxene). Most apparent, in hand specimens, is that amphiboles form oblique cleavage planes (at around 120 degrees), whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensile Strength
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or F_\text within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials the ultimate tensile strength is close to the yield point, whereas in ductile materials the ultimate tensile strength can be higher. The ultimate tensile strength is usually found by performing a tensile test and recording the engineering stress versus strain. The highest point of the stress–strain curve is the ultimate tensile strength and has units of stress. The equivalent point for the case of compression, instead of tension, is called the compressive strength. Tensile strengths are rarely of any consequence in the design of ductile members, but they are important with brittle members. They are tabulated for common materials such as alloys, composite materials, ceramics, plastics, and wood. Definition The ultimate tensile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saponite
Saponite is a trioctahedral mineral of the smectite group. Its chemical formula is . It is soluble in sulfuric acid. It was first described in 1840 by Svanberg. Varieties of saponite are griffithite, bowlingite and sobotkite. It is soft, massive, and plastic, and exists in veins and cavities in serpentinite and basalt. The name is derived from the Greek ''sapo'', soap. Other names include bowlingite; mountain soap; piotine; soapstone. Occurrence Saponite was first described in 1840 for an occurrence in Lizard Point, Landewednack, Cornwall, England. It occurs in hydrothermal veins, in basalt vesicles, skarns, amphibolite and serpentinite. Associated minerals include celadonite, chlorite, native copper, epidote, orthoclase, dolomite, calcite and quartz. Saponite is found in Ząbkowice Śląskie in Silesia, Svärdsjö in Dalarna, Sweden and in Cornwall, UK. The soap stone of Cornwall is used in the porcelain factory. Saponite is also found in the "dark rims" of ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepiolite
Sepiolite, also known in English language, English by the German language, German name meerschaum ( , ; ; meaning "sea foam"), is a soft white clay mineral, often used to make tobacco pipes (known as meerschaum pipes). A complex magnesium silicate, a typical chemical formula for which is Mg4Si6O15(OH)2·6H2O, it can be present in fibrous, fine-particulate, and solid forms. The fibrous clay minerals have recently been shown to exist as a continuous polysomatic series where the endmembers are sepiolite and palygorskite. There is a continuous variation in chemical composition from sepiolite, the most magnesic and trioctahedral endmember, to palygorskite, the least magnesic, most Al- Fe- bearing, dioctahedral endmember. Originally named ''meerschaum'' by Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1788, it was named ''sepiolite'' by Ernst Friedrich Glocker in 1847 for an occurrence in Bettolino, Baldissero Canavese, Torino Province, Piedmont, Italy. The name comes from Ancient Greek, Greek ''sepion' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)