|
Aplysioviolin
Aplysioviolin is a purple-colored molecule secreted by sea hares of the genera ''Aplysia'' and '' Dolabella'' to deter predators. Aplysioviolin is a chemodeterrent, serving to dispel predators on olfactory and gustatory levels as well as by temporarily blinding predators with the molecule's dark color. Aplysioviolin is an important component of secreted ink and is strongly implicated in the sea hares' predatory escape mechanism. While the ink mixture as a whole may produce dangerous hydrogen peroxide and is relatively acidic, the aplysioviolin component alone has not been shown to produce human toxicity. Biosynthetic origin Aplysioviolin is a metabolic product of ''Aplysia californica'' species of sea hare, and is a major component to its ink mixture. Sea hares first consume red algae as nutriment, and extract from it the light-harvesting pigment phycoerythrin, cleaving it to separate the red-colored chromophore phycoerythrobilin from its covalently-bound protein structure. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aplysia
''Aplysia'' () is a genus of medium-sized to extremely large sea slugs, specifically sea hares, which are one clade of large sea slugs, marine gastropod mollusks. These benthic herbivorous creatures can become rather large compared with most other mollusks. They graze in tidal and subtidal zones of tropical waters, mostly in the Indo-Pacific Ocean (23 species); but they can also be found in the Atlantic Ocean (12 species), with a few species occurring in the Mediterranean. ''Aplysia'' species, when threatened, frequently release clouds of ink, it is believed in order to blind the attacker (though they are in fact considered edible by relatively few species). Following the lead of Eric R. Kandel, the genus has been studied as a model organism by neurobiologists, because its gill and siphon withdrawal reflex, as studied in ''Aplysia californica'', is mediated by electrical synapses, which allow several neurons to fire synchronously. This quick neural response is necessary f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tekhelet
''Tekhelet'' ( he, תְּכֵלֶת ''təḵēleṯ''; alternate spellings include ''tekheleth'', ''t'chelet'', ''techelet'' and ''techeiles'') is a "blue-violet", "blue", or "turquoise" dye highly prized by ancient Mediterranean civilizations. In the Hebrew Bible and Jewish tradition, it was used in the clothing of the High Priest, the tapestries in the Tabernacle, and the ''tzitzit'' (fringes) affixed to the corners of one's four-cornered garments, including the ''tallit''. Tekhelet is most notably mentioned in the third paragraph of the Shema, quoting . Neither the source nor method of production of ''tekhelet'' is specified in the Bible. According to later rabbinic sources, it was produced exclusively from a marine creature known as the ''Ḥillazon''.Talmudbr>Menachot 44a Tosefta Menachotbr>9:6/ref> Knowledge of how to produce ''tekhelet'' was lost in medieval times, and since then ''tzitzit'' did not include ''tekhelet''. However, in modern times, many Jews believe that exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aplysia Californica
The California sea hare (''Aplysia californica'') is a species of sea slug in the sea hare family, Aplysiidae.Rosenberg, G.; Bouchet, P. (2011). Aplysia californica J. G. Cooper, 1863. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=240765 on 2012-03-31 It is found in the Pacific Ocean, off the coast of California in the United States and northwestern Mexico. Distribution ''A. californica'' is found along the coast of California, United States, and northwestern Mexico (including the Gulf of California). ''Aplysia'' species inhabit the photic zone to graze on algae, mainly the intertidal, usually not deeper than . Description The maximum length recorded for the California sea hare is when crawling, thus fully extended, although most adult specimens are half this size or smaller. Adult animals can weigh up to . A closely related species, ''Aplysia vaccaria'', the black sea hare, can grow to be larger still. A Californi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Catfish
The Ariidae or ariid catfish are a family of catfish that mainly live in marine waters with many freshwater and brackish water species. They are found worldwide in tropical to warm temperate zones. The family includes about 143 species. Taxonomy The relationships of this family are not yet clear. Two of the genera, '' Gogo'' and '' Ancharius'', have been moved to a separate family called Anchariidae. The Ariidae are divided into three subfamilies: ''Galeichthys'' is the only genus classified in the subfamily Galeichthyinae and similarly '' Bagre'' is the only genus in the subfamily Bagreinae, while the rest of the genera are classified in the subfamily Ariinae. Previously, the family Ariidae has been grouped in the superfamily Doradoidea, but then it was moved into Bagroidea (along with Austroglanididae, Claroteidae, Schilbeidae, Pangasiidae, Bagridae, Malapteruridae, and Pimelodidae. It has also been classified in a superfamily Arioidea containing Ariidae and Anchariidae. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirality
Chirality is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object. An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is distinguishable from its mirror image; that is, it cannot be superimposed onto it. Conversely, a mirror image of an ''achiral'' object, such as a sphere, cannot be distinguished from the object. A chiral object and its mirror image are called ''enantiomorphs'' (Greek, "opposite forms") or, when referring to molecules, '' enantiomers''. A non-chiral object is called ''achiral'' (sometimes also ''amphichiral'') and can be superposed on its mirror image. The term was first used by Lord Kelvin in 1893 in the second Robert Boyle Lecture at the Oxford University Junior Scientific Club which was published in 1894: Human hands are perhaps the most recognized example of chirality. The left hand is a non-superimposable mirror image of the right hand; no matter ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Microscope
