|
Antiaromatic Compounds
Antiaromaticity is a chemical property of a cyclic molecule with a π electron system that has higher energy, i.e., it is less stable due to the presence of 4n delocalised (π or lone pair) electrons in it, as opposed to aromaticity. Unlike aromatic compounds, which follow Hückel's rule ( ''n''+2π electrons) and are highly stable, antiaromatic compounds are highly unstable and highly reactive. To avoid the instability of antiaromaticity, molecules may change shape, becoming non-planar and therefore breaking some of the π interactions. In contrast to the diamagnetic ring current present in aromatic compounds, antiaromatic compounds have a paramagnetic ring current, which can be observed by NMR spectroscopy. Examples of antiaromatic compounds are pentalene (A), biphenylene (B), cyclopentadienyl cation (C). The prototypical example of antiaromaticity, cyclobutadiene, is the subject of debate, with some scientists arguing that antiaromaticity is not a major factor contributing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pi Electron
In chemistry, pi bonds (π bonds) are covalent chemical bonds, in each of which two lobes of an orbital on one atom overlap with two lobes of an orbital on another atom, and in which this overlap occurs laterally. Each of these atomic orbitals has an electron density of zero at a shared nodal plane that passes through the two bonded nuclei. This plane also is a nodal plane for the molecular orbital of the pi bond. Pi bonds can form in double and triple bonds but do not form in single bonds in most cases. The Greek letter π in their name refers to p orbitals, since the orbital symmetry of the pi bond is the same as that of the p orbital when seen down the bond axis. One common form of this sort of bonding involves p orbitals themselves, though d orbitals also engage in pi bonding. This latter mode forms part of the basis for metal-metal multiple bonding. Pi bonds are usually weaker than sigma bonds. The C-C double bond, composed of one sigma and one pi bond, has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentalene
Pentalene is a polycyclic hydrocarbon composed of two fused cyclopentadiene rings. It has chemical formula . It is antiaromatic, because it has 4''n'' π electrons where ''n'' is any integer. For this reason it dimerizes even at temperatures as low as −100 °C. The derivative 1,3,5-tri-''tert''-butylpentalene was synthesized in 1973. Because of the ''tert''-butyl substituents this compound is thermally stable. Pentalenes can also be stabilized by benzannulation for example in the compounds benzopentalene and dibenzopentalene. Dilithium pentalenide was isolated in 1962, long before pentalene itself in 1997. It is prepared from reaction of dihydropentalene (pyrolysis of an isomer of dicyclopentadiene) with ''n''-butyllithium in solution and forms a stable salt. In accordance with its structure proton NMR shows 2 signals in a 2 to 1 ratio. The addition of two electrons removes the antiaromaticity; it becomes a planar 10π-electron aromatic species and is thus a bicyclic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground State
The ground state of a quantum-mechanical system is its stationary state of lowest energy; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state. In quantum field theory, the ground state is usually called the vacuum state or the vacuum. If more than one ground state exists, they are said to be degenerate. Many systems have degenerate ground states. Degeneracy occurs whenever there exists a unitary operator that acts non-trivially on a ground state and commutes with the Hamiltonian of the system. According to the third law of thermodynamics, a system at absolute zero temperature exists in its ground state; thus, its entropy is determined by the degeneracy of the ground state. Many systems, such as a perfect crystal lattice, have a unique ground state and therefore have zero entropy at absolute zero. It is also possible for the highest excited state to have absolute zero te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baird's Rule
In organic chemistry, Baird's rule estimates whether the lowest triplet state of planar, cyclic structures will have aromatic properties or not. The quantum mechanical basis for its formulation was first worked out by physical chemist N. Colin Baird at the University of Western Ontario in 1972. The lowest triplet state of an annulene is, according to Baird's rule, aromatic when it has 4''n'' π-electrons and antiaromatic when the π-electron count is 4''n'' + 2, where ''n'' is any positive integer. This trend is opposite to that predicted by Hückel's rule for the ground state, which is usually the lowest singlet state (S0). Baird's rule has thus become known as the photochemical analogue of Hückel's rule. Through various theoretical investigations, this rule has also been found to extend to the lowest lying singlet excited state (S1) of small annulenes. See also * Möbius–Hückel concept * Möbius aromaticity In organic chemistry, Möbius aromaticity is a special typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triplet State
In quantum mechanics, a triplet is a quantum state of a system with a spin of quantum number =1, such that there are three allowed values of the spin component, = −1, 0, and +1. Spin, in the context of quantum mechanics, is not a mechanical rotation but a more abstract concept that characterizes a particle's intrinsic angular momentum. It is particularly important for systems at atomic length scales, such as individual atoms, protons, or electrons. Almost all molecules encountered in daily life exist in a singlet state, but molecular oxygen is an exception. At room temperature, O2 exists in a triplet state, which can only undergo a chemical reaction by making the forbidden transition into a singlet state. This makes it kinetically nonreactive despite being thermodynamically one of the strongest oxidants. Photochemical or thermal activation can bring it into the singlet state, which makes it kinetically as well as thermodynamically a very strong oxidant. __TOC__ Two spin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singlet State
In quantum mechanics, a singlet state usually refers to a system in which all electrons are paired. The term 'singlet' originally meant a linked set of particles whose net angular momentum is zero, that is, whose overall spin quantum number s=0. As a result, there is only one spectral line of a singlet state. In contrast, a doublet state contains one unpaired electron and shows splitting of spectral lines into a doublet; and a triplet state has two unpaired electrons and shows threefold splitting of spectral lines. History Singlets and the related spin concepts of doublets and triplets occur frequently in atomic physics and nuclear physics, where one often needs to determine the total spin of a collection of particles. Since the only observed fundamental particle with zero spin is the extremely inaccessible Higgs boson, singlets in everyday physics are necessarily composed of sets of particles whose individual spins are non-zero, e.g. or 1. The origin of the term "singlet" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pauli Repulsion
In chemistry and physics, the exchange interaction (with an exchange energy and exchange term) is a quantum mechanical effect that only occurs between identical particles. Despite sometimes being called an exchange force in an analogy to classical force, it is not a true force as it lacks a force carrier. The effect is due to the wave function of indistinguishable particles being subject to exchange symmetry, that is, either remaining unchanged (symmetric) or changing sign (antisymmetric) when two particles are exchanged. Both bosons and fermions can experience the exchange interaction. For fermions, this interaction is sometimes called Pauli repulsion and is related to the Pauli exclusion principle. For bosons, the exchange interaction takes the form of an effective attraction that causes identical particles to be found closer together, as in Bose–Einstein condensation. The exchange interaction alters the expectation value of the distance when the wave functions of two or mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strain (chemistry)
In chemistry, a molecule experiences strain when its chemical structure undergoes some stress which raises its internal energy in comparison to a strain-free reference compound. The internal energy of a molecule consists of all the energy stored within it. A strained molecule has an additional amount of internal energy which an unstrained molecule does not. This extra internal energy, or strain energy, can be likened to a compressed spring.Anslyn and Dougherty, ''Modern Physical Organic Chemistry'', University Science Books, 2006, Much like a compressed spring must be held in place to prevent release of its potential energy, a molecule can be held in an energetically unfavorable conformation by the bonds within that molecule. Without the bonds holding the conformation in place, the strain energy would be released. Summary Thermodynamics The equilibrium of two molecular conformations is determined by the difference in Gibbs free energy of the two conformations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Strain
In organic chemistry, ring strain is a type of instability that exists when bonds in a molecule form angles that are abnormal. Strain is most commonly discussed for small rings such as cyclopropanes and cyclobutanes, whose internal angles are substantially smaller than the idealized value of approximately 109°. Because of their high strain, the heat of combustion for these small rings is elevated. Ring strain results from a combination of angle strain, conformational strain or Pitzer strain (torsional eclipsing interactions), and transannular strain, also known as van der Waals strain or Prelog strain. The simplest examples of angle strain are small cycloalkanes such as cyclopropane and cyclobutane. Ring strain energy can be attributed to the energy required for the distortion of bond and bond angles in order to close a ring. Ring strain energy is believed to be the cause of accelerated rates in altering ring reactions. Its interactions with traditional bond energies c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
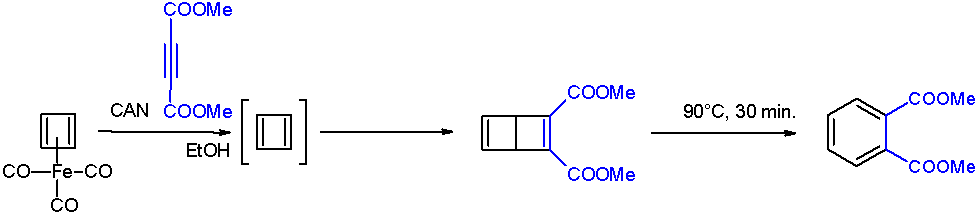
Cyclobutadiene Smaller
Cyclobutadiene is an organic compound with the formula . It is very reactive owing to its tendency to dimerize. Although the parent compound has not been isolated, some substituted derivatives are robust and a single molecule of cyclobutadiene is quite stable. Since the compound degrades by a bimolecular process, the species can be observed by matrix isolation techniques at temperatures below 35 K. It is thought to adopt a rectangular structure. Structure and reactivity The compound is the prototypical antiaromatic hydrocarbon with 4 π-electrons. It is the smallest 'n'' annulene ( annulene). Its rectangular structure is the result of the Jahn–Teller effect, which distorts the molecule and lowers its symmetry, converting the triplet to a singlet ground state. The electronic states of cyclobutadiene have been explored with a variety of computational methods. The rectangular structure is consistent with the existence of two different 1,2-dideutero-1,3-cyclobutadiene valence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density Functional Theory
Density-functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics, chemistry and materials science to investigate the electronic structure (or nuclear structure) (principally the ground state) of many-body systems, in particular atoms, molecules, and the condensed phases. Using this theory, the properties of a many-electron system can be determined by using functionals, i.e. functions of another function. In the case of DFT, these are functionals of the spatially dependent electron density. DFT is among the most popular and versatile methods available in condensed-matter physics, computational physics, and computational chemistry. DFT has been very popular for calculations in solid-state physics since the 1970s. However, DFT was not considered accurate enough for calculations in quantum chemistry until the 1990s, when the approximations used in the theory were greatly refined to better model the exchange and correlation interactio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |