|
Archelosauria
Archelosauria is a clade grouping turtles and archosaurs (birds and crocodilians) and their fossil relatives, to the exclusion of lepidosaurs (the clade containing lizards, snakes and the tuatara). The majority of phylogenetic analyses based on molecular data (e.g. DNA and proteins) have supported a sister-group relationship between turtles and archosaurs. On the other hand, Archelosauria has not been supported by most morphological analyses, which have instead found turtles to either be descendants of parareptiles, early-diverging diapsids outside of Sauria, or close relatives of lepidosaurs within the clade Ankylopoda. Classification Multiple sequence alignments of DNA and protein sequences and phylogenetic inferences have shown that turtles are the closest living relatives to birds and crocodilians. There are about 1000 ultra-conserved elements in the genome that are unique to turtles and archosaurs, but which are not found in lepidosaurs. Other genome-wide analyses also sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pantestudines
Pantestudines or Pan-Testudines is the group of all reptiles more closely related to turtles than to any other living animal. It includes both modern turtles (crown group turtles, also known as Testudines) and all of their extinct relatives (also known as stem-turtles). Classification The identity of the ancestors and closest relatives of the turtle lineage was a longstanding scientific mystery, though new discoveries and better analyses in the early 21st century began to clarify turtle relationships. Analysis of fossil data has shown that turtles are diapsid reptiles, most closely related either to the archosaurs (crocodiles, bird, and relatives) or the lepidosaurs (lizards, tuatara, and relatives). Genetic analysis strongly favors the hypothesis that turtles are the closest relatives of the archosaurs, though studies using only fossil evidence often continue to recover them as relatives of lepidosaurs. Studies using only fossils, as well as studies using a combination of fossil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauria
Sauria is the clade containing the most recent common ancestor of archosaurs (such as crocodilians, dinosaurs, etc.) and lepidosaurs ( lizards and kin), and all its descendants. Since most molecular phylogenies recover turtles as more closely related to archosaurs than to lepidosaurs as part of Archelosauria, Sauria can be considered the crown group of diapsids, or reptiles in general. Depending on the systematics, Sauria includes all modern reptiles or most of them (including birds, a type of archosaur) as well as various extinct groups. Sauria lies within the larger total group Sauropsida, which also contains various stem-reptiles which are more closely related to reptiles than to mammals. Prior to its modern usage, "Sauria" was used as a name for the suborder occupied by lizards, which before 1800 were considered crocodilians. Systematics Recent genomic studiesCrawford, Nicholas G., et al. "More than 1000 ultraconserved elements provide evidence that turtles are the sister g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauromorpha
Archosauromorpha (Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) rather than lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizards, and snakes). Archosauromorphs first appeared during the late Middle Permian or Late Permian, though they became much more common and diverse during the Triassic period. Although Archosauromorpha was first named in 1946, its membership did not become well-established until the 1980s. Currently Archosauromorpha encompasses four main groups of reptiles: the stocky, herbivorous allokotosaurs and rhynchosaurs, the hugely diverse Archosauriformes, and a polyphyletic grouping of various long-necked reptiles including ''Protorosaurus'', tanystropheids, and ''Prolacerta''. Other groups including pantestudines (turtles and their extinct relatives) and the semiaquatic choristoderes have also been placed in Archosauromorpha by some authors. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
