|
Apical Ectodermal Cap (AEC)
Apical means "pertaining to an apex". It may refer to: *Apical ancestor, refers to the last common ancestor of an entire group, such as a species (biology) or a clan (anthropology) *Apical (anatomy), an anatomical term of location for features located opposite the base of an organism or structure *Apical (chemistry), a position in certain molecular geometries in chemistry *Apical (dentistry), direction towards the root tip of a tooth *Apical consonant, a consonant produced with the tip of the tongue *Apical dendrite, a type of dendrite found on pyramidal neurons *Apical dominance, the phenomenon whereby the main, central stem of a plant is dominant over other side stems *Apical membrane, in cell biology the surface of a plasma membrane that faces inward to the lumen *Apical meristem, or apex, on a flower See also *Apex (other) The apex is the highest point of something. The word may also refer to: Arts and media Fictional entities * Apex (comics), a teenaged super villa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apex (other)
The apex is the highest point of something. The word may also refer to: Arts and media Fictional entities * Apex (comics), a teenaged super villainess in the Marvel Universe * Ape-X, a super-intelligent ape in the Squadron Supreme universe *Apex, a genetically engineered human population in the TV series ''The Crossing'' * APEX Medical Hospital, a fictional hospital in the Filipino TV series '' Abot-Kamay na Pangarap'' Music * ''Apex'' (album), by Canadian heavy metal band Unleash the Archers * Apex (band), a Polish heavy metal band * Apex (musician) (1981–2017), British drum and bass music producer and DJ * The Apex Theory, the former name of the alternative rock band Mt. Helium * Lord Apex, a rapper from West London, UK Video games * Apex (tournament), a fighting game tournament focusing on ''Super Smash Bros.'' * '' Racing Evoluzione'', also known as ''Apex'', a 2003 video game for the Xbox * Overwatch Apex, a South Korean ''Overwatch'' tournament series * ''Apex Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Ancestor
Common descent is a concept in evolutionary biology applicable when one species is the ancestor of two or more species later in time. According to modern evolutionary biology, all living beings could be descendants of a unique ancestor commonly referred to as the last universal common ancestor (LUCA) of all life on Earth. Common descent is an effect of speciation, in which multiple species derive from a single ancestral population. The more recent the ancestral population two species have in common, the more closely they are related. The most recent common ancestor of all currently living organisms is the last universal ancestor, which lived about 3.9 billion years ago. The two earliest pieces of evidence for life on Earth are graphite found to be biogenic in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in western Greenland and microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. All currently living organisms on Earth share ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical (anatomy)
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Terminolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
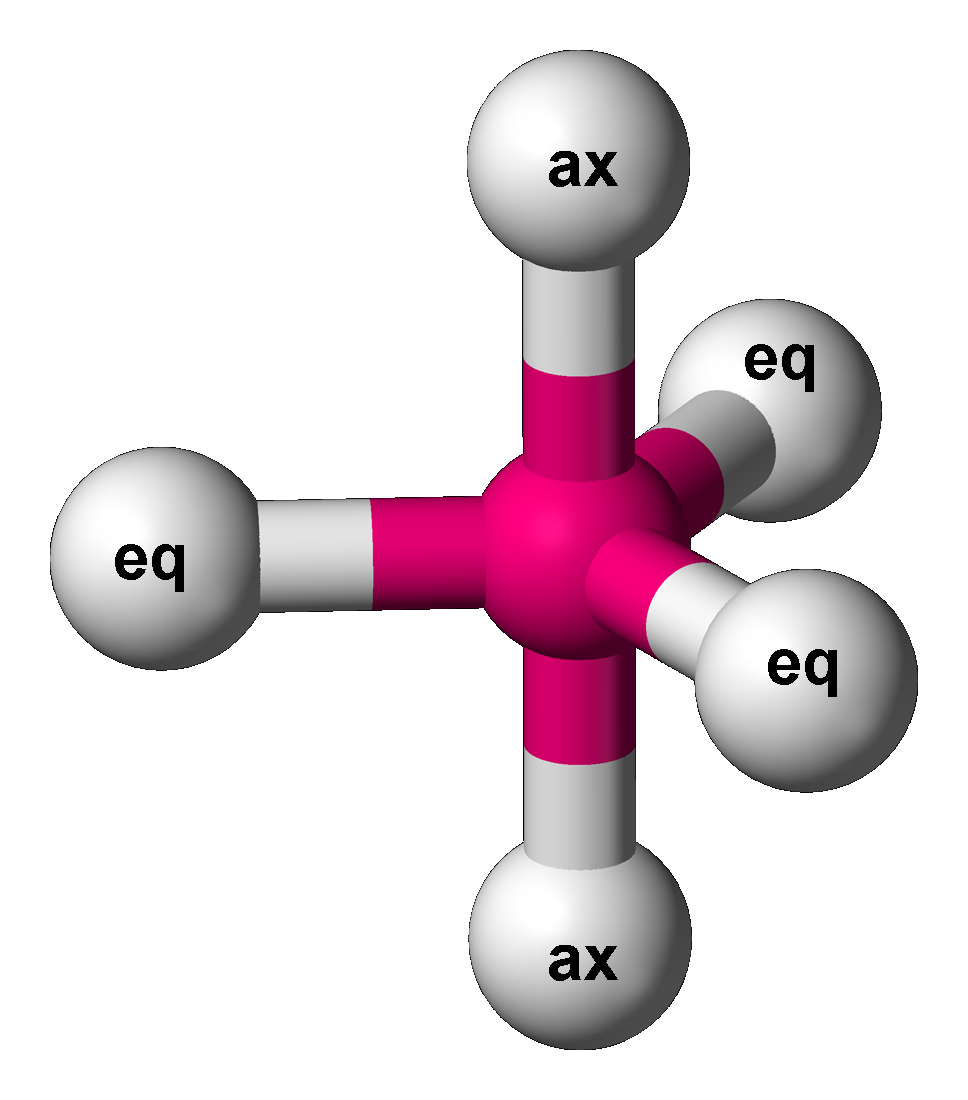
Apical (chemistry)
In chemistry, a trigonal bipyramid formation is a molecular geometry with one atom at the center and 5 more atoms at the corners of a triangular bipyramid. This is one geometry for which the bond angles surrounding the central atom are not identical (see also pentagonal bipyramidal molecular geometry, pentagonal bipyramid), because there is no geometrical arrangement with five terminal atoms in equivalent positions. Examples of this molecular geometry are phosphorus pentafluoride (), and phosphorus pentachloride () in the gas phase. Axial (or apical) and equatorial positions The five atoms bonded to the central atom are not all equivalent, and two different types of position are defined. For phosphorus pentachloride as an example, the phosphorus atom shares a plane with three chlorine atoms at 120° angles to each other in ''equatorial'' positions, and two more chlorine atoms above and below the plane (''axial'' or ''apical'' positions). According to the VSEPR theory of molecula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical (dentistry)
This is a list of definitions of commonly used terms of location and direction in dentistry. This set of terms provides orientation within the oral cavity, much as anatomical terms of location provide orientation throughout the body. Terms Combining of terms Most of the principal terms can be combined using their corresponding classical compound, combining forms (such as ''mesio-'' for ''mesial'' and ''disto-'' for ''distal''). They provide names for directions (vectors) and axes; for example, the coronoapical axis is the long axis of a tooth. Such combining yields terms such as those in the following list. The abbreviations should be used only in restricted contexts, where they are explicitly defined and help avoid extensive repetition (for example, a journal article that uses the term "mesiodistal" dozens of times might use the abbreviation "MD"). The abbreviations are ambiguous: ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Consonant
An apical consonant is a phone (speech sound) produced by obstructing the air passage with the tip of the tongue (apex) in conjunction with upper articulators from lips to postalveolar, and possibly prepalatal. It contrasts with laminal consonants, which are produced by creating an obstruction with the blade of the tongue, just behind the tip. Sometimes ''apical'' is used exclusively for an articulation that involves only the tip of the tongue and ''apicolaminal'' for an articulation that involves both the tip and the blade of the tongue. However, the distinction is not always made and the latter one may be called simply ''apical'', especially when describing an apical dental articulation. As there is some laminal contact in the alveolar region, the apicolaminal dental consonants are also labelled as '' denti-alveolar''. It is not a very common distinction and is typically applied only to fricatives and affricates. Thus, many varieties of English have either apical or lamin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Dendrite
An apical dendrite is a dendrite that emerges from the apex of a pyramidal cell. Apical dendrites are one of two primary categories of dendrites, and they distinguish the pyramidal cells from spiny stellate cells in the cortices. Pyramidal cells are found in the prefrontal cortex, the hippocampus, the entorhinal cortex, the olfactory cortex, and other areas. Dendrite arbors formed by apical dendrites are the means by which synaptic inputs into a cell are integrated.Cline HT. Dendritic arbor development and synaptogenesis. ''Current Opinion in Neurobiology'' 2001; 11: 118–126 The apical dendrites in these regions contribute significantly to memory, learning, and sensory associations by modulating the excitatory and inhibitory signals received by the pyramidal cells. Background Two types of dendrites present on pyramidal cells are apical and basal dendrites. Apical dendrites are the most distal along the ascending trunk, and reside in layer 1. These distal apical dendrites re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Dominance
In botany, apical dominance is the phenomenon whereby the main, central stem of the plant is dominant over (i.e., grows more strongly than) other side stems; on a branch the main stem of the branch is further dominant over its own side twigs. Plant physiology describes apical dominance as the control exerted by the terminal bud (and shoot apex) over the outgrowth of lateral buds. Overview Apical dominance occurs when the shoot apex inhibits the growth of lateral buds so that the plant may grow vertically. It is important for the plant to devote energy to growing upward so that it can get more light to undergo photosynthesis. If the plant utilizes available energy for growing upward, it may be able to outcompete other individuals in the vicinity. Plants that were capable of outcompeting neighboring plants likely had higher fitness. Apical dominance is therefore most likely adaptive. Typically, the end of a shoot contains an apical bud, which is the location where shoot gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell, being selectively permeable to ions and organic molecule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Meristem
In cell biology, the meristem is a structure composed of specialized tissue found in plants, consisting of stem cells, known as meristematic cells, which are undifferentiated cells capable of continuous cellular division. These meristematic cells play a fundamental role in plant growth, regeneration, and acclimatization, as they serve as the source of all differentiated plant tissues and organs. They contribute to the formation of structures such as fruits, leaves, and seeds, as well as supportive tissues like stems and roots. Meristematic cells are totipotent, meaning they have the ability to differentiate into any plant cell type. As they divide, they generate new cells, some of which remain meristematic cells while others differentiate into specialized cells that typically lose the ability to divide or produce new cell types. Due to their active division and undifferentiated nature, meristematic cells form the foundation for the formation of new plant organs and the cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |