|
Anticommuting
In mathematics, anticommutativity is a specific property of some non-commutative mathematical operations. Swapping the position of two arguments of an antisymmetric operation yields a result which is the ''inverse'' of the result with unswapped arguments. The notion '' inverse'' refers to a group structure on the operation's codomain, possibly with another operation. Subtraction is an anticommutative operation because commuting the operands of gives for example, Another prominent example of an anticommutative operation is the Lie bracket. In mathematical physics, where symmetry is of central importance, these operations are mostly called antisymmetric operations, and are extended in an associative setting to cover more than two arguments. Definition If A, B are two abelian groups, a bilinear map f\colon A^2 \to B is anticommutative if for all x, y \in A we have :f(x, y) = - f(y, x). More generally, a multilinear map g : A^n \to B is anticommutative if for all x_1, \d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permutation
In mathematics, a permutation of a set is, loosely speaking, an arrangement of its members into a sequence or linear order, or if the set is already ordered, a rearrangement of its elements. The word "permutation" also refers to the act or process of changing the linear order of an ordered set. Permutations differ from combinations, which are selections of some members of a set regardless of order. For example, written as tuples, there are six permutations of the set , namely (1, 2, 3), (1, 3, 2), (2, 1, 3), (2, 3, 1), (3, 1, 2), and (3, 2, 1). These are all the possible orderings of this three-element set. Anagrams of words whose letters are different are also permutations: the letters are already ordered in the original word, and the anagram is a reordering of the letters. The study of permutations of finite sets is an important topic in the fields of combinatorics and group theory. Permutations are used in almost every branch of mathematics, and in many other fields of scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heidelberg
Heidelberg (; Palatine German language, Palatine German: ''Heidlberg'') is a city in the States of Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg, situated on the river Neckar in south-west Germany. As of the 2016 census, its population was 159,914, of which roughly a quarter consisted of students. Located about south of Frankfurt, Heidelberg is the List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, fifth-largest city in Baden-Württemberg. Heidelberg is part of the densely populated Rhine-Neckar, Rhine-Neckar Metropolitan Region. Heidelberg University, founded in 1386, is Germany's oldest and one of Europe's most reputable universities. Heidelberg is a Science, scientific hub in Germany and home to several internationally renowned #Research, research facilities adjacent to its university, including the European Molecular Biology Laboratory and four Max Planck Society, Max Planck Institutes. The city has also been a hub for the arts, especially literature, throughout the centurie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constituent states, Berlin is surrounded by the State of Brandenburg and contiguous with Potsdam, Brandenburg's capital. Berlin's urban area, which has a population of around 4.5 million, is the second most populous urban area in Germany after the Ruhr. The Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's third-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr and Rhine-Main regions. Berlin straddles the banks of the Spree, which flows into the Havel (a tributary of the Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the city's main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel and Dahme, the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee. Due to its l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
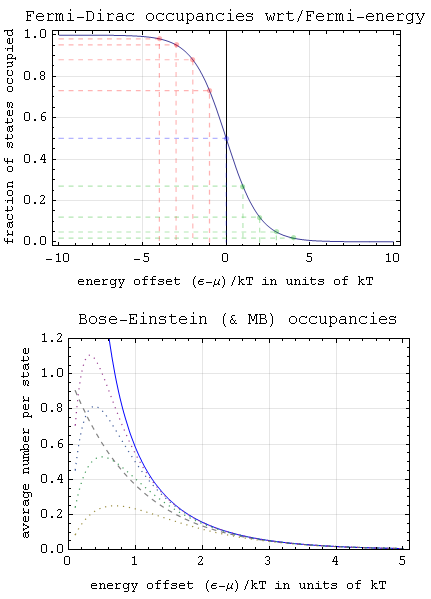
Particle Statistics
Particle statistics is a particular description of multiple particles in statistical mechanics. A key prerequisite concept is that of a statistical ensemble (an idealization comprising the state space of possible states of a system, each labeled with a probability) that emphasizes properties of a large system as a whole at the expense of knowledge about parameters of separate particles. When an ensemble describes a system of particles with similar properties, their number is called the particle number and usually denoted by ''N''. Classical statistics In classical mechanics, all particles (elementary particle, fundamental and composite particles, atoms, molecules, electrons, etc.) in the system are considered identity (philosophy), distinguishable. This means that individual particles in a system can be tracked. As a consequence, switching the positions of any pair of particles in the system leads to a different configuration of the system. Furthermore, there is no restriction on p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetry In Mathematics
Symmetry occurs not only in geometry, but also in other branches of mathematics. Symmetry is a type of invariance: the property that a mathematical object remains unchanged under a set of operations or transformations. Given a structured object ''X'' of any sort, a symmetry is a mapping of the object onto itself which preserves the structure. This can occur in many ways; for example, if ''X'' is a set with no additional structure, a symmetry is a bijective map from the set to itself, giving rise to permutation groups. If the object ''X'' is a set of points in the plane with its metric structure or any other metric space, a symmetry is a bijection of the set to itself which preserves the distance between each pair of points (i.e., an isometry). In general, every kind of structure in mathematics will have its own kind of symmetry, many of which are listed in the given points mentioned above. Symmetry in geometry The types of symmetry considered in basic geometry include reflec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graded-commutative Ring
In algebra, a graded-commutative ring (also called a skew-commutative ring) is a graded ring that is commutative in the graded sense; that is, homogeneous elements ''x'', ''y'' satisfy :xy = (-1)^ yx, where , ''x'' , and , ''y'' , denote the degrees of ''x'' and ''y''. A commutative (non-graded) ring, with trivial grading, is a basic example. An exterior algebra is an example of a graded-commutative ring that is not commutative in the non-graded sense. A cup product on cohomology satisfies the skew-commutative relation; hence, a cohomology ring is graded-commutative. In fact, many examples of graded-commutative rings come from algebraic topology and homological algebra. References * David Eisenbud, ''Commutative Algebra. With a view toward algebraic geometry'', Graduate Texts in Mathematics, vol 150, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1995. * See also *DG algebra *graded-symmetric algebra *alternating algebra *supercommutative algebra In mathematics, a supercommuta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exterior Algebra
In mathematics, the exterior algebra, or Grassmann algebra, named after Hermann Grassmann, is an algebra that uses the exterior product or wedge product as its multiplication. In mathematics, the exterior product or wedge product of vectors is an algebraic construction used in geometry to study areas, volumes, and their higher-dimensional analogues. The exterior product of two vectors u and v, denoted by u \wedge v, is called a bivector and lives in a space called the ''exterior square'', a vector space that is distinct from the original space of vectors. The magnitude of u \wedge v can be interpreted as the area of the parallelogram with sides u and v, which in three dimensions can also be computed using the cross product of the two vectors. More generally, all parallel plane surfaces with the same orientation and area have the same bivector as a measure of their oriented area. Like the cross product, the exterior product is anticommutative, meaning t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commutator
In mathematics, the commutator gives an indication of the extent to which a certain binary operation fails to be commutative. There are different definitions used in group theory and ring theory. Group theory The commutator of two elements, and , of a group , is the element : . This element is equal to the group's identity if and only if and commute (from the definition , being equal to the identity if and only if ). The set of all commutators of a group is not in general closed under the group operation, but the subgroup of ''G'' generated by all commutators is closed and is called the ''derived group'' or the ''commutator subgroup'' of ''G''. Commutators are used to define nilpotent and solvable groups and the largest abelian quotient group. The definition of the commutator above is used throughout this article, but many other group theorists define the commutator as :. Identities (group theory) Commutator identities are an important tool in group theory. The expr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commutativity
In mathematics, a binary operation is commutative if changing the order of the operands does not change the result. It is a fundamental property of many binary operations, and many mathematical proofs depend on it. Most familiar as the name of the property that says something like or , the property can also be used in more advanced settings. The name is needed because there are operations, such as division and subtraction, that do not have it (for example, ); such operations are ''not'' commutative, and so are referred to as ''noncommutative operations''. The idea that simple operations, such as the multiplication and addition of numbers, are commutative was for many years implicitly assumed. Thus, this property was not named until the 19th century, when mathematics started to become formalized. A similar property exists for binary relations; a binary relation is said to be symmetric if the relation applies regardless of the order of its operands; for example, equality is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lie Ring
In mathematics, a Lie algebra (pronounced ) is a vector space \mathfrak g together with an operation called the Lie bracket, an alternating bilinear map \mathfrak g \times \mathfrak g \rightarrow \mathfrak g, that satisfies the Jacobi identity. The Lie bracket of two vectors x and y is denoted ,y/math>. The vector space \mathfrak g together with this operation is a non-associative algebra, meaning that the Lie bracket is not necessarily associative. Lie algebras are closely related to Lie groups, which are groups that are also smooth manifolds: any Lie group gives rise to a Lie algebra, which is its tangent space at the identity. Conversely, to any finite-dimensional Lie algebra over real or complex numbers, there is a corresponding connected Lie group unique up to finite coverings (Lie's third theorem). This correspondence allows one to study the structure and classification of Lie groups in terms of Lie algebras. In physics, Lie groups appear as symmetry groups of physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Product
In mathematics, the cross product or vector product (occasionally directed area product, to emphasize its geometric significance) is a binary operation on two vectors in a three-dimensional oriented Euclidean vector space (named here E), and is denoted by the symbol \times. Given two linearly independent vectors and , the cross product, (read "a cross b"), is a vector that is perpendicular to both and , and thus normal to the plane containing them. It has many applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and computer programming. It should not be confused with the dot product (projection product). If two vectors have the same direction or have the exact opposite direction from each other (that is, they are ''not'' linearly independent), or if either one has zero length, then their cross product is zero. More generally, the magnitude of the product equals the area of a parallelogram with the vectors for sides; in particular, the magnitude of the product of two perpendic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |