hyomandibula on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
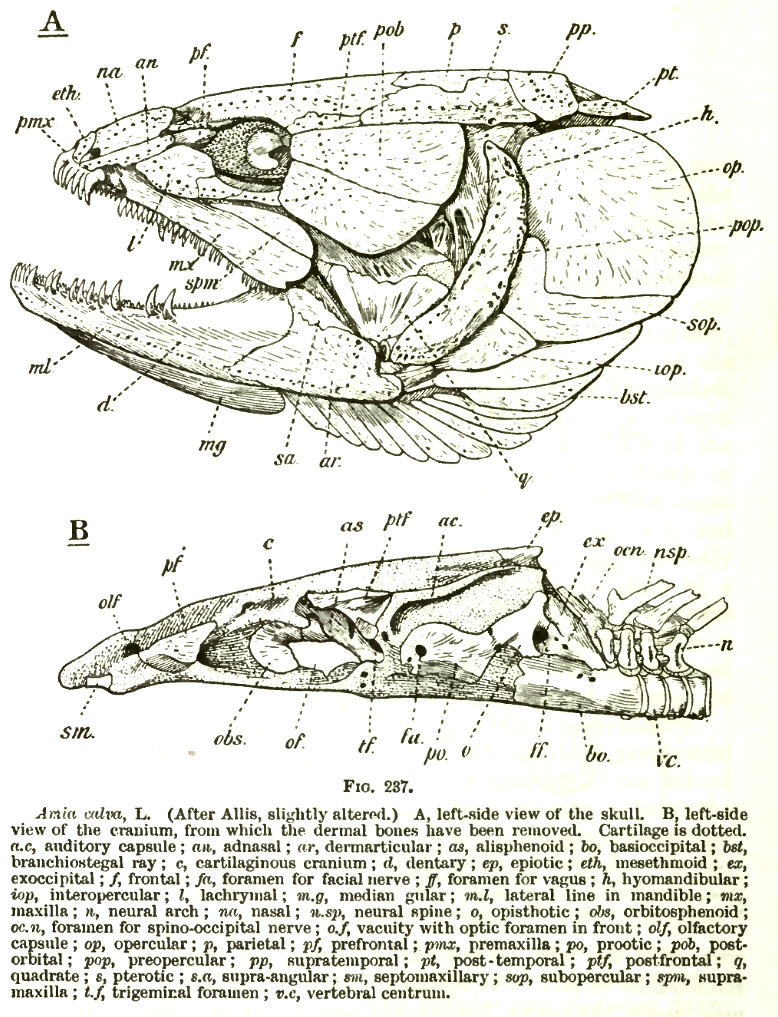 The hyomandibula, commonly referred to as hyomandibular
The hyomandibula, commonly referred to as hyomandibular
 The hyomandibula, commonly referred to as hyomandibular
The hyomandibula, commonly referred to as hyomandibular one
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. I ...
( la, os hyomandibulare, from el, hyoeides, "upsilon-shaped" (υ), and Latin: mandibula
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
, "jawbone") is a set of bones that is found in the hyoid
The hyoid bone (lingual bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. ...
region in most fishes. It usually plays a role in suspending the jaws and/or operculum ( teleostomi only). It is commonly suggested that in tetrapods
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant taxon, extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (p ...
(land animals), the hyomandibula evolved into the columella ( stapes).
Evolutionary context
In jawless fishes a series ofgill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they ar ...
s opened behind the mouth, and these gills became supported by cartilaginous
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck a ...
elements. The first set of these elements surrounded the mouth to form the jaw. There are ample evidences
For example: (1) both sets of bones are made from neural crest cells (rather than mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical Emb ...
al tissue like most other bones); (2) both structures form the upper and lower bars that bend forward and are hinged in the middle; and (3) the musculature of the jaw seem homologous to the gill arches of jawless fishes. (Gilbert 2000)
that vertebrate jaws are homologous
Homology may refer to:
Sciences
Biology
*Homology (biology), any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor
*Sequence homology, biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences
* Homologous chrom ...
to the gill arches of jawless fishes. The upper portion of the second embryonic arch supporting the gill became the hyomandibular bone of jawed fishes, which supports the skull and therefore links the jaw to the cranium.
Gilbert 2000, ''Embryonic homologies''
When vertebrates found their way onto land, the hyomandibula, with its location near the ear, began to function as a sound amplifier beside its function to support the skull. As evolution later attached the cranium of terrestrial vertebrates to the rest of the skull, the hyomandibula lost its supportive function and became an interior organ, the stapes, and thus its secondary function had become its primary function.
See also
*Fish anatomy
Fish anatomy is the study of the form or morphology of fish. It can be contrasted with fish physiology, which is the study of how the component parts of fish function together in the living fish. In practice, fish anatomy and fish physiology ...
* Palatoquadrate
Notes
References
* * * (3rd and 4th paras, ''One of the most celebrated cases...'') * {{diversity of fish Fish anatomy