|
Arthur River, Tasmania
Arthur River is the name of a small township on the northern part of the West Coast of Tasmania, Australia. At the , Arthur River and the surrounding area had a population of 32. It is south of the town of Marrawah. Named after Sir George Arthur, Lieutenant Governor of Van Diemens Land (1824–36), the town draws its name from the river. The river is fed by several tributaries including the Frankland River, which was named after its discoverer, George Frankland, then the colony's surveyor-general. The region has been exploited commercially for timber and fisheries, but today is mostly a centre for tourism. Bushwalking, fishing and four-wheel-driving are the most common activities undertaken by travellers in the region to get a glimpse of the unspoiled wilderness. The population in the area peaks during the summer months when shack users come here to enjoy the weather. On the coast near the mouth of the Arthur River is a plaque titled ''The Edge of the World. North West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur River (Tasmania)
The Arthur River ( Peerapper: ''Tunganrick'') is a major perennial river located in the north-west region of Tasmania, Australia. Location and features The Arthur River rises on the slopes of the Magnet Range, south of and flows generally north and then west, around the northern perimeter of the Savage River National Park. The river is joined by 25 tributaries including the Waratah, Wandle, Hellyer, Keith, Lyons, Rapid, Julius, Salmon and Frankland rivers. The Arthur River reaches its mouth at the settlement of where it empties into the Southern Ocean. The river descends over its course. The river was named in honour of Sir George Arthur, the Lieutenant Governor A lieutenant governor, lieutenant-governor, or vice governor is a high officer of state, whose precise role and rank vary by jurisdiction. Often a lieutenant governor is the deputy, or lieutenant, to or ranked under a governor — a "second-in-comm ... of Van Diemens Land between 1824 and 1836. On the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marrawah, Tasmania
Marrawah is a small town in the north of the West Coast of Tasmania, Australia. Marrawah is located in the former shire of Wellington, now part of the Circular Head Council area. At the 2006 census, Marrawah had a population of 407. Marrawah is mainland Tasmania's westernmost settlement and the furthest settlement from Hobart. It is located north-west of Hobart and north-west of Launceston and lies at the western end of the A2 sealed road. Marrawah also marked the end of Tasmania's westernmost railway, the Smithton to Marrawah Tramway. Farming, including dairy farming, and tourism are the main commercial activities. The area has several important Aboriginal sites, such as Aboriginal carvings at Mount Cameron West and Sundown Point. Green Point Beach near Marrawah is also known as a good location for surfing, kitesurfing and windsurfing. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roaring Forties
The Roaring Forties are strong westerly winds found in the Southern Hemisphere, generally between the latitudes of 40°S and 50°S. The strong west-to-east air currents are caused by the combination of air being displaced from the Equator towards the South Pole, the Earth's rotation, and the scarcity of landmasses to serve as windbreaks at those latitudes. The Roaring Forties were a major aid to ships sailing the Brouwer Route from Europe to the East Indies or Australasia during the Age of Sail, and in modern times are favoured by yachtsmen on round-the-world voyages and competitions. The boundaries of the Roaring Forties are not consistent: The wind-stream shifts north or south depending on the season. The strong and continuous winds in the Roaring Forties make this zone highly prospective for wind power such as in New Zealand and Tasmania. Similar but even stronger conditions that occur at more southerly latitudes are called the Furious Fifties and the Shrieking or Scre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
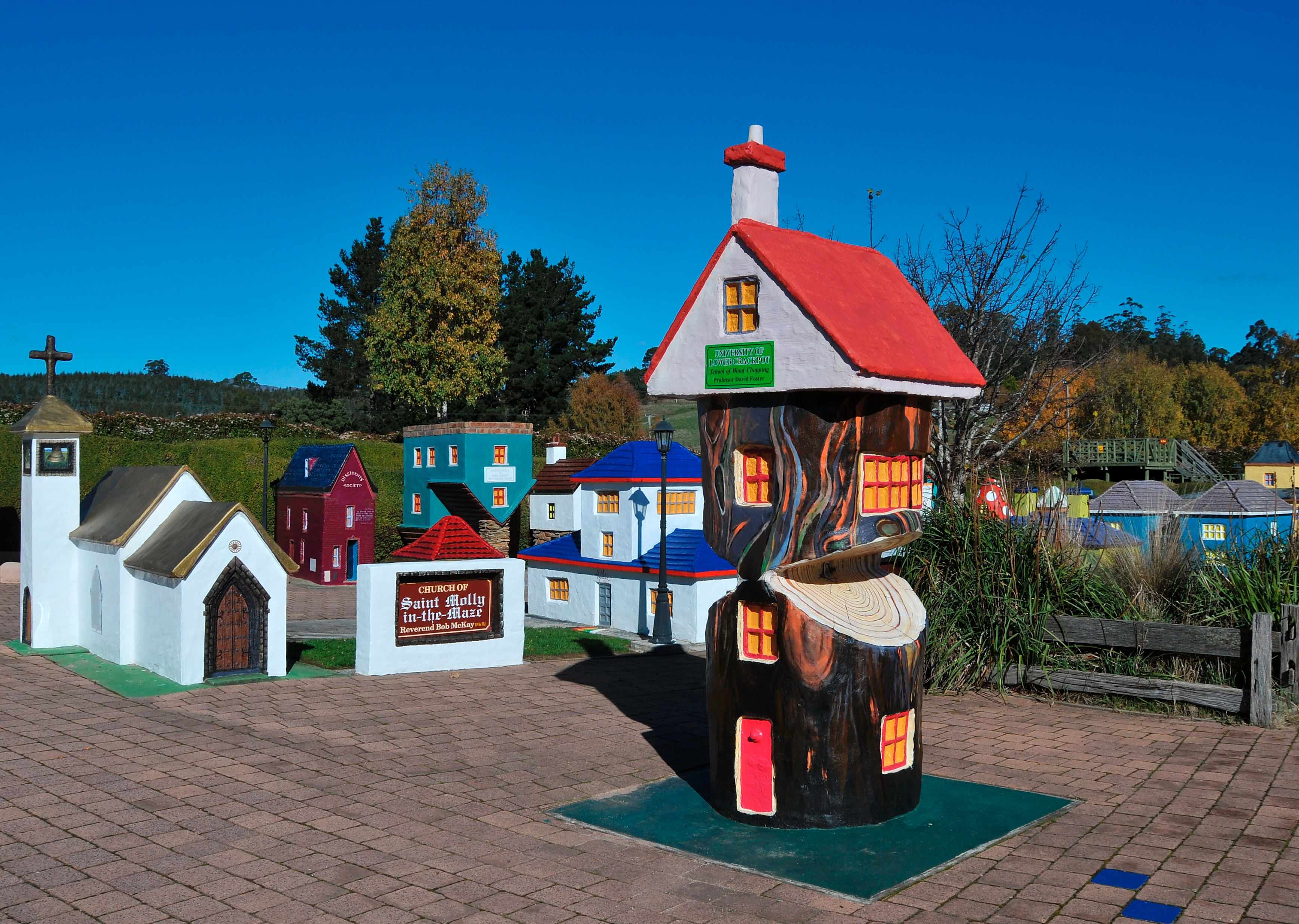
Brian Inder
Brian Inder (12 December 1930 - 21 August 2019) is a tourism pioneer of North Western Tasmania, Australia. On his property at Promised Land near Lake Barrington he has established the world's largest maze complexes, called Tasmazia.Gill Vowles, Maze venture shows the way'Hobart Mercury, December 4, 2005. Accessed October 8, 2008 When dairy farming was proving difficult in the early 1980s, Inder moved to Lavender farming and manufacture of herbal products which proved more profitable. A childhood dream of establishing a hedge maze proved initially difficult, so he developed a model town called the ''Village of Lower Crackpot''. A gift shop, pancake parlour, and honey tasting soon followed making Tasmazia the largest commercial tourism attraction on the North West Coast. When the nearby town of Sheffield was facing commercial decline, Inder was instrumental in establishing Sheffield as a ''town of murals'' with a mural fest. Other festivals he played a leading role in establishi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four-wheel-drive
Four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 ("four by four") or 4WD, refers to a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case providing an additional output drive shaft and, in many instances, additional gear ranges. A four-wheel drive vehicle with torque supplied to both axles is described as "all-wheel drive" (AWD). However, "four-wheel drive" typically refers to a set of specific components and functions, and intended off-road application, which generally complies with modern use of the terminology. Definitions Four-wheel-drive systems were developed in many different markets and used in many different vehicle platforms. There is no universally accepted set of terminology that describes the various architectures and functions. The terms used by various manufacturers often reflect marketing rather than engineering considerations or significant technical dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Frankland
George Frankland (1800 – 30 December 1838) was an English surveyor and Surveyor-General of Van Diemen's Land (now Tasmania). In 1823, Frankland was appointed surveyor-general at Poona, India, where he became acquainted with Edward Dumaresq. In 1827 Frankland arrived in Van Diemen's Land as first assistant surveyor, in March 1828 he became Surveyor General of Tasmania. Frankland soon began a trigonometric survey of the island, but suffered some criticism due to his slow progress. John Helder Wedge and James Erskine Calder criticized Frankland's ability as a surveyor. Frankland travelled on several expeditions and recorded his observations, considering it his duty ''"to observe and record every remarkable fact connected with the Natural history of the island whose surface and native production have, in a manner, been placed so peculiarly in his custody."'' Frankland made sketches of some of the country he explored and did the artwork for the proclamation to encourage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankland River (Tasmania)
The Frankland River is a major perennial river located in the north-west region of Tasmania, Australia. Location and features Formed by the confluence of the Horton and Lindsay rivers, the Frankland River rises in the Sumac Forest Reserve and flows generally west by north. The Frankland River reaches its mouth in remote country east of the settlement of where it empties into the Arthur River. The river descends over its course. The river draws its name from George Frankland, an English surveyor and Surveyor-General of Van Diemen's Land between 1827 and 1838. See also *Rivers of Tasmania This page discusses the rivers and hydrography of the state of Tasmania, Australia. In the geography of Tasmania, the state is covered with a network of rivers and lake systems. As an island, all rivers eventually empty into the waters that su ... References Rivers of Tasmania North West Tasmania {{Tasmania-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
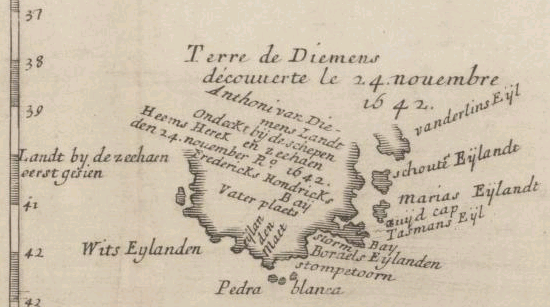
Van Diemens Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania used by the British during the European exploration of Australia in the 19th century. A British settlement was established in Van Diemen's Land in 1803 before it became a separate colony in 1825. Its penal colonies became notorious destinations for the transportation of convicts due to the harsh environment, isolation and reputation for being inescapable. Macquarie Harbour and Port Arthur are among the most well-known penal settlements on the island. With the passing of the Australian Constitutions Act 1850, Van Diemen's Land (along with New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Victoria, and Western Australia) was granted responsible self-government with its own elected representative and parliament. On 1 January 1856, the colony of Van Diemen's Land was officially changed to Tasmania. The last penal settlement was closed in Tasmania in 1877. Toponym The island was named in honour of Anthony van D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Arthur
Sir George Arthur, 1st Baronet (21 June 1784 – 19 September 1854) was Lieutenant Governor of British Honduras from 1814 to 1822 and of Van Diemen's Land (present-day Tasmania) from 1823 to 1836. The campaign against Aboriginal Tasmanians, known as the Black War, occurred during this term of office. He later served as Lieutenant Governor of Upper Canada from 1838 to 1841, and Governor of Bombay from 1842 to 1846. Early life George Arthur was born in Plymouth, England. He was the youngest son of John Arthur, from a Cornish family, and his wife, Catherine, daughter of Thomas Cornish. He entered the army in 1804 as an ensign and was promoted lieutenant in June 1805. He served during the Napoleonic Wars, including Sir James Craig's expedition to Italy in 1806. In 1807 he went to Egypt, and was severely wounded in the attack upon Rosetta. He recuperated and was promoted to captain under Sir James Kempt in Sicily in 1808, and participated in the Walcheren expedition in 1809. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign ''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'. The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ... country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division Of Braddon (state)
The electoral division of Braddon (named Darwin until 1955) is one of the five electorates in the Tasmanian House of Assembly, it includes north-west and western Tasmania as well as King Island. Braddon takes its name from the former Premier of Tasmania, Sir Edward Braddon. The division shares its name and boundaries with the federal division of Braddon. Braddon and the other House of Assembly electoral divisions are each represented by five members elected under the Hare-Clark electoral system. History and electoral profile Prior to 1955, the electorate was known as Darwin. The electoral constituency includes; King Island, the North-west towns of Devonport, Burnie, Wynyard, Ulverstone, Penguin, and Smithton, as well as the West Coast towns of Strahan, Zeehan and Queenstown. , ''Tasmanian Electoral Commission'' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
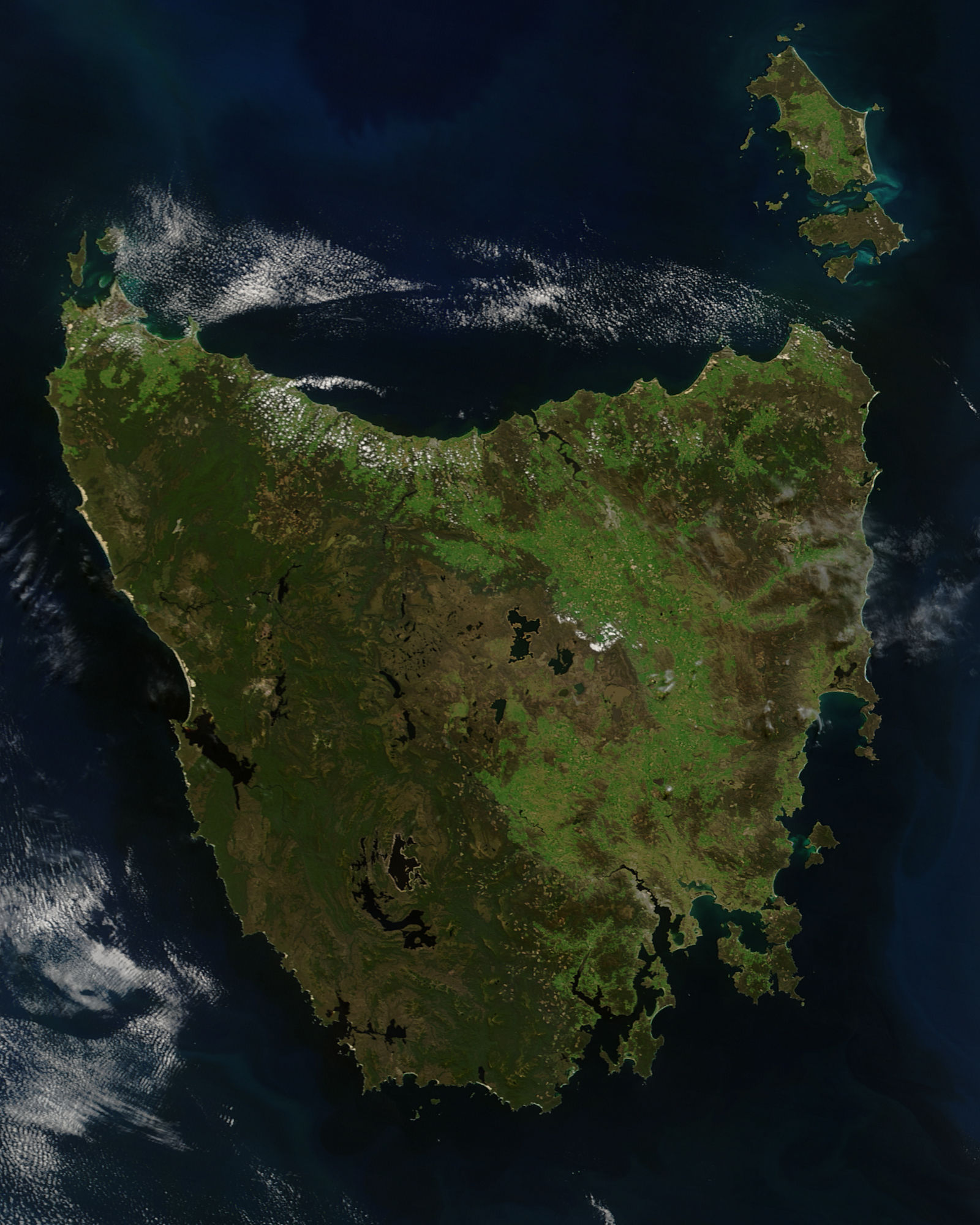
Tasmania
) , nickname = , image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Tasmania , established_title2 = Federation , established_date2 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Abel Tasman , demonym = , capital = Hobart , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 29 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpeg)