|
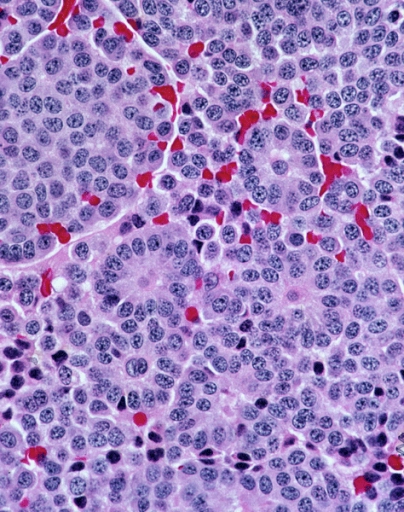
Apudomas
In pathology, an apudoma is an endocrine tumour that arises from an APUD cell from structures such as the ampulla of Vater. They were historically thought to be derived from neural crest cells, but this has since been shown to be untrue (see neuroendocrine tumor).The term dates back to at least 1975. Because the label "apudoma" is very general, it is preferred to use a more specific term when possible. See also * VIPoma * Carcinoid tumor A carcinoid (also carcinoid tumor) is a slow-growing type of neuroendocrine tumor originating in the cells of the neuroendocrine system. In some cases, metastasis may occur. Carcinoid tumors of the midgut ( jejunum, ileum, appendix, and cecum ... References External links Endocrine neoplasia {{oncology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinoid Tumor
A carcinoid (also carcinoid tumor) is a slow-growing type of neuroendocrine tumor originating in the cells of the neuroendocrine system. In some cases, metastasis may occur. Carcinoid tumors of the midgut ( jejunum, ileum, appendix, and cecum) are associated with carcinoid syndrome. Carcinoid tumors are the most common malignant tumor of the appendix, but they are most commonly associated with the small intestine, and they can also be found in the rectum and stomach. They are known to grow in the liver, but this finding is usually a manifestation of metastatic disease from a primary carcinoid occurring elsewhere in the body. They have a very slow growth rate compared to most malignant tumors. The median age at diagnosis for all patients with neuroendocrine tumors is 63 years. Signs and symptoms While most carcinoids are asymptomatic through the natural life and are discovered only upon surgery for unrelated reasons (so-called ''coincidental carcinoids''), all carcinoids are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APUD Cell
350px, Actions of the major digestive hormones secreted by APUD cells APUD cells (DNES cells) constitute a group of apparently unrelated endocrine cells, which were named by the scientist A.G.E. Pearse, who developed the APUD concept in the early 1960s. These cells share the common function of secreting a low molecular weight polypeptide hormone. There are several different types which secrete the hormones secretin, cholecystokinin and several others. The name is derived from an acronym, referring to the following: * Amine Precursor Uptake – for high uptake of amine precursors including 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) and dihydroxyphenylalanine ( DOPA). * Decarboxylase – for high content of the enzyme amino acid decarboxylase (for conversion of precursors to amines). Cells in APUD system # ''Adenohypophysis'' # Neurons of ''Hypothalamus'' # C-cells of ''Thyroid'' # Chief Cells of ''Parathyroid'' # ''Adrenal Medullary'' Cells # Glomus cells in ''Carotid Body'' # Melanocy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"), and the affix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in card ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrine
The endocrine system is a messenger system comprising feedback loops of the hormones released by internal glands of an organism directly into the circulatory system, regulating distant target organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems. In humans, the major endocrine glands are the thyroid gland and the adrenal glands. The study of the endocrine system and its disorders is known as endocrinology. Glands that signal each other in sequence are often referred to as an axis, such as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. In addition to the specialized endocrine organs mentioned above, many other organs that are part of other body systems have secondary endocrine functions, including bone, kidneys, liver, heart and gonads. For example, the kidney secretes the endocrine hormone erythropoietin. Hormones can be amino acid complexes, steroids, eicosanoids, leukotrienes, or prostaglandins. The endocrine system can be c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumour
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampulla Of Vater
The ampulla of Vater, also known as the or the hepatopancreatic duct, is formed by the union of the pancreatic duct and the common bile duct. The ampulla is specifically located at the major duodenal papilla. The ampulla of Vater is an important landmark halfway along the second part of the duodenum that marks the anatomical transition from foregut to midgut, and hence the point where the celiac trunk stops supplying the gut and the superior mesenteric artery takes over. Structure The cystic duct leaves the gallbladder and joins with the common hepatic duct to form the common bile duct. This duct subsequently joins with the pancreatic duct; this junction is known as the ampulla of Vater. The pancreatic duct delivers substances such as bicarbonate and digestive enzymes to the duodenum. The bile from the gallbladder contains salts which emulsify large fat droplets into much smaller units. This provides a large surface area for the lipase enzymes to act on. The bicarbonate n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Crest Cells
Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells unique to vertebrates that arise from the embryonic ectoderm germ layer, and in turn give rise to a diverse cell lineage—including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, peripheral and enteric neurons and glia. After gastrulation, neural crest cells are specified at the border of the neural plate and the non-neural ectoderm. During neurulation, the borders of the neural plate, also known as the neural folds, converge at the dorsal midline to form the neural tube. Subsequently, neural crest cells from the roof plate of the neural tube undergo an epithelial to mesenchymal transition, delaminating from the neuroepithelium and migrating through the periphery where they differentiate into varied cell types. The emergence of neural crest was important in vertebrate evolution because many of its structural derivatives are defining features of the vertebrate clade. Underlying the development of neural crest is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroendocrine Tumor
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine ( hormonal) and nervous systems. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung, and the rest of the body. Although there are many kinds of NETs, they are treated as a group of tissue because the cells of these neoplasms share common features, such as looking similar, having special secretory granules, and often producing biogenic amines and polypeptide hormones. Classification WHO The World Health Organization (WHO) classification scheme places neuroendocrine tumors into three main categories, which emphasize the tumor grade rather than the anatomical origin: * well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumours, further subdivided into tumors with benign and those with uncertain behavior * well-differentiated (low grade) neuroendocrine carcinomas with low-grade malignant behavior * poorly differentiated (high gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VIPoma
A VIPoma or vipoma () is a rare endocrine tumor that overproduces vasoactive intestinal peptide (thus ''VIP'' + ''-oma''). The incidence is about 1 per 10,000,000 per year. VIPomas usually (about 90%) originate from the non-β islet cells of the pancreas. They are sometimes associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. Roughly 50–75% of VIPomas are malignant, but even when they are benign, they are problematic because they tend to cause a specific syndrome: the massive amounts of VIP cause a syndrome of profound and chronic watery diarrhea and resultant dehydration, hypokalemia, achlorhydria, acidosis, flushing and hypotension (from vasodilation), hypercalcemia, and hyperglycemia. This syndrome is called Verner–Morrison syndrome (VMS), WDHA syndrome (from watery diarrhea–hypokalemia–achlorhydria), or pancreatic cholera syndrome (PCS). The eponym reflects the physicians who first described the syndrome. Symptoms and signs The major clinical features are prolong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)
