|
Arne Sithonis
Arne (Greek: Ἄρνη) is a mythologized princess of an ancient Greek island, who according to legend betrayed her motherland, after the legendary king Minos had bribed her with gold into supporting Crete. After she had accepted the bribe that "her greed demanded", Minos' troops attacked the island. For this misdeed the gods punished her by turning her into a black-footed, black-winged jackdaw, and she would be forever attracted to golden and shining objects. Localization and chronology The only source on Arne's story is Ovid's mythological poem ''Metamorphoses'' from 8 BC, where—depending on the manuscript—her name is given as ''Arne Sithonis'' or ''Arne Sithon'' ("the Sithonian Arne", meaning "the Thracian Arne"; ''see below''). Attempts have been made to identify the island as Siphnos due to paleographical similarities, but no independent legend connects an ''Arne'' to Siphnos or any other island of the Cyclades. Like ''Sithoniae (nurus)'', ''Sithonios (agros)'' and ''Sith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which survive intact, between 60 and 30 BC. The history is arranged in three parts. The first covers mythic history up to the destruction of Troy, arranged geographically, describing regions around the world from Egypt, India and Arabia to Europe. The second covers the time from the Trojan War to the death of Alexander the Great. The third covers the period to about 60 BC. ''Bibliotheca'', meaning 'library', acknowledges that he was drawing on the work of many other authors. Life According to his own work, he was born in Agyrium in Sicily (now called Agira). With one exception, antiquity affords no further information about his life and doings beyond his written works. Only Jerome, in his ''Chronicon'' under the "year of Abraham 1968" (49 BC), w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arne (mythology)
In Greek mythology, Arne (; grc, Ἄρνη), also called Melanippe or Antiopa, was the daughter of Aeolus and Melanippe (also Hippe or Euippe), daughter of Chiron.Diodorus Siculus, 4.67.3–5 Mythology Arne was born as a foal as her mother had been transformed into a horse as a disguise, but was returned to the human form and renamed Arne. According to John Tzetzes, Arne was the nurse of the young Poseidon, who denied knowing where he was when Cronus came searching for him.Tzetzes ad Lycophron, 644 Aeolus entrusted her to the care of one Desmontes. However, Poseidon fathered Aeolus and BoeotusScholia on Homer, ''Iliad'' B, 494, p. 80, 43 ed. Bekk. as cited in Hellanicus' ''Boeotica'' with her while he was in the form of a bull. Enraged, Desmontes entombed and blinded her and placed her twin sons on Mount Pelion. She was later rescued by her sons and married king Metapontus of Icaria, and Poseidon restored her vision. Through Boeotus, she was the ancestress of the Boeotian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arne (name)
Arne is a common masculine given name for males in Scandinavia. It is also a surname in England. The name Arne originates from the old Norse name Árni, which in turn is derived from the old Norse name for "eagle", ''Ǫrn''. The oldest attestation of the name is from a runestone in Vagnhärad dating to the 11th century. The word arne also refers to the central stone on the floor of traditional Norwegian homes upon which the fire that provides the heating/cooking needs was lit. Similarly, "Arne" is Danish for the flame in a fireplace or old-fashioned oven or stove. Given name People * Arne Bang-Hansen, Norwegian actor * Arne Beurling, Swedish mathematician * Arne Borg, Swedish swimmer * Arne Carlson, American politician * Arne Dahl, American politician * Arne Duncan, American politician * Arne Friedrich, German professional footballer * Per-Arne Håkansson (1963), Swedish politician * Arne Jacobsen, Danish architect and designer, exemplar of the "Danish Modern" style. * Arne E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arne (other)
Arne may refer to: Places * Arne, Dorset, England, a village ** Arne RSPB reserve, a nature reserve adjacent to the village * Arné, Hautes-Pyrénées, Midi-Pyrénées, France * Arne (Boeotia), an ancient city in Boeotia, Greece * Arne (Thessaly), an ancient city in Thessaly, Greece * Arne, or modern Tell Aran, an ancient Arameans city near Aleppo, Syria * Arne Township, Benson County, North Dakota, United States * 959 Arne, an asteroid People * Arne (name), a given name and a surname, including a list of people with the name * Arne & Carlos, a Norwegian design duo Mythology * Arne (Greek myth), three figures in Greek mythology See also * Aarne Aarne as a surname may refer to: *Antti Aarne (1867–1925), Finnish folklorist * Els Aarne (1917–1995), Estonian composer *Johan Victor Aarne (1863–1934), Finnish metalsmith As a given name it may refer to: *Aarne Ahi (born 1943), Estonian ... * Aarne–Thompson classification systems * Arn (other) {{disambiguatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paros
Paros (; el, Πάρος; Venetian: ''Paro'') is a Greek island in the central Aegean Sea. One of the Cyclades island group, it lies to the west of Naxos, from which it is separated by a channel about wide. It lies approximately south-east of Piraeus. The Municipality of Paros includes numerous uninhabited offshore islets totaling of land. Its nearest neighbor is the municipality of Antiparos, which lies to its southwest. In ancient Greece, the city-state of Paros was located on the island. Historically, Paros was known for its fine white marble, which gave rise to the term "Parian" to describe marble or china of similar qualities. Today, abandoned marble quarries and mines can be found on the island, but Paros is primarily known as a popular tourist spot. Geography Paros' geographic co-ordinates are 37° N. latitude, and 25° 10' E. longitude. The area is . Its greatest length from N.E. to S.W. is , and its greatest breadth . The island is of a round, plump-pear shape, form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthenius Of Nicaea
Parthenius of Nicaea ( el, Παρθένιος ὁ Νικαεύς) or Myrlea ( el, ὁ Μυρλεανός) in Bithynia was a Greeks, Greek Philologist, grammarian and poet. According to the ''Suda'', he was the son of Heraclides and Eudora, or according to Hermippus of Berytus, his mother's name was Tetha. He was taken prisoner by Helvius Cinna in the Mithridatic Wars and carried to Rome in 72 BC. He subsequently visited Naples, Neapolis, where he taught Greek language, Greek to Virgil, according to Macrobius. Parthenius is said to have lived until the accession of Tiberius in 14 AD. Parthenius was a writer of elegy, elegies, especially dirges, and of short epic poems. He is sometimes called "the last of the Alexandrians". ''Erotica Pathemata'' His only surviving work, the ''Erotica Pathemata'' (, ''Of the Sorrows of Love''), was set out, the poet says in his preface, "in the shortest possible form" and dedicated to the poet Cornelius Gallus, as "a storehouse from which to draw mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aloeus
Aloeus (; Ancient Greek: Ἀλωεύς probably derived from ἀλοάω ''aloaō'' "to thresh, to tread" as well as "to crush, to smash") can indicate one of the two characters in Greek mythology: *Aloeus or Haloeus, a Thessalian prince as the son of Poseidon and princess Canace, daughter of King Aeolus and Enarete. He was the brother of Hopleus, Nireus, Epopeus and Triops. His first wife was his niece Iphimedeia, and later Eriboea, daughter of Eurymachus. In some accounts, Aloeus was the father of Salmoneus who founded Elis, the girls Elate and Platanus, and the twin giants, Otus and Ephialtes, collectively known as the Aloadae. These giants made war on the gods and captured the god Ares in a bag. Aloeus's wife Eeriboea reported this to the gods, for which Aloeus had her flayed alive. In Virgil's ''Aeneid'', the sons of Aloeus were found in the underworld and there Aeneas sees them being punished by Rhadamanthus. This scene from Virgil was a precursor to Dante's depiction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iphimedia
In Greek mythology, Iphimedeia (; Ancient Greek: Ἰφιμέδεια) or Iphimede (Ἰφιμέδη) was a Thessalian princess. She was attested in Homer's ''Odyssey'' in the Catalogue of women as being a mortal. Family Iphimedia was the daughter of Triopas of Thessaly (a son of Poseidon and Canace) and probably by Hiscilla, daughter of King Myrmidon of Phthia. Her possible brothers were Erysichthon and Phorbas. Iphimedea had by Poseidon the twins Otus and Ephialtes who were called the Aloadae after their stepfather.Homer, ''Odyssey'11.305 Pindar, ''Pythian Ode'4.89 Hyginus, ''Fabulae'28/ref> One account called these men's natural father as Aloeus, husband and paternal uncle of Iphimede. The latter mothered as well Pancratis (or Pancrato) to Aloeus. She was probably also the mother of Elate and Platanus, the sisters of the Aloadae. Mythology Early years Iphimedeia also fell in love with Poseidon, god of the sea, and would often come to the sea shore where she poured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic regions of Greece, geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which separates the Gulf of Corinth from the Saronic Gulf. From the late Middle Ages until the 19th century the peninsula was known as the Morea ( grc-x-byzant, Μωρέας), (Morèas) a name still in colloquial use in its demotic Greek, demotic form ( el, Μωριάς, links=no), (Moriàs). The peninsula is divided among three administrative regions of Greece, administrative regions: most belongs to the Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese region, with smaller parts belonging to the West Greece and Attica (region), Attica regions. Geography The Peloponnese is a peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland, in area, and constitutes the southernmost part of mainland Greece. It is connected to the mainlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theseus
Theseus (, ; grc-gre, Θησεύς ) was the mythical king and founder-hero of Athens. The myths surrounding Theseus his journeys, exploits, and friends have provided material for fiction throughout the ages. Theseus is sometimes described as the son of Aegeus, King of Athens, and sometimes as the son of the god Poseidon. He was raised by his mother, Aethra, and, upon discovering his connection to Aegeus, travels overland to Athens, having many adventures on the way. When he reaches Athens, he finds that Aegeus is married to Medea (formerly wife of Jason), who plots against him. The most famous legend about Theseus is his slaying of the Minotaur, half man and half bull. He then goes on to unite Attica under Athenian rule: the ''synoikismos'' ('dwelling together'). As the unifying king, he is credited with building a palace on the fortress of the Acropolis. Pausanias reports that after ''synoikismos'', Theseus established a cult of Aphrodite ('Aphrodite of all the People' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
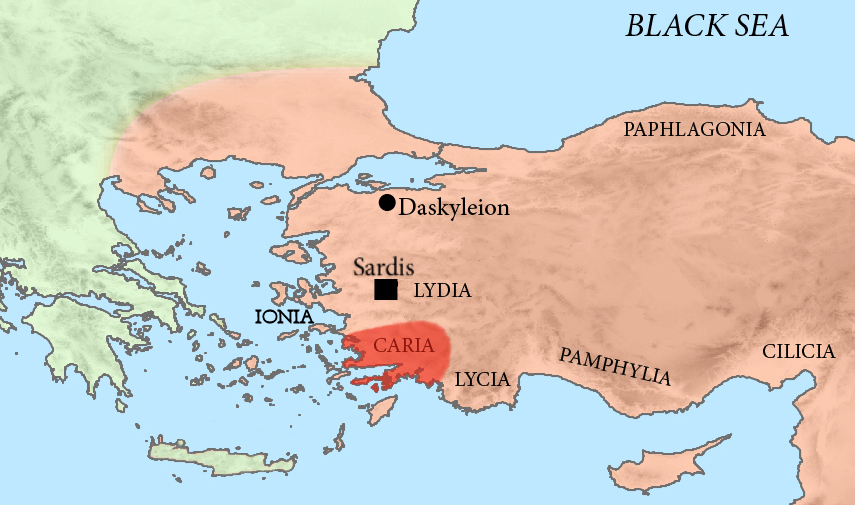
Karian
The Carians (; grc, Κᾶρες, ''Kares'', plural of , ''Kar'') were the ancient inhabitants of Caria in southwest Anatolia. Historical accounts Karkisa It is not clear when the Carians enter into history. The definition is dependent on corresponding Caria and the Carians to the "Karkiya" or "Karkisa" mentioned in the Hittite records. Bronze Age Karkisa are first mentioned as having aided the Assuwa League against the Hittite King Tudhaliya I. Later in 1323 BC, King Arnuwandas II was able to write to Karkiya for them to provide asylum for the deposed Manapa-Tarhunta of "the land of the Seha River", one of the principalities within the Luwian Arzawa complex in western Anatolia. This they did, allowing Manapa-Tarhunta to take back his kingdom. In 1274 BC, Karkisa are also mentioned among those who fought on the Hittite Empire side against the Egyptians in the Battle of Kadesh. Taken as a whole, Hittite records seem to point at a Luwian ancestry for the Carians and, as such, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |