|
Arun River (China–Nepal)
The Arun River ( ne, अरुण नदी) is a trans-boundary river and is part of the Kosi or Sapt Koshi river system in Nepal. It originates in Tibet Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China where it is called the Phung Chu or Bum-chu. Name In Tibet, the river is called ''Bum-chu'', also transliterated ''Phung-Chu'' or from Chinese as ''Peng Qu'' or ''Pumqu''. ''Men Qu'' or ''Moinqu'' is an upper tributary draining glaciers from Shishapangma. In Nepal the river's name changes to ''Arun''. Tibet The Tibetan name ''Bum-chu'' may refer to a religious ceremony attempting to divine prospects for the coming year from the level of water in a pot or well, ''chu'' is the Tibetan word for water. The river originates near Gutso in Nyalam County of Tibet. Around downstream the Men-chu joins it. The Tingri county occupies the upper reaches of the Bum-chu and the lateral valleys formed by its tributaries, the foremost of which are Lolo-chu, Shel-chu, Rongpu-chu, Trakar-chu, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Arun
The River Arun () is a river in the English county of West Sussex. At long, it is the longest river entirely in Sussex and one of the longest starting in Sussex after the River Medway, River Wey and River Mole. From the series of small streams that form its source in the area of St Leonard's Forest in the Weald, the Arun flows westwards through Horsham to Nowhurst where it is joined by the North River. Turning to the south, it is joined by its main tributary, the western River Rother, and continues through a gap in the South Downs to Arundel to join the English Channel at Littlehampton. It is one of the faster flowing rivers in England, and is tidal as far inland as Pallingham Quay, upstream from the sea at Littlehampton. The Arun gives its name to the Arun local government district of West Sussex. The first major improvements to the river were made between the 1540s and the 1570s, when Arundel became a port, and navigation up to Pallingham was improved, but barges had di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tingri County
Tingri County or ''Dhringgri County'' (; ), is a county under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Xigazê in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. The county comprises the upper valley of the Bum-chu or Arun River, with the valleys of its tributaries plus the valleys of the Rongshar Tsangpo and the Lapchi Gang Tsanpo which flow south into Nepal. It is bordered on the south by the main range of the Himalayas including Mount Everest (Tib. Chomolungma), Makalu and Cho Oyu. The present county administration is located at Shelkar, about east of Tingri (town). It is one of the four counties that comprise the Qomolangma National Nature Preserve (Tingri, Dinjie, Nyalam, and Kyirong).Department of Forestry, Government of the Tibet Autonomous Region, People's Republic of China, ‘’Report on Protected Lands in the Tibet Autonomous Region’’ Lhasa: Tibet Autonomous Region Government Publishing House, 2006 Towns and townships * Shelkar Town (, ) * Gangga Town ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperate Broadleaf And Mixed Forest
Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest is a temperate climate terrestrial habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature, with broadleaf tree ecoregions, and with conifer and broadleaf tree mixed coniferous forest ecoregions. These forests are richest and most distinctive in central China and eastern North America, with some other globally distinctive ecoregions in the Caucasus, the Himalayas, Southern Europe, Australasia, Southwestern South America and the Russian Far East. Ecology The typical structure of these forests includes four layers. * The uppermost layer is the canopy composed of tall mature trees ranging from high. Below the canopy is the three-layered, shade-tolerant understory that is roughly shorter than the canopy. * The top layer of the understory is the sub-canopy composed of smaller mature trees, saplings, and suppressed juvenile canopy layer trees awaiting an opening in the canopy. * Below the sub-canopy is the shrub layer, composed of low growi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1988 Nepal Earthquake
The 1988 Nepal earthquake ( ne, विसं २०४५ को भूकम्प) occurred in Nepal near the Indian border and affected much of northern Bihar. The magnitude 6.9 earthquake shook the region on August 21, killing at least 709 persons and injuring thousands. The earthquake struck in two installments of 10 seconds and 15 seconds each and left cracks in 50,000 buildings, including Raj Bhavan and the old Secretariat Building in Patna, Bihar. See also *List of earthquakes in 1988 *List of earthquakes in India *List of earthquakes in Nepal References External links M6.9 - Nepal-India border region– United States Geological Survey Earthquakes in Bihar, India– Amateur Seismic Centre * {{DEFAULTSORT:Nepal Earthquake, 1988 1988 Nepal Earthquake, 1988 1988 1988 earthquakes Natural disasters in Bihar Earthquake An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains. The major monsoon systems of the world consist of the West African, Asia–Australian, the North American, and South American monsoons. The term was first used in English in British India and neighboring countries to refer to the big seasonal winds blowing from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea in the southwest bringing heavy rainfall to the area. Etymology The etymology of the word monsoon is not wholl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
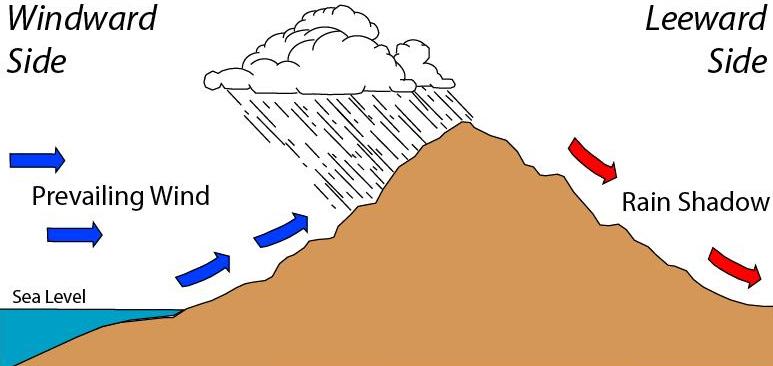
Rain Shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side. Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carried by the prevailing onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas. When encountering elevated landforms, the moist air is driven upslope towards the peak, where it expands, cools, and its moisture condenses and starts to precipitate. If the landforms are tall and wide enough, most of the humidity will be lost to precipitation over the windward side (also known as the ''rainward'' side) before ever making it past the top. As the air descends the leeward side of the landforms, it is compressed and heated, producing foehn winds that ''absorb'' moisture downslope and cast a broad "shadow" of dry climate region behind the mountain crests. This climate typically takes the form of shrub–steppe, xeric shrublands or even deserts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chatra Gorge
The Chatra Gorge is a canyon cut by the Kosi River across the Mahabharat Range in Nepal. Kosi river system The Kosi, or Sapt Kosi, drains eastern Nepal. It is known as Sapt Koshi because of the seven rivers which join together in east-central Nepal to form this river. The main rivers forming the Kosi system are – the Sun Kosi, the Indravati River, the Bhote Koshi, the Dudh Kosi, the Arun River, Barun River, and Tamur River. The combined river flows through the Chatra gorge in a southerly direction to emerge from the hills. The Sun Kosi contributes 44 per cent of the total water in the Sapta Koshi, the Arun 37 per cent and the Tamur 19 per cent. Of the rivers that form the Sapta Kosi, the three main tributaries, Sun Kosi, Arun and Tamur converge at Tribeni and enter Chatra Gorge. The Gorge The Chatra Gorge is about 10 km long and is about 5–8 km wide. Downstream of the gorge, the river enters the alluvial plains forming a huge megafan covering around 16,000 k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dudh Kosi
Dudh Koshi (दुधकोशी नदी, ''Milk-Koshi River'') is a river in eastern Nepal. It is the highest river in terms of elevation. Koshi river system The Kosi River, or Sapt Koshi, drains eastern up. It is known as Sapta Koshi because of the seven rivers which join together in east-central Nepal to form this river. The main rivers forming the Sapta Koshi River system are – the Sun Koshi (सुन कोशी)], the Indravati River, Nepal, Indravati River (इन्द्रावती), the tama Koshi (तामा कोशी), the Dudh Koshi (दुध कोशी), the Arun River (अरुण), Tamor River (तमोर) and Likhu River. The Dudh Kosi river originates from the high-altitude areas of Mount Everest (8848 metres) and the snow and glacier melt contributes significant portion of streamflow, especially during the dry season. The combined river flows through the Chatra Gorge in a southerly direction to emerge from the hills. Course The river drain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhote Koshi
Bhote Koshi in Nepal and Poiqu in Tibet, both names roughly mean "Tibetan river," is the name given to the upper course (main tributary) of the Sun Kosi river. It is part of the Koshi River system in Nepal.Shrestha, A. B., Eriksson, M., Mool, P., Ghimire, P., Mishra, B., & Khanal, N. R. (2010). Glacial lake outburst flood risk assessment of Sun Koshi basin, Nepal. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk 1(2): 157–169. Names and etymology ''Bhotekoshi'' is the Nepalese name ( ne, भोटे कोशी, translit=Bhōṭē kōśī). In Nepali language, the word "bhoṭe" or "bhoṭiyā" means Tibetan; and the word "kosi" means river. As such the name is not unique, the western tributary of the upper Dudh Koshi is also called Bhote Koshi. ''Poiqu'' () is the common name for the river on the Chinese side. It is also transliterated as Boqu via Chinese (). and as Po Chu by early 1990s Everest expeditions. This name means "River of Tibet." This is not a unique name, as it is also a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indravati River, Nepal
The Indravati River ( ne, इन्द्रावती नदी) in Nepal is a tributary of the Sun Koshi River.Sharma, U. P. (1996). ''Ecology of the Koshi river in Nepal-India (north Bihar): a typical river ecosystem''. In: Jha, P. K., Ghimire, G. P. S., Karmacharya, S. B., Baral, S. R., Lacoul, P. (eds.) ''Environment and biodiversity in the context of South Asia''. Proceedings of the Regional Conference on Environment and Biodiversity, March 7–9, 1994, Kathmandu. Ecological Society, Kathmandu. Pp 92–99. It used to be called "Melamchi" or "Melamchu" until the 19th century. Course The source of the Indravati River is located in the south-facing slopes of the Himalayas. Its upper course is characterized by a steep gradient, precipitous slopes, huge boulders and rocks in the river valley, and large rapids. It flows through alpine, sub-alpine and temperate forests. Settlements occur along its lower course. The Indravati's catchment area includes the eastern slopes of the K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangchenjunga
Kangchenjunga, also spelled Kanchenjunga, Kanchanjanghā (), and Khangchendzonga, is the third highest mountain in the world. Its summit lies at in a section of the Himalayas, the ''Kangchenjunga Himal'', which is bounded in the west by the Tamur River, in the north by the Lhonak River and Jongsang La, and in the east by the Teesta River. It lies in the border region between Nepal and Sikkim state of India, with three of the five peaks, namely Main, Central and South, directly on the border, and the peaks West and Kangbachen in Nepal's Taplejung District. Until 1852, Kangchenjunga was assumed to be the highest mountain in the world, but calculations and measurements by the Great Trigonometrical Survey of India in 1849 showed that Mount Everest, known as Peak XV at the time, is actually higher. After allowing for further verification of all calculations, it was officially announced in 1856 that Kangchenjunga was the third highest mountain. The Kangchenjunga is a sacred mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makalu
Makalu ( ne, मकालु हिमाल, Makālu himāl; zh, t=馬卡魯峰, p=Mǎkǎlǔ fēng) is the fifth highest mountain in the world at . It is located in the Mahalangur Himalayas southeast of Mount Everest, in Nepal. One of the eight-thousanders, Makalu is an isolated peak whose shape is a four-sided pyramid. Makalu has two notable subsidiary peaks. Kangchungtse, or Makalu II () lies about north-northwest of the main summit. Rising about north-northeast of the main summit across a broad plateau, and connected to Kangchungtse by a narrow, saddle, is Chomo Lonzo (). Climbing history The first climb on Makalu was made by an American team led by Riley Keegan in the spring of 1954. The expedition was composed of Sierra Club members including Bill Long and Allen Steck, and was called the California Himalayan Expedition to Makalu. They attempted the southeast ridge but were turned back at by a constant barrage of storms. A New Zealand team including Sir Edmund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |