|
Marrawah, Tasmania
Marrawah is a small town in the north of the West Coast of Tasmania, Australia. Marrawah is located in the former shire of Wellington, now part of the Circular Head Council area. At the 2006 census, Marrawah had a population of 407. Marrawah is mainland Tasmania's westernmost settlement and the furthest settlement from Hobart. It is located north-west of Hobart and north-west of Launceston and lies at the western end of the A2 sealed road. Marrawah also marked the end of Tasmania's westernmost railway, the Smithton to Marrawah Tramway. Farming, including dairy farming, and tourism are the main commercial activities. The area has several important Aboriginal sites, such as Aboriginal carvings at Mount Cameron West and Sundown Point. Green Point Beach near Marrawah is also known as a good location for surfing, kitesurfing and windsurfing. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Head Council
Circular Head Council is a local government body in Tasmania covering the far north-west mainland. It is classified as a rural local government area with a population of 8,066, and its major towns and localities include Arthur River, Marrawah and Stanley, with Smithton being the largest and principal town. The origin of the name “Circular Head” is unknown. History and attributes Circular Head was established on 1 January 1907, the boundaries were altered in 1993 as part of a reorganisation. The region includes the smaller islands immediately off the north-west tip of the state including Robbins Island, Hunter Island and Three Hummock Island. Circular Head is classified as rural, agricultural and large (RAL) under the Australian Classification of Local Governments. Government Localities Not in above list * Corinna * Couta Rocks * Meunna * Milabena Milabena is a rural locality in the local government areas of Waratah-Wynyard and Circular Head in the North We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
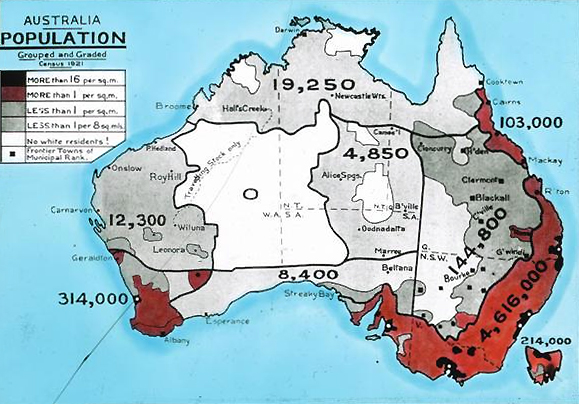
Census In Australia
The Census in Australia, officially the Census of Population and Housing, is the national census in Australia that occurs every five years. The census collects key demographic, social and economic data from all people in Australia on census night, including overseas visitors and residents of Australian external territories, only excluding foreign diplomats. The census is the largest and most significant statistical event in Australia and is run by the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS). Every person must complete the census, although some personal questions are not compulsory. The penalty for failing to complete the census after being directed to by the Australian Statistician is one federal penalty unit, or . The ''Australian Bureau of Statistics Act 1975'' and ''Census and Statistics Act 1905'' authorise the ABS to collect, store, and share anonymised data. The most recent census was held on 10 August 2021, with the data planned to be released starting from mid-2022. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Grim
Cape Grim, officially Kennaook / Cape Grim, is the northwestern point of Tasmania, Australia. The Peerapper name for the cape is recorded as ''Kennaook''. It is the location of the Cape Grim Baseline Air Pollution Station and of the Cape Grim Air Archive which is operated by the Australian Bureau of Meteorology in a joint programme with the CSIRO. The station was established in 1976 and has been operating ever since. Geography Cape Grim's isolated geographic location makes it unique. The next land mass directly west of Cape Grim is not Africa, but the southern tip of Argentina. Winds that make their way to Cape Grim from Antarctica and the Indian Ocean hit no significant land mass. Air pollution values collected at Cape Grim are the closest attainable representation of a global average. History The headland was first charted and named Cape Grim by Matthew Flinders on 7 December 1798, as he sailed from the east in the ''Norfolk'' and found a long swell coming from the south- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolnorth Wind Farm
Woolnorth Wind Farm is a wind power complex, comprising two wind farms — Bluff Point and Studland Bay. They are located at the Woolnorth property at Woolnorth (which includes the location known as Cape Grim), in the far north-west of Tasmania, Australia. Both wind farms are operated by Woolnorth Wind Farm Holdings, a joint venture between Hydro Tasmania (who own a 25% share) and Shenhua Group (75% share). Farms Bluff Point Wind Farm was constructed in two stages. The first consisted of six 1.75 MW Vestas V66 turbines and was commissioned in 2002. Stage two, commissioned in 2004, expanded the wind farm with a further 31 of the same turbines, for a total generating capacity of 65 MW. Studland Bay Wind Farm was commissioned in 2007 and consists of 25 Vestas V90 turbines, each with a capacity of 3 MW, for a total capacity of 75 MW. Tours to the wind farms are available and operated by a private commercial entity. Operations The generation table useeljmkt nemlogto obtain gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windsurfing
Windsurfing is a wind propelled water sport that is a combination of sailing and surfing. It is also referred to as "sailboarding" and "boardsailing", and emerged in the late 1960s from the aerospace and surf culture of California. Windsurfing gained a popular following across Europe and North America by the late 1970s and had achieved significant global popularity by the 1980s. Windsurfing became an olympic sport in 1984. Newer variants include windfoiling, kiteboarding and wingfoiling. Hydrofoil fins under the board allow the boards to safely lift out of the water and fly silently and smoothly above the surface even in lighter winds. Windsurfing is a recreational, family friendly sport, most popular at flat water locations around the world that offer safety and accessibility for beginner and intermediate participants. Technique and equipment have evolved over the years Major competitive disciplines include slalom, wave and freestyle. Increasingly, "foiling" is replacing trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitesurfing
Kiteboarding or kitesurfing is a sport that involves using wind power with a large power kite to pull a rider across a water, land, or snow surface. It combines aspects of paragliding, surfing, windsurfing, skateboarding, snowboarding, and wakeboarding. Kiteboarding is among the less expensive and the more convenient sailing sports. After some concepts emerged in the late 1970s and early 1980s and some designs were successfully tested, the sport received a wider audience in the late 1990s and became mainstream at the turn of the century. It has freestyle, wave-riding, and racing competitions. The sport held the speed sailing record, reaching before being eclipsed by the Vestas Sailrocket. Worldwide, there are 1.5 million kitesurfers, while the industry sells around 100,000 to 150,000 kites per year. Most power kites are leading edge inflatable kites or foil kites attached by about of flying lines to a control bar and a harness. The kitesurfer rides on either a bidir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surfing
Surfing is a surface water sport in which an individual, a surfer (or two in tandem surfing), uses a board to ride on the forward section, or face, of a moving wave of water, which usually carries the surfer towards the shore. Waves suitable for surfing are primarily found on ocean shores, but can also be found in standing waves in the open ocean, in lakes, in rivers in the form of a tidal bore, or in wave pools. The term ''surfing'' refers to a person riding a wave using a board, regardless of the stance. There are several types of boards. The Moche of Peru would often surf on reed craft, while the native peoples of the Pacific surfed waves on alaia, paipo, and other such water craft. Ancient cultures often surfed on their belly and knees, while the modern-day definition of surfing most often refers to a surfer riding a wave standing on a surfboard; this is also referred to as stand-up surfing. Another prominent form of surfing is body boarding, where a surfer rides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Age
''The Age'' is a daily newspaper in Melbourne, Australia, that has been published since 1854. Owned and published by Nine Entertainment, ''The Age'' primarily serves Victoria (Australia), Victoria, but copies also sell in Tasmania, the Australian Capital Territory and border regions of South Australia and southern New South Wales. It is delivered both in print and digital formats. The newspaper shares some articles with its sister newspaper ''The Sydney Morning Herald''. ''The Age'' is considered a newspaper of record for Australia, and has variously been known for its investigative reporting, with its journalists having won dozens of Walkley Awards, Australia's most prestigious journalism prize. , ''The Age'' had a monthly readership of 5.321 million. History Foundation ''The Age'' was founded by three Melbourne businessmen: brothers John and Henry Cooke (who had arrived from New Zealand in the 1840s) and Walter Powell. The first edition appeared on 17 October 1854. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marrawah Tramway
The Marrawah Tramway was a long narrow gauge forest railway near Marrawah in Tasmania with a gauge of . The construction was initiated around 1911 to harvest timber in the Mowbray Swamp. The tramway was bought by the state government in October 1913 and the steel rails extended to Marrawah. It was decommissioned in 1961.Nic Haygarth''Marrawah Tramway - Getting started at Brittons Swamp.''6 November 2016. Downloaded on 17 January 2018. Early work In the early 1880s, the late Mr. J. S. Lee constructed a short length of tramway from Lee's “Old Jetty” to his newly built mill at Leesville. The line was extended from the Leesville settlement to Mowbray Swamp, an expanse of unbelievably rich blackwood forest. The original tram, which was built around the edge of the swamp, turned south at what in later years became known as the ''Five Mile'', and skirted the higher land to the west. This tram , which ultimately became a spur line of the tramway, was later extended through Christm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A2 Highway (Tasmania)
The Bass Highway is a highway in Tasmania ) , nickname = , image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdi ..., Australia. It connects the three cities across the north of the state – Burnie, Tasmania, Burnie, Devonport, Tasmania, Devonport and Launceston, Tasmania, Launceston. The road was named due to its proximity to the Bass Strait. It is a part of the National Highway (Australia), National Highway, designated as National Highway 1, together with the Midland Highway (Tasmania), Midland and Brooker Highway, Brooker highways in Tasmania. The highway passes through or near the following localities: *Launceston, Tasmania, Launceston * Prospect, Tasmania, Prospect and other Launceston suburbs * Hadspen, Tasmania, Hadspen * Carrick, Tasmania, Carrick * Hagley, Tasmania, Hagley * Westbury, Tasman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellington Shire, Tasmania
Wellington ( mi, Te Whanganui-a-Tara or ) is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the second-largest city in New Zealand by metro area, and is the administrative centre of the Wellington Region. It is the world's southernmost capital of a sovereign state. Wellington features a temperate maritime climate, and is the world's windiest city by average wind speed. Legends recount that Kupe discovered and explored the region in about the 10th century, with initial settlement by Māori iwi such as Rangitāne and Muaūpoko. The disruptions of the Musket Wars led to them being overwhelmed by northern iwi such as Te Āti Awa by the early 19th century. Wellington's current form was originally designed by Captain William Mein Smith, the first Surveyor General for Edward Wakefield's New Zealand Company, in 1840. The Wellington urban area, which only includes urbanised areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division Of Braddon (state)
The electoral division of Braddon (named Darwin until 1955) is one of the five electorates in the Tasmanian House of Assembly, it includes North West Tasmania, north-west and Western Tasmania, western Tasmania as well as King Island (Tasmania), King Island. Braddon takes its name from the former Premier of Tasmania, Edward Braddon, Sir Edward Braddon. The division shares its name and boundaries with the Division of Braddon, federal division of Braddon. Braddon and the other House of Assembly electoral divisions are each represented by five members elected under the Hare-Clark electoral system. History and electoral profile Prior to 1955, the electorate was known as Darwin. The electoral constituency includes; King Island (Tasmania), King Island, the North-west towns of Devonport, Tasmania, Devonport, Burnie, Tasmania, Burnie, Wynyard, Tasmania, Wynyard, Ulverstone, Tasmania, Ulverstone, Penguin, Tasmania, Penguin, and Smithton, Tasmania, Smithton, as well as the West Coast t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |