|
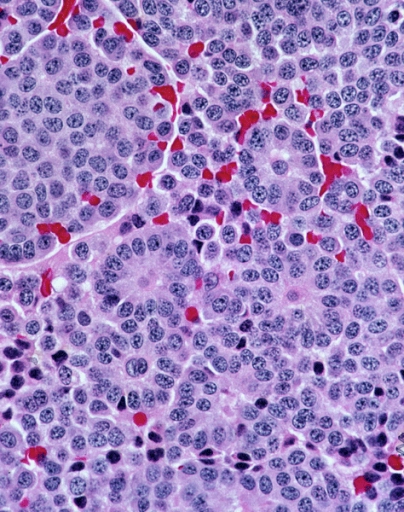
Carcinoid
A carcinoid (also carcinoid tumor) is a slow-growing type of neuroendocrine tumor originating in the cells of the neuroendocrine system. In some cases, metastasis may occur. Carcinoid tumors of the midgut ( jejunum, ileum, appendix, and cecum) are associated with carcinoid syndrome. Carcinoid tumors are the most common malignant tumor of the appendix, but they are most commonly associated with the small intestine, and they can also be found in the rectum and stomach. They are known to grow in the liver, but this finding is usually a manifestation of metastatic disease from a primary carcinoid occurring elsewhere in the body. They have a very slow growth rate compared to most malignant tumors. The median age at diagnosis for all patients with neuroendocrine tumors is 63 years. Signs and symptoms While most carcinoids are asymptomatic through the natural life and are discovered only upon surgery for unrelated reasons (so-called ''coincidental carcinoids''), all carcinoids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroendocrine Tumor
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine ( hormonal) and nervous systems. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung, and the rest of the body. Although there are many kinds of NETs, they are treated as a group of tissue because the cells of these neoplasms share common features, such as looking similar, having special secretory granules, and often producing biogenic amines and polypeptide hormones. Classification WHO The World Health Organization (WHO) classification scheme places neuroendocrine tumors into three main categories, which emphasize the tumor grade rather than the anatomical origin: * well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumours, further subdivided into tumors with benign and those with uncertain behavior * well-differentiated (low grade) neuroendocrine carcinomas with low-grade malignant behavior * poorly differentiated (high gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinoid Cancer
A carcinoid (also carcinoid tumor) is a slow-growing type of neuroendocrine tumor originating in the cells of the neuroendocrine system. In some cases, metastasis may occur. Carcinoid tumors of the midgut (jejunum, ileum, appendix, and cecum) are associated with carcinoid syndrome. Carcinoid tumors are the most common malignant tumor of the appendix, but they are most commonly associated with the small intestine, and they can also be found in the rectum and stomach. They are known to grow in the liver, but this finding is usually a manifestation of metastatic disease from a primary carcinoid occurring elsewhere in the body. They have a very slow growth rate compared to most malignant tumors. The median age at diagnosis for all patients with neuroendocrine tumors is 63 years. Signs and symptoms While most carcinoids are asymptomatic through the natural life and are discovered only upon surgery for unrelated reasons (so-called ''coincidental carcinoids''), all carcinoids are con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinoid Syndrome
Carcinoid syndrome is a paraneoplastic syndrome comprising the signs and symptoms that occur secondary to carcinoid tumors. The syndrome includes flushing and diarrhea, and less frequently, heart failure, vomiting and bronchoconstriction. It is caused by endogenous secretion of mainly serotonin and kallikrein. Signs and symptoms The carcinoid syndrome occurs in approximately 5% of carcinoid tumors and becomes manifest when vasoactive substances from the tumors enter the systemic circulation escaping hepatic degradation. If the primary tumor is from the gastrointestinal tract (hence releasing serotonin into the hepatic portal circulation), carcinoid syndrome generally does not occur until the disease is so advanced that it overwhelms the liver's ability to metabolize the released serotonin. * Flushing: The most important clinical finding is flushing of the skin, usually of the head and the upper part of thorax. * Diarrhea: It may be associated with abdominal cramping. This sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cecum
The cecum or caecum is a pouch within the peritoneum that is considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. It is typically located on the right side of the body (the same side of the body as the appendix, to which it is joined). The word cecum (, plural ceca ) stems from the Latin '' caecus'' meaning blind. It receives chyme from the ileum, and connects to the ascending colon of the large intestine. It is separated from the ileum by the ileocecal valve (ICV) or Bauhin's valve. It is also separated from the colon by the cecocolic junction. While the cecum is usually intraperitoneal, the ascending colon is retroperitoneal. In herbivores, the cecum stores food material where bacteria are able to break down the cellulose. In humans, the cecum is involved in absorption of salts and electrolytes and lubricates the solid waste that passes into the large intestine. Structure Development The cecum and appendix are formed by the enlargement of the postarterial segment of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niacin Deficiency
Pellagra is a disease caused by a lack of the vitamin niacin (vitamin B3). Symptoms include inflamed skin, diarrhea, dementia, and sores in the mouth. Areas of the skin exposed to either sunlight or friction are typically affected first. Over time affected skin may become darker, stiffen, peel, or bleed. There are two main types of pellagra, primary and secondary. Primary pellagra is due to a diet that does not contain enough niacin and tryptophan. Secondary pellagra is due to a poor ability to use the niacin within the diet. This can occur as a result of alcoholism, long-term diarrhea, carcinoid syndrome, Hartnup disease, and a number of medications such as isoniazid. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and may be assisted by urine testing. Treatment is with either niacin or nicotinamide supplementation. Improvements typically begin within a couple of days. General improvements in diet are also frequently recommended. Decreasing sun exposure via sunscreen and proper clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pellagra
Pellagra is a disease caused by a lack of the vitamin niacin (vitamin B3). Symptoms include inflamed skin, diarrhea, dementia, and sores in the mouth. Areas of the skin exposed to either sunlight or friction are typically affected first. Over time affected skin may become darker, stiffen, peel, or bleed. There are two main types of pellagra, primary and secondary. Primary pellagra is due to a diet that does not contain enough niacin and tryptophan. Secondary pellagra is due to a poor ability to use the niacin within the diet. This can occur as a result of alcoholism, long-term diarrhea, carcinoid syndrome, Hartnup disease, and a number of medications such as isoniazid. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and may be assisted by urine testing. Treatment is with either niacin or nicotinamide supplementation. Improvements typically begin within a couple of days. General improvements in diet are also frequently recommended. Decreasing sun exposure via sunscreen and pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vermiform Appendix
The appendix (or vermiform appendix; also cecal r caecalappendix; vermix; or vermiform process) is a finger-like, blind-ended tube connected to the cecum, from which it develops in the embryo. The cecum is a pouch-like structure of the large intestine, located at the junction of the small and the large intestines. The term " vermiform" comes from Latin and means "worm-shaped". The appendix was once considered a vestigial organ, but this view has changed since the early 2000s. Research suggests that the appendix may serve an important purpose. In particular, it may serve as a reservoir for beneficial gut bacteria. Structure The human appendix averages in length but can range from . The diameter of the appendix is , and more than is considered a thickened or inflamed appendix. The longest appendix ever removed was long. The appendix is usually located in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen, near the right hip bone. The base of the appendix is located beneath the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flushing (physiology)
Flushing is to become markedly red in the face and often other areas of the skin, from various physiological conditions. Flushing is generally distinguished, despite a close physiological relation between them, from blushing, which is milder, generally restricted to the face, cheeks or ears, and generally assumed to reflect emotional stress, such as embarrassment, anger, or romantic stimulation. Flushing is also a cardinal symptom of carcinoid syndrome—the syndrome that results from hormones (often serotonin or histamine) being secreted into systemic circulation. Causes * abrupt cessation of physical exertion (resulting in heart output in excess of current muscular need for blood flow) * abdominal cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome (ACNES), usually in patients who have had abdominal surgery * alcohol flush reaction * antiestrogens such as tamoxifen * atropine poisoning * body contact with warm or hot water (hot tub, bath, shower) * butorphanol reaction with some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niacin (nutrient)
Vitamin B3, colloquially referred to as niacin, is a vitamin family that includes three forms or vitamers: niacin (nicotinic acid), nicotinamide (niacinamide), and nicotinamide riboside. All three forms of vitamin B3 are converted within the body to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD). NAD is required for human life and people are unable to make it within their bodies without either vitamin B3 or tryptophan. Nicotinamide riboside was identified as a form of vitamin B3 in 2004. Niacin (the nutrient) can be manufactured by plants and animals from the amino acid tryptophan. Niacin is obtained in the diet from a variety of whole and processed foods, with highest contents in fortified packaged foods, meat, poultry, red fish such as tuna and salmon, lesser amounts in nuts, legumes and seeds. Niacin as a dietary supplement is used to treat pellagra, a disease caused by niacin deficiency. Signs and symptoms of pellagra include skin and mouth lesions, anemia, headaches, and ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinoma
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesodermal or ectodermal germ layer during embryogenesis. Carcinomas occur when the DNA of a cell is damaged or altered and the cell begins to grow uncontrollably and become malignant. It is from the el, καρκίνωμα, translit=karkinoma, lit=sore, ulcer, cancer (itself derived from meaning ''crab''). Classification As of 2004, no simple and comprehensive classification system has been devised and accepted within the scientific community. Traditionally, however, malignancies have generally been classified into various types using a combination of criteria, including: The cell type from which they start; specifically: * Epithelial cells ⇨ carcinoma * Non-hematopoietic mesenchymal cells ⇨ sarcoma * Hematopoietic cells **Bone marrow- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterochromaffin Cell
Enterochromaffin (EC) cells (also known as Kulchitsky cells) are a type of enteroendocrine cell, and neuroendocrine cell. They reside alongside the epithelium lining the lumen of the digestive tract and play a crucial role in gastrointestinal regulation, particularly intestinal motility and secretion. They were discovered by Nikolai Kulchitsky. EC cells modulate neuron signalling in the enteric nervous system (ENS) via the secretion of the neurotransmitter serotonin and other peptides. As enteric afferent and efferent nerves do not protrude into the intestinal lumen, EC cells act as a form of sensory transduction. Serotonin in the ENS acts in synergy with other digestive hormones to regulate sensory and motor gastrointestinal reflexes. EC cells respond to both chemical and neurological stimuli. They are also reactive to mechanosensation, which is the case in the peristaltic reflex of the gut, and can be stimulated by a bolus moving through the bowel. Upon activation, EC cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine may be used instead of ileum. Its main function is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the jejunum. The ileum follows the duodenum and jejunum and is separated from the cecum by the ileocecal valve (ICV). In humans, the ileum is about 2–4 m long, and the pH is usually between 7 and 8 (neutral or slightly basic). ''Ileum ''is derived from the Greek word ''eilein'', meaning "to twist up tightly". Structure The ileum is the third and final part of the small intestine. It follows the jejunum and ends at the ileocecal junction, where the terminal ileum communicates with the cecum of the large intestine through the ileocecal valve. The ileum, along with the jejunum, is sus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |