|
Appendiceal Cancer
Appendix cancer are very rare cancers of the vermiform appendix. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors are rare tumors with malignant potential. Primary lymphomas can occur in the appendix. Breast cancer, colon cancer, and tumors of the female genital tract may metastasize to the appendix. Diagnosis Carcinoid tumors are the most common tumors of the appendix. Other common forms are mucinous adenocarcinomas, adenocarcinoma not otherwise specified (NOS), and signet ring cell adenocarcinoma listed from highest to lowest incidence. Carcinoid A carcinoid is a neuroendocrine tumor (NET) of the intestines. Incidence rates among carcinoids occur at about .15 per 100,000 per year. This subgroup makes up a large amount of neoplasias both malignant and benign. Almost 3 out of 4 of these tumors are associated with the region at the end of the appendix, and tend to be diagnosed in the 4th to 5th decades in life. Both women and Caucasian individuals show a minor prevalence regarding Neuroendocrine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinoid
A carcinoid (also carcinoid tumor) is a slow-growing type of neuroendocrine tumor originating in the cells of the neuroendocrine system. In some cases, metastasis may occur. Carcinoid tumors of the midgut (jejunum, ileum, appendix, and cecum) are associated with carcinoid syndrome. Carcinoid tumors are the most common malignant tumor of the appendix, but they are most commonly associated with the small intestine, and they can also be found in the rectum and stomach. They are known to grow in the liver, but this finding is usually a manifestation of metastatic disease from a primary carcinoid occurring elsewhere in the body. They have a very slow growth rate compared to most malignant tumors. The median age at diagnosis for all patients with neuroendocrine tumors is 63 years. Signs and symptoms While most carcinoids are asymptomatic through the natural life and are discovered only upon surgery for unrelated reasons (so-called ''coincidental carcinoids''), all carcinoids are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colectomy
Colectomy ('' col-'' + '' -ectomy'') is bowel resection of the large bowel ( colon). It consists of the surgical removal of any extent of the colon, usually segmental resection (partial colectomy). In extreme cases where the entire large intestine is removed, it is called total colectomy, and proctocolectomy ('' procto-'' + ''colectomy'') denotes that the rectum is included. Indications Some of the most common indications for colectomy are: * Colon cancer * Diverticulitis and diverticular disease of the large intestine * Trauma * Inflammatory bowel disease such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease. Colectomy neither cures nor eliminates Crohn's disease, instead only removing part of the entire diseased large intestine. A colectomy is considered a "cure" for ulcerative colitis because the disease attacks only the large intestine and therefore will not be able to flare up again if the entire large intestine (cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon and si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
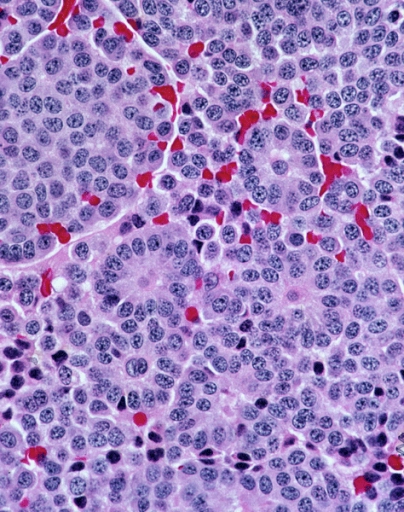
Histopathology Of Low-grade Appendiceal Mucinous Neoplasm
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία ''-logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks"). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroendocrine Tumor
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung, and the rest of the body. Although there are many kinds of NETs, they are treated as a group of tissue because the cells of these neoplasms share common features, such as looking similar, having special secretory granules, and often producing biogenic amines and polypeptide hormones. Classification WHO The World Health Organization (WHO) classification scheme places neuroendocrine tumors into three main categories, which emphasize the tumor grade rather than the anatomical origin: * well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumours, further subdivided into tumors with benign and those with uncertain behavior * well-differentiated (low grade) neuroendocrine carcinomas with low-grade malignant behavior * poorly differentiated (high grade) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |