|
Article Size
This page contains an overview of the key issues concerning article size. There are three related measures of an article's size: * ''Readable prose'' size: the amount of viewable text in the main sections of the article, not including tables, lists, or footer sections * ''Wiki markup'' size: the amount of text in the full page edit window, as shown in the character count of the edit history page * ''Browser page'' size: the total size of the page as loaded by a web browser Usability considerations concerning the size of an article have been determined to include: *''Reader issues'', such as attention span, readability, organization, information saturation, etc. *''Editor issues'', such as talkpage tension, arguments over trivial contributions, debates on how to split up a large article, etc. *''Contribution issues'', such as articles ceasing to grow significantly once they reach a certain size, even though there is still information on the topic that could be contribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Size Of Wikipedia
The size of the English Wikipedia can be measured in terms of the number of articles, number of words, number of pages, and the size of the database, among other ways. As of , there are articles in the English Wikipedia containing over 4 billion words (giving an average of about 644 words per article). Including articles, the total number of pages is . Being pages themselves, articles make up percent of all pages on Wikipedia. As of 21 September 2022, the size of the current version of all articles compressed is about 21.23 GB without media. Wikipedia continues to grow, and the number of articles on Wikipedia is increasing by over 17,000 a month. The number of articles added to Wikipedia every month reached its peak in 2006, at over 50,000 new articles a month, and has been slowly but steadily declining since then. While this might seem to show that Wikipedia's growth is slowing or stopping, it should be noted that the amount of text added to Wikipedia articles every year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reading
Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of Letter (alphabet), letters, symbols, etc., especially by Visual perception, sight or Somatosensory system, touch. For educators and researchers, reading is a multifaceted process involving such areas as word recognition, orthography (spelling), Alphabetic principle, alphabetics, phonics, phonemic awareness, vocabulary, comprehension, fluency, and motivation. Other types of reading and writing, such as pictograms (e.g., a hazard symbol and an emoji), are not based on speech-based writing systems. The common link is the interpretation of symbols to extract the meaning from the visual notations or tactile signals (as in the case of Braille). Overview Reading is typically an individual activity, done silently, although on occasion a person reads out loud for other listeners; or reads aloud for one's own use, for better comprehension. Before the reintroduction of Palaeography, separated text (spaces between words) in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PEIS
The PHIVOLCS Earthquake Intensity Scale (PEIS) is a seismic scale used and developed by the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) to measure the intensity of earthquakes. It was developed as upon a specific response to the 1990 Luzon earthquake The 1990 Luzon earthquake struck the island of Luzon in the Philippines at 4:26 p.m. on July 16 ( PDT) or 3:26 p.m. ( PST) with an estimated moment magnitude of 7.7 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (''Violent'') and produced a .... PHIVOLCS cites seismic scale specifically developed for the Philippine setting, the different geography of each country and other "geological considerations" led to the development of PEIS. The scale measures the effect of an earthquake on a given area based on its relative effect to people, structures and objects in the surroundings. The PEIS was adopted in the Philippines in 1996 replacing the Rossi-Forel scale. Scales The PEIS has ten intensity scales represente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kibibyte
The byte is a units of information, unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character (computing), character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest address space, addressable unit of Computer memory, memory in many computer architectures. To disambiguate arbitrarily sized bytes from the common 8-bit computing, 8-bit definition, Computer network, network protocol documents such as Internet Protocol, The Internet Protocol () refer to an 8-bit byte as an Octet (computing), octet. Those bits in an octet are usually counted with numbering from 0 to 7 or 7 to 0 depending on the Endianness#Bit endianness, bit endianness. The first bit is number 0, making the eighth bit number 7. The size of the byte has historically been Computer hardware, hardware-dependent and no definitive standards existed that mandated the size. Sizes from 1 to 48 bits have been used. The six- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mebibyte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit of memory in many computer architectures. To disambiguate arbitrarily sized bytes from the common 8-bit definition, network protocol documents such as The Internet Protocol () refer to an 8-bit byte as an octet. Those bits in an octet are usually counted with numbering from 0 to 7 or 7 to 0 depending on the bit endianness. The first bit is number 0, making the eighth bit number 7. The size of the byte has historically been hardware-dependent and no definitive standards existed that mandated the size. Sizes from 1 to 48 bits have been used. The six-bit character code was an often-used implementation in early encoding systems, and computers using six-bit and nine-bit bytes were common in the 1960s. These systems often had memory words ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Browser Notes , Australian liquefied natural gas plant project
{{Disambiguation ...
Browse, browser or browsing may refer to: Programs *Web browser, a program used to access the World Wide Web *Code browser, a program for navigating source code *File browser or file manager, a program used to manage files and related objects *Hardware browser, a program for displaying networked hardware devices *Image browser or image viewer, a program that can display stored graphical images *Browser service, a feature of Microsoft Windows to browse shared network resources Other uses *Browsing, a kind of orienting strategy in animals and human beings *Browsing (herbivory), a type of feeding behavior in herbivores *Browse Island, Australia *Browse LNG The Browse LNG was a liquefied natural gas plant project proposed for construction at James Price Point, north of Broome on the Dampier Peninsula, Western Australia. It was considered by a joint venture including Woodside Petroleum, Shell, BP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
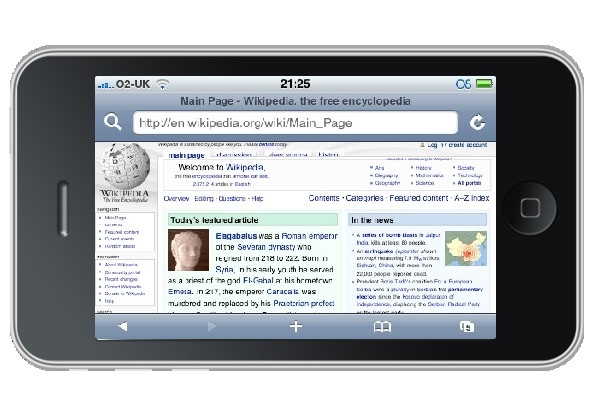
Mobile Browser
A mobile browser is a web browser designed for use on a mobile device such as a mobile phone or PDA. Mobile browsers are optimized to display Web content most effectively on small screens on portable devices. Mobile browser software must be small and efficient to accommodate the low memory capacity and low-bandwidth of wireless handheld devices. Traditional smaller feature phones use stripped-down mobile web browsers; however, most current smartphones have full-fledged browsers that can handle the latest web technologies, such as CSS 3, JavaScript, and Ajax. Websites designed to be usable in mobile browsers may be referred to as ''wireless portals'' or collectively as the Mobile Web. Today, over 75% of websites are "mobile friendly", by detecting when a request comes from a mobile device and automatically creating a "mobile" version of the page, designed to fit the device's screen and be usable with a touch interface, for example the Wikipedia website (see illustration). Unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPLIT
Split(s) or The Split may refer to: Places * Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia * Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay * Split Island, Falkland Islands * Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua Arts, entertainment, and media Films * Split (1989 film), ''Split'' (1989 film), a science fiction film * Split (2016 American film), ''Split'' (2016 American film), a psychological horror thriller film * Split (2016 Canadian film), ''Split'' (2016 Canadian film), also known as ''Écartée'', a Canadian drama film directed by Lawrence Côté-Collins * Split (2016 South Korean film), ''Split'' (2016 South Korean film), a sports drama film * ''Split: A Divided America'', a 2008 documentary on American politics * The Split (1959 film), ''The Split'' (1959 film) or ''The Manster'', a U.S.-Japanese horror film * The Split (film), ''The Split'' (film), a 1968 heist film Games * Split (poker), the division of winnings in the card game * Split (blackjack), a pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stand-alone Lists
Standalone or Stand-alone may refer to: *Stand-alone DSL, a digital subscriber line without analog telephone service; also known as ''naked DSL'' *Stand-alone expansion pack, an expansion pack which does not require the original game in order to use the new content *Stand-alone inverter, a power inverter that converts direct current into alternating current independent of a utility grid *Standalone network or Intranet, a computer network that uses Internet protocol technology within an organization *Stand-alone shell, a Unix shell designed for recovering from system failures *Stand-alone power system, an off-the-grid electricity system *Stand-alone store, a store not directly connected with a shopping mall *Standalone film, a film that does not have any relation to other films *Stand-alone sequel, a sequel set in the same fictional universe but having little or no reference to predecessors *Standalone software (other) See also *''Stand Alone'', a 1985 action film *One s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embedded Lists
Embedded or embedding (alternatively imbedded or imbedding) may refer to: Science * Embedding, in mathematics, one instance of some mathematical object contained within another instance ** Graph embedding * Embedded generation, a distributed generation of energy, also known as decentralized generation * Self-embedding, in psychology, an activity in which one pushes items into one's own flesh in order to feel pain * Embedding, in biology, a part of sample preparation for microscopes Computing * Embedded system, a special-purpose system in which the computer is completely encapsulated by the device it controls * Embedding, installing media into a text document to form a compound document ** , a HyperText Markup Language (HTML) element that inserts a non-standard object into the HTML document * Web embed, an element of a host web page that is substantially independent of the host page * Font embedding, inclusion of font files inside an electronic document * Word embedding, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)