The optical microscope, also referred to as a light microscope, is a type of microscope that commonly uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images of small objects. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of microscope and were possibly invented in their present compound form in the 17th century. Basic optical microscopes can be very simple, although many complex designs aim to improve resolution and sample contrast. The object is placed on a stage and may be directly viewed through one or two eyepieces on the microscope. In high-power microscopes, both eyepieces typically show the same image, but with a stereo microscope, slightly different images are used to create a 3-D effect. A camera is typically used to capture the image (micrograph). The sample can be lit in a variety of ways. Transparent objects can be lit from below and solid objects can be lit with light coming through ( bright field) or around (dark field) the objective lens. Polarised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrian Purple
Tyrian purple ( grc, πορφύρα ''porphúra''; la, purpura), also known as Phoenician red, Phoenician purple, royal purple, imperial purple, or imperial dye, is a reddish-purple natural dye. The name Tyrian refers to Tyre, Lebanon. It is secreted by several species of predatory sea snails in the family Muricidae, rock snails originally known by the name 'Murex'. In ancient times, extracting this dye involved tens of thousands of snails and substantial labor, and as a result, the dye was highly valued. The colored compound is 6,6′-dibromoindigo. History Biological pigments were often difficult to acquire, and the details of their production were kept secret by the manufacturers. Tyrian purple is a pigment made from the mucus of several species of Murex snail. Production of Tyrian purple for use as a fabric dye began as early as 1200 BCE by the Phoenicians, and was continued by the Greeks and Romans until 1453 CE, with the fall of Constantinople. The pigment was expensiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: Domestic purposes onsumer textilesand technical textiles. In consumer textiles, aesthetics and comfort are the most important factors, but in technical textiles, functional properties are the priority. Geotextiles, industrial textiles, medical textiles, and many other areas are examples of technical textiles, whereas clothing and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyeing
Dyeing is the application of dyes or pigments on textile materials such as fibers, yarns, and fabrics with the goal of achieving color with desired color fastness. Dyeing is normally done in a special solution containing dyes and particular chemical material. Dye molecules are fixed to the fiber by absorption, diffusion, or bonding with temperature and time being key controlling factors. The bond between dye molecule and fiber may be strong or weak, depending on the dye used. Dyeing and printing are different applications; in printing, color is applied to a localized area with desired patterns. In dyeing, it is applied to the entire textile. The primary source of dye, historically, has been nature, with the dyes being extracted from animals or plants. Since the mid-19th century, however, humans have produced artificial dyes to achieve a broader range of colors and to render the dyes more stable to washing and general use. Different classes of dyes are used for different types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APV Rudiger
APV may refer to: * Actuarial present value, a probability weighted present value often used in insurance * Adjusted present value, a variation of the net present value (NPV) * Advanced Power Virtualization (renamed PowerVM), a software virtualization technique used by IBM *Alavuden Peli-Veikot, a multi-sport club in Alavus, Finland * Allen Parkway Village, a housing development in Fourth Ward, Houston * Apple Valley Airport (California), from its IATA airport code * Approach Procedure with Vertical guidance, a type of Instrument approach in aviation * APV (NMDAR antagonist), or AP5, a selective NMDA receptor antagonist * APV plc, a former company making process equipment * Asia Pacific Vision, a television content provider *Chevrolet Lumina APV, a minivan manufactured and marketed by General Motors * Suzuki APV, a microvan manufactured and marketed by Suzuki * Amazon Prime Video Amazon Prime Video, also known simply as Prime Video, is an American Video on demand#Subscription ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycocyanobilin
Phycocyanobilin is a blue phycobilin, i.e., a tetrapyrrole chromophore found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of red algae, glaucophytes, and some cryptomonads. Phycocyanobilin is present only in the phycobiliproteins allophycocyanin and phycocyanin, of which it is the terminal acceptor of energy. It is covalently linked to these phycobiliproteins by a thioether In organic chemistry, an organic sulfide (British English sulphide) or thioether is an organosulfur functional group with the connectivity as shown on right. Like many other sulfur-containing compounds, volatile sulfides have foul odors. A su ... bond. Phycocyanobilin, PCB, has the ability to bind to human serum albumin, HSA, protein found mainly in the blood of humans. This PCB-HCA complex benefits the structure of HSA, increasing the thermal stability of HSA, as well as increasing its ability to prevent against proteolytic activity of other proteins. References Further reading * Photosynt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
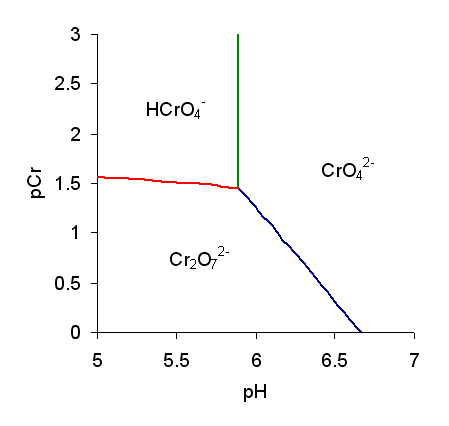
Chromic Acid
The term chromic acid is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixture for glass. Chromic acid may also refer to the molecular species, H2CrO4 of which the trioxide is the anhydride. Chromic acid features chromium in an oxidation state of +6 (or VI). It is a strong and corrosive oxidising agent. Molecular chromic acid Molecular chromic acid, H2CrO4, has much in common with sulfuric acid, H2SO4. Only sulfuric acid can be classified as part of the 7 strong acids list. Due to the laws pertinent to the concept of "first order ionization energy", the first proton is lost most easily. It behaves extremely similar to sulfuric acid deprotonation. Since the process of polyvalent acid-base titrations have more than one proton (especially when the acid is starting substance and the base is the titrant), proton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)