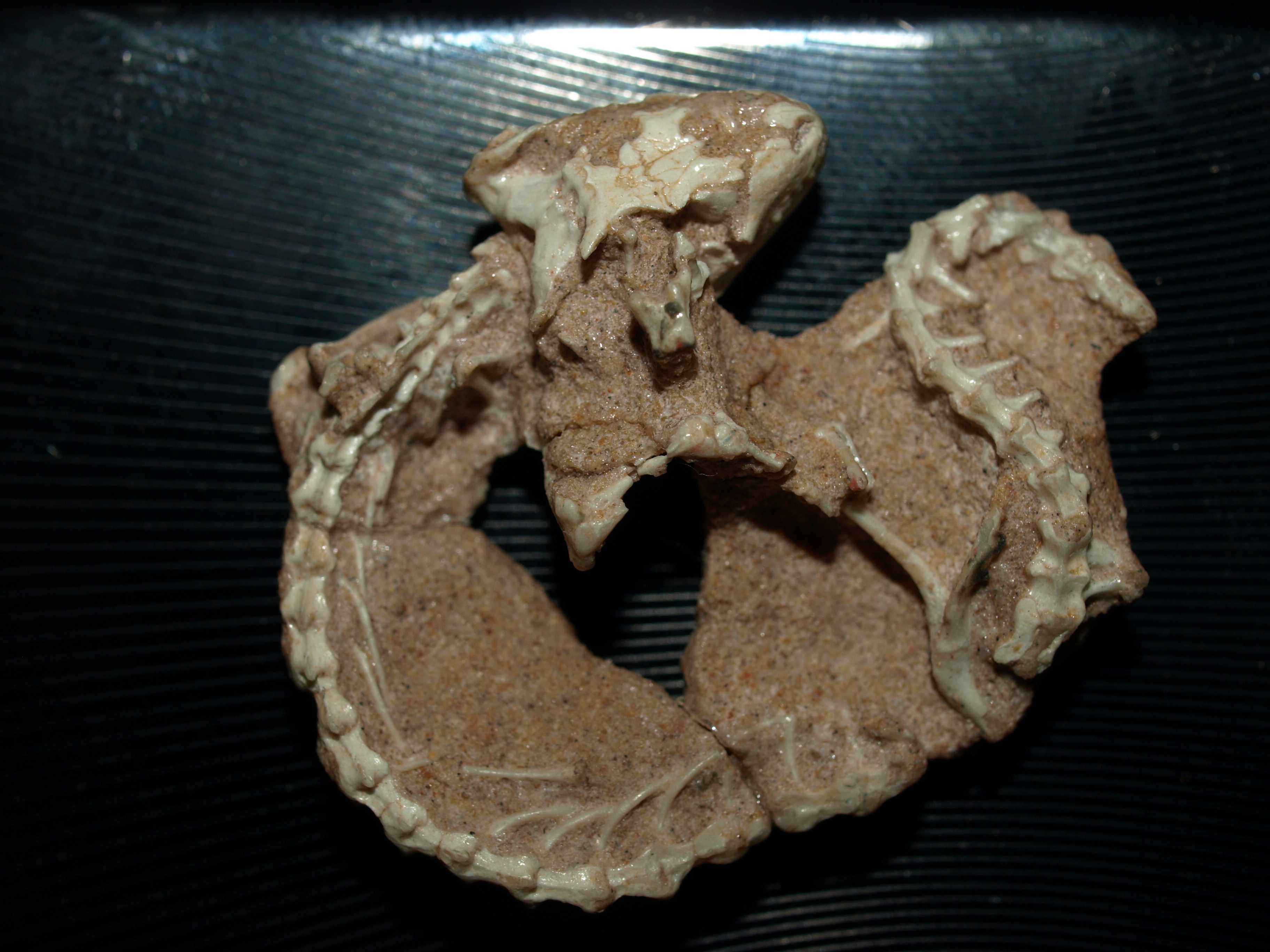
Ankylopoda
Ankylopoda was a proposed clade that hypothetically contains turtles and lepidosaurs (tuatara, lizards and snakes) and their fossil relatives. This clade is supported based on microRNAs as well as the fossil record. However, it was strongly contradicted by molecular evidence which supports Archelosauria. Classification The cladogram below follows the most likely result found by another analysis of turtle relationships, this one using only fossil evidence, published by Rainer Schoch and Hans-Dieter Sues in 2015. This study found ''Eunotosaurus'' to be an actual early stem-turtle, though other versions of the analysis found weak support for it as a parareptile. See also * Archelosauria Archelosauria is a clade grouping turtles and archosaurs (birds and crocodilians) and their fossil relatives, to the exclusion of lepidosaurs (the clade containing lizards, snakes and the tuatara). The majority of phylogenetic analyses based on m ..., an alternative clade that places turtles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parareptile
Parareptilia ("at the side of reptiles") is a subclass or clade of basal sauropsids (reptiles), typically considered the sister taxon to Eureptilia (the group that likely contains all living reptiles and birds). Parareptiles first arose near the end of the Carboniferous period and achieved their highest diversity during the Permian period. Several ecological innovations were first accomplished by parareptiles among reptiles. These include the first reptiles to return to marine ecosystems (mesosaurs), the first bipedal reptiles ( bolosaurids such as ''Eudibamus''), the first reptiles with advanced hearing systems ( nycteroleterids and others), and the first large herbivorous reptiles (the pareiasaurs). The only parareptiles to survive into the Triassic period were the procolophonoids, a group of small generalists, omnivores, and herbivores. The largest family of procolophonoids, the procolophonids, rediversified in the Triassic, but subsequently declined and became extinct by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia although some lizards are more closely related to these two excluded groups than they are to other lizards. Lizards range in size from chameleons and geckos a few centimeters long to the 3-meter-long Komodo dragon. Most lizards are quadrupedal, running with a strong side-to-side motion. Some lineages (known as "legless lizards"), have secondarily lost their legs, and have long snake-like bodies. Some such as the forest-dwelling ''Draco'' lizards are able to glide. They are often territorial, the males fighting off other males and signalling, often with bright colours, to attract mates and to intimidate rivals. Lizards are mainly carnivorous, often being sit-and-wait predators; many smaller species eat insects, while the Komodo eats mammals a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (genus)
''Python'' is a genus of constricting snakes in the Pythonidae Family (biology), family native to the tropics and subtropics of the Eastern Hemisphere. The name ''Python'' was proposed by François Marie Daudin in 1803 for non-venomous flecked snakes. Currently, 10 python species are recognized as Valid name (zoology), valid taxa. Three formerly considered python subspecies have been promoted, and a new species recognized. Taxonomy The Generic name (biology), generic name ''Python'' was proposed by François Marie Daudin in 1803 for non-venomous snakes with a flecked skin and a long split tongue. In 1993, seven python species were recognized as valid taxa. On the basis of phylogenetic analyses, between seven and 13 python species are recognized. Distribution and habitat In Africa, pythons are native to the tropics south of the Sahara, but not in the extreme south-western tip of southern Africa (Western Cape) or in Madagascar. In Asia, they occur from Bangladesh, Nepal, Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anolis
''Anolis'' is a genus of anoles (), iguanian lizards in the family Dactyloidae, native to the Americas. With more than 425 species, it represents the world's most species-rich amniote tetrapod genus, although many of these have been proposed to be moved to other genera, in which case only about 45 ''Anolis'' species remain. Previously, it was classified under the family Polychrotidae that contained all the anoles, as well as ''Polychrus'', but recent studies place it in the Dactyloidae. Taxonomy This very large genus displays considerable paraphyly, but phylogenetic analysis suggests a number of subgroups or clades. Whether these clades are best recognized as subgenera within ''Anolis'' or separate genera remains a matter of dispute. If the clades are recognized as full genera, about 45 species remain in ''Anolis'', with the remaining moved to ''Audantia'' (9 species), ''Chamaelinorops'' (7 species), ''Ctenonotus'' (more than 40 species), ''Dactyloa'' (''circa'' 95 species), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamata
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest order of reptiles, comprising lizards, snakes, and amphisbaenians (worm lizards), which are collectively known as squamates or scaled reptiles. With over 10,900 species, it is also the second-largest order of extant (living) vertebrates, after the perciform fish. Members of the order are distinguished by their skins, which bear horny scales or shields, and must periodically engage in molting. They also possess movable quadrate bones, making possible movement of the upper jaw relative to the neurocranium. This is particularly visible in snakes, which are able to open their mouths very wide to accommodate comparatively large prey. Squamata is the most variably sized order of reptiles, ranging from the dwarf gecko (''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'') to the Reticulated python (''Malayopython reticulatus'') and the now-extinct mosasaurs, which reached lengths over . Among other reptiles, squamates are most close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra-conserved Element
An ultra-conserved element (UCE) was originally defined as a genome segment longer than 200 base pairs (bp) that is absolutely conserved, with no insertions or deletions and 100% identity, between orthologous regions of the human, rat, and mouse genomes. 481 ultra-conserved elements have been identified in the human genome. If ribosomal DNA (rDNA regions) are excluded, these range in size from 200 bp to 781 bp. UCRs are found on all chromosomes except for 21 and Y. A database collecting genomic information about ultra-conserved elements ( UCbase) is available at http://ucbase.unimore.it. Since its creation, this term's usage has broadened to include more evolutionary distant species or shorter segments, for example 100 bp instead of 200 bp. By some definitions, segments need not be syntetic between species. Human UCEs also show high conservation with more evolutionarily distant species, such as chicken and fugu. Out of 481 identified human UCEs, approximately 97% align with high id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidosauria
The Lepidosauria (, from Greek meaning ''scaled lizards'') is a subclass or superorder of reptiles, containing the orders Squamata and Rhynchocephalia. Squamata includes snakes, lizards, and amphisbaenians. Squamata contains over 9,000 species, making it by far the most species-rich and diverse order of reptiles in the present day. Rhynchocephalia was a formerly widespread and diverse group of reptiles in the Mesozoic Era. However, it is represented by only one living species: the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus),'' a superficially lizard-like reptile native to New Zealand. Lepidosauria is a monophyletic group (i.e. a clade), containing all descendants of the last common ancestor of squamates and rhynchocephalians. Lepidosaurs can be distinguished from other reptiles via several traits, such as large keratinous scales which may overlap one another. Purely in the context of modern taxa, Lepidosauria can be considered the sister taxon to Archosauria, which includes Aves (birds) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |