|
Ardoreosomus
''Ardoreosomus'' (meaning: "tropical body") is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish. It was described from the Induan aged Candelaria Formation of Nevada, United States, which was located near the equator during the Early Triassic epoch. It contains only one species, ''A. occidentalis'' (monotypy). ''Ardoreosomus'' is a ptycholepiform, closely resembling '' Boreosomus'' and '' Ptycholepis''; however, ''Ardoreosomus'' is distinguished from other ptycholepiforms in having a more strongly angled hyomandibula and lacking an opercular process, among other features. See also * Prehistoric fish * List of prehistoric bony fish * Paleontology in Nevada Paleontology in Nevada refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Nevada. Nevada has a rich fossil record of plants and animal life spanning the past 650 million years of time. The earliest fo ... References Prehistoric ray-finned fish genera {{Triassic-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptycholepiformes
Ptycholepiformes are an extinct order of prehistoric ray-finned fish that existed during the Triassic period and the Early Jurassic epoch. The order includes the genera '' Acrorhabdus'', ''Ardoreosomus'', ''Boreosomus'', '' Chungkingichthys'', '' Ptycholepis'', and '' Yuchoulepis''. Although several families have been proposed, some studies place all these genera in the same family, Ptycholepididae. Ptycholepiformes had a widespread distribution during the Early Triassic, but were restricted to mainly Europe and North America afterwards. They are known from both marine and freshwater deposits. Appearance Typical features of ptycholepiforms are the fusiform body covered in rhombic ganoid scales, the anterior position of the dorsal fin. In most coeval ray-fins the dorsal fin has a more posterior position), usually situated opposite to the anal fin. Moreover, ptycholepiforms show a series of elongate, horizontal suborbital bones. The skull is usually relatively large. The scal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candelaria Formation, Nevada
The Candelaria Formation is a Formation (geology), geologic formation in Nevada, United States. The formation comprises shales and limestones deposited in an open marine depositional environment, environment and preserves fossils dating back to the Induan (Griesbachian to Dienerian) age (geology), age of the Early Triassic epoch (geology), epoch.Candelaria Formation at Fossilworks.org Fossil content Among others, the following fossils of ammonoids, bivalves and ray-finned fishes have been recovered from the formation: * ''Ambites, Ambites lilangensis'' * ''Ambites, Ambites aff. radiatus'' * ''Ardoreosomus, Ardoreosomus occidentalis'' * ''Candelarialepis, Candelarialepis argentus'' * ''C ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptycholepis
''Ptycholepis'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish having the head and opercular bones ornamented with ridges of ganoin, minute teeth, and thick scales (which are much longer than deep and are grooved longitudinally on the outer side). ''Ptycholepis'' belongs to the family Ptycholepidae (= Boreosomidae/Chungkingichthyidae). Other genera of this family are '' Acrorhabdus'' (Spitsbergen, Early Triassic), ''Ardoreosomus'' (Nevada, United States; Early Triassic), ''Boreosomus'' (global, Early Triassic), '' Chungkingichthys'' (China, Early Triassic) and ''Yuchoulepis'' (China, Early Triassic). A typical feature of this family is the dorsal fin, which inserts at the level of the pelvic fins in the front part of the body. Other characters include the striated skull bones and scales, and the small teeth. File:Ptycholepis bollensis.jpg, ''Ptycholepis bollensis'' File:Ptycholepis bollensis - Holzmaden.jpg, ''Ptycholepis bollensis'' File:Ptycholepis bollensis - Lyme Regis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boreosomus
''Boreosomus'' (meaning: "boreal body") is an extinct genus of Triassic ray-finned fish. It was first described from the Arctic island of Spitsbergen (Svalbard, Norway), but was later also discovered in other parts of the world. ''Boreosomus'' belongs to the family Ptycholepidae (= Boreosomidae/Chungkingichthyidae). Other genera of this family are '' Acrorhabdus'' (Spitsbergen), ''Ardoreosomus'' (Nevada, United States), '' Chungkingichthys'' (China), '' Ptycholepis'' (global) and ''Yuchoulepis'' (China). Description The type species is ''Boreosomus arcticus'' (= ''Acrolepis arctica'' Woodward, 1912). A characteristic feature of this family is the dorsal fin, which inserts at the level of the pelvic fins in the middle portion of the body. Most contemporary ray-fins have their dorsal fin in a more posterior position, often opposite to the anal fin. Also typical for ptycholepids are the somewhat rectangular, horizontally arranged suborbital bones. Fossil record ''Boreosomus'' h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induan
The Induan is the first age of the Early Triassic epoch in the geologic timescale, or the lowest stage of the Lower Triassic series in chronostratigraphy. It spans the time between 251.902 Ma and Ma (million years ago). The Induan is sometimes divided into the Griesbachian and the Dienerian subages or substages. The Induan is preceded by the Changhsingian (latest Permian) and is followed by the Olenekian. The Induan is roughly coeval with the regional Feixianguanian Stage of China. Geology Stratigraphy The Triassic is the first period of the Mesozoic era. It is subdivided into the Lower, Middle, and Upper Triassic series, which are further subdivided into stages. The Induan is the first stage of the Lower Triassic, from 251.9 million to 251.2 million years ago, spanning the first 700,000 years after the Permian–Triassic extinction event. Stages can be defined globally or regionally. For global stratigraphic correlation, the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Triassic span the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Prehistoric Bony Fish
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College Albert A. List College of Jewish Studies, known simply as List College, is the undergraduate school of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America (JTS). It was founded by Solomon Schechter in 1909 as the Teachers Institute with the original goa ..., an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union club Other uses * Angle of list, the leaning to either port or starboard of a ship * List (information), an ordered collection of pieces of information ** List (abstract data type), a method to organize data in computer science * List on Sylt, previously called List, the northernmost village in Germany, on the island of Sylt * ''List'', an alternative term for ''roll'' in flight dynamics * To ''list'' a building, etc., in the UK it means to designate it a listed building that may not be a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Fish
The evolution of fish began about 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion. It was during this time that the early chordates developed the skull and the vertebral column, leading to the first craniates and vertebrates. The first fish lineages belong to the Agnatha, or jawless fish. Early examples include ''Haikouichthys''. During the late Cambrian, eel-like jawless fish called the conodonts, and small mostly armoured fish known as ostracoderms, first appeared. Most jawless fish are now extinct; but the extant lampreys may approximate ancient pre-jawed fish. Lampreys belong to the Cyclostomata, which includes the extant hagfish, and this group may have split early on from other agnathans. The earliest Gnathostomata, jawed vertebrates probably developed during the late Ordovician period. They are first represented in the fossil record from the Silurian by two groups of fish: the armoured fish known as Placodermi, placoderms, which evolved from the ostracoderms; and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
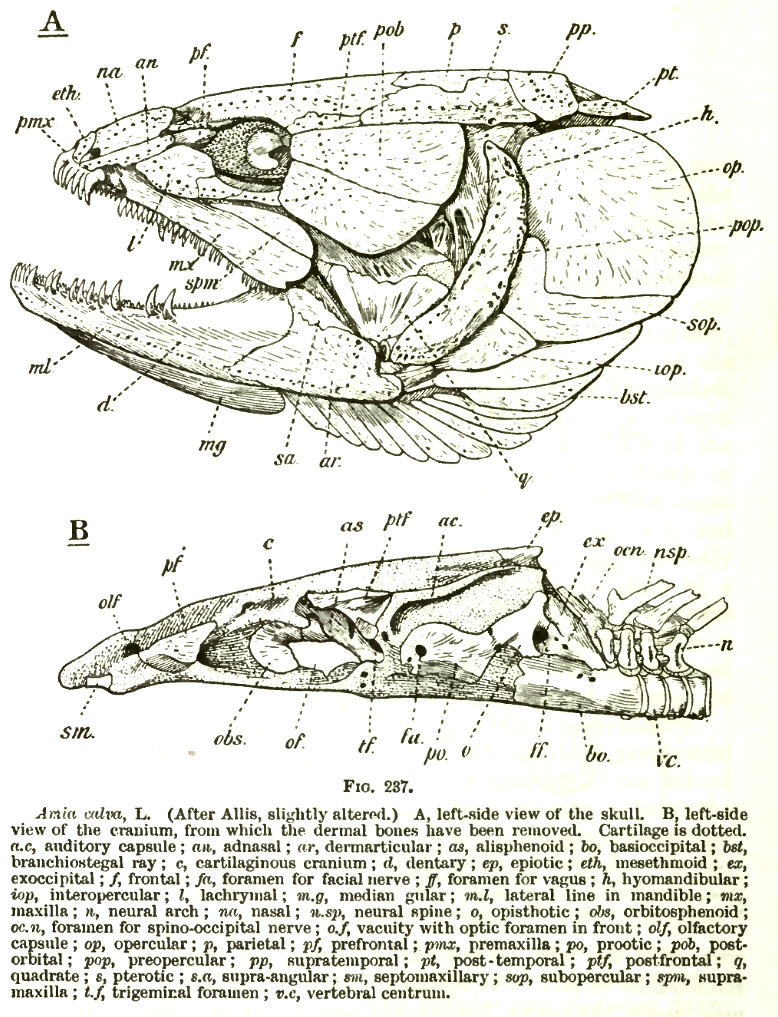
Hyomandibula
The hyomandibula, commonly referred to as hyomandibular one( la, os hyomandibulare, from el, hyoeides, "upsilon-shaped" (υ), and Latin: mandibula, "jawbone") is a set of bones that is found in the hyoid region in most fishes. It usually plays a role in suspending the jaws and/or operculum (teleostomi only). It is commonly suggested that in tetrapods (land animals), the hyomandibula evolved into the columella (stapes). Evolutionary context In jawless fishes a series of gills opened behind the mouth, and these gills became supported by cartilaginous elements. The first set of these elements surrounded the mouth to form the jaw. There are ample evidences For example: (1) both sets of bones are made from neural crest cells (rather than mesodermal tissue like most other bones); (2) both structures form the upper and lower bars that bend forward and are hinged in the middle; and (3) the musculature of the jaw seem homologous to the gill arches of jawless fishes. (Gilbert 2000) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypy
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, '' Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda.' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoch (geology)
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely define gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |