|
Anti-Fascist Committee For A Free Germany
The Anti-Fascist Committee for a Free Germany (German: ''Antifaschistische Komitee Freies Deutschland'', or AKFD) was an organization of former Wehrmacht soldiers modeled after the National Committee for a Free Germany. The organization was formed in Greece during the last months of the German occupation and lasted from August to December 1944. Falk Harnack was one of its co-founders. Historical background During the period of the Axis occupation of Greece (1941-44) a large number of German anti-fascist soldiers defected from the ranks of the German armed forces (Wehrmacht) and joined the Greek partisans of the Greek People's Liberation Army (Greek: Ελληνικός Λαϊκός Απελευθερωτικός Στρατός (ΕΛΑΣ), Ellinikós Laïkós Apeleftherotikós Stratós (ELAS)). ELAS was the military wing of the National Liberation Front (Greece) (Greek: Εθνικό Απελευθερωτικό Μέτωπο, Ethnikó Apeleftherotikó Métopo (EAM)). Defections acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Germany (1867–1918)
The national flag of Germany is a tricolour consisting of three equal horizontal bands displaying the national colours of Germany: black, red, and gold (german: Schwarz-Rot-Gold). The flag was first sighted in 1848 in the German Confederation. It was officially adopted as the national flag of the Weimar Republic from 1919 to 1933, and has been in use since its reintroduction in West Germany in 1949. Since the mid-19th century, Germany has two competing traditions of national colours, black-red-gold and black-white-red. Black-red-gold were the colours of the 1848 Revolutions, the Weimar Republic of 1919–1933 and the Federal Republic (since 1949). They were also adopted by the German Democratic Republic (1949–1990). The colours black-white-red appeared for the first time in 1867, in the constitution of the North German Confederation. This nation state for Prussia and other north and central German states was expanded to the south German states in 1870–71, under the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerhard Reinhardt
Gerhard Reinhardt (May 4, 1916 – August 22, 1989) was an East German politician and German Resistance fighter against Nazism. Life and work Reinhardt was born in Werdau, in the Kingdom of Saxony, a state of the German Empire. He was born into a family of textile workers and himself learned how to be a locksmith, finishing his training with journeyman years spent traveling through several countries in Europe, including France, Switzerland and Austria. In 1930, he joined the Young Communist League of Germany. After the Nazis seized power in 1933, Reinhardt became active in the German Resistance. He was arrested and in 1936, sentenced to a prison term in the Zuchthaus in Waldheim, Saxony.Gottfried Hamacher et al. (Ed.)''Gegen Hitler. Deutsche in der Résistance, in den Streitkräften der Antihitlerkoalition und der Bewegung »Freies Deutschland«. Kurzbiografien'' (PDF) (Series: Manuskripte/Rosa-Luxemburg-Stiftung; Vol. 53). Dietz, Berlin (2005), p. 171. He worked as a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropaia
Tropaia ( el, Τρόπαια) is a village and a former municipality in Arcadia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it is part of the municipality Gortynia Gortynia ( el, Γορτυνία) is a municipality in the Arcadia regional unit, Peloponnese, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Dimitsana. The municipality has an area of 1,050.882 km2. Municipality The municipality Gortynia ..., of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 187.228 km2. As of 2011 it has a population of 2,887. The village is located near the Ladona Lake. References Populated places in Arcadia, Peloponnese {{Peloponnese-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which separates the Gulf of Corinth from the Saronic Gulf. From the late Middle Ages until the 19th century the peninsula was known as the Morea ( grc-x-byzant, Μωρέας), (Morèas) a name still in colloquial use in its demotic form ( el, Μωριάς, links=no), (Moriàs). The peninsula is divided among three administrative regions: most belongs to the Peloponnese region, with smaller parts belonging to the West Greece and Attica regions. Geography The Peloponnese is a peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland, in area, and constitutes the southernmost part of mainland Greece. It is connected to the mainland by the Isthmus of Corinth, where the Corinth Canal was constructed in 1893. However, it is also connected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area, and the capital city, capital of the geographic regions of Greece, geographic region of Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia, the administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Central Macedonia and the Decentralized Administration of Macedonia and Thrace. It is also known in Greek language, Greek as (), literally "the co-capital", a reference to its historical status as the () or "co-reigning" city of the Byzantine Empire alongside Constantinople. Thessaloniki is located on the Thermaic Gulf, at the northwest corner of the Aegean Sea. It is bounded on the west by the delta of the Vardar, Axios. The Thessaloniki (municipality), municipality of Thessaloniki, the historical center, had a population of 317,778 in 2021, while the Thessaloniki metro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volos
Volos ( el, Βόλος ) is a coastal port city in Thessaly situated midway on the Greek mainland, about north of Athens and south of Thessaloniki. It is the sixth most populous city of Greece, and the capital of the Magnesia regional unit of the Thessaly Region. Volos is also the only outlet to the sea from Thessaly, the country's largest agricultural region. With a population of 144,449 (2011), the city is an important industrial centre, and its port provides a bridge between Europe and Asia. Volos is the newest of the Greek port cities, with a large proportion of modern buildings erected following catastrophic earthquakes in 1955. It includes the municipal units of Volos, Nea Ionia and Iolkos, as well as smaller suburban communities. The economy of the city is based on manufacturing, trade, services and tourism. Home to the University of Thessaly, the city also offers facilities for conferences, exhibitions and major sporting, cultural and scientific events. Volos par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petros Kokkalis
Professor Petros Kokkalis (18.9.1896 - 15.1.1962), a distinguished professor of Medicine in the University of Athens has been one of thleading figures of Medicine in pre WWII Greece introducing pioneering methods ithoracic surgery and neurosurgery His main medical achievements include the introduction of thoracoplasty in Greece and removal of the phrenic nerve for the treatment of tuberculosis, as well as the first pneumonectomy with the Tourniquet method and the first pericardiectomy for the release of compressive pericarditis. Biography Kokkalis was born in Livadeia, Greece, the second child of Socrates Dim. Kokkalis (1856 – 1944), the philologist-headmaster from Arahova, and of Polyxeni Nakou (1866 – 1937). He married in 1938 to Niki Kouletsi (1913-1997) and had two children, Socrates (1939) and Avgi-Polyxeni (1944-2015). Kokkalis registered at the Medical School of the University of Athens in 1911 but after 1913 he continued his studies at the Medical School of the Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstantinos Despotopoulos
Konstantinos Despotopoulos ( el, Κωνσταντίνος Δεσποτόπουλος; 8 February 1913 – 7 February 2016) was a Greek philosopher and intellectual who became a university professor and the Minister of National Education and Religious Affairs of Greece. Biography Konstantinos Despotopoulos was born in Smyrna (now Izmir), then part of the Ottoman Empire, in 1913. Following the destruction of the city and the flight of its Greek population at the end of the Greco-Turkish War of 1919–22, his family settled in Athens. He attended the 1st Gymnasium of Athens, which he graduated with perfect marks, and received his PhD from the University of Athens in Philosophy, again with perfect marks. He taught Philosophy of Law and general philosophy courses at the University of Athens, the University of Nancy, and the Panteion University. In 1984 he was elected a member of the Academy of Athens, serving as its chairman in 1993. He was a foreign Fellow of the Romanian Academy and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stefanos Sarafis
Stefanos Sarafis ( el, Στέφανος Σαράφης, 23 October 1890 – 31 May 1957) was an officer of the Hellenic Army and Major General in EAM-ELAS), who played an important role during the Greek Resistance. Early life and career Sarafis was born at Trikala in 1890. He was an Aromanian. Sarafis studied law in the University of Athens. During the Balkan Wars, he enlisted in the Greek Army as a sergeant and was promoted to lieutenant in 1913. He became a Venizelist and played an active role in the various military conspiracies that were formed during the troubled 1920s. He participated in the two failed Venizelist coup attempts of 1933 and 1935. The latter was led by Nikolaos Plastiras and intended to overthrow the government of Prime Minister Panagis Tsaldaris. The failure of the coup resulted in the execution of its leader for treason and dishonorable discharges for several of the participants. Sarafis himself was condemned to life imprisonment but was pardoned b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
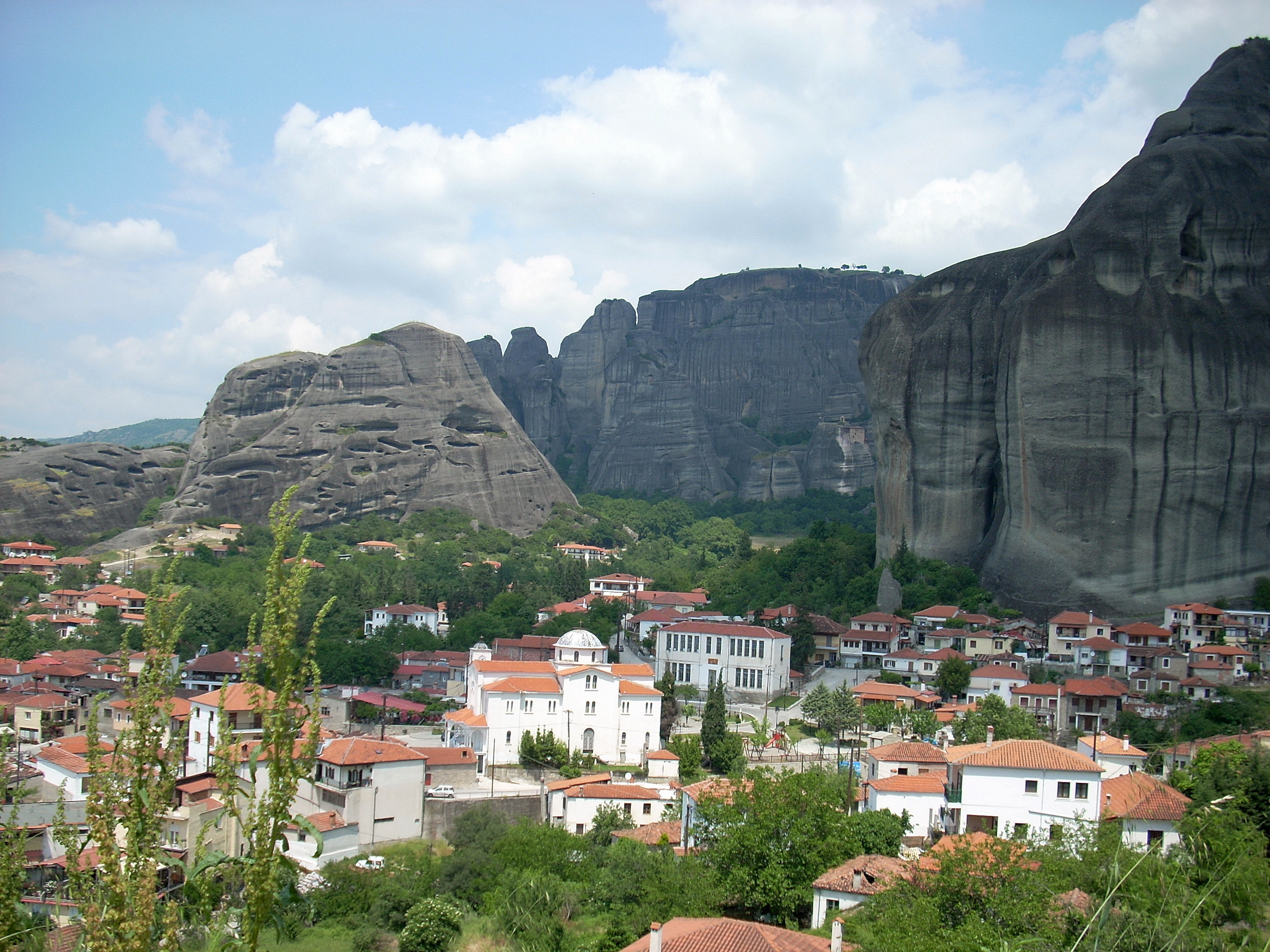
Kalambaka
Kalabaka ( el, Καλαμπάκα, ''Kalabáka'', alternative transliterations are ''Kalambaka'' and ''Kalampaka'') is a town and seat of the municipality of Meteora in the Trikala regional unit, part of Thessaly in Greece. The population was 12,000 at the 2011 census, of which 8,330 in the town proper. The Meteora monasteries are located near the town. Kalabaka is the northwestern terminal of the old Thessaly Railways, now part of OSE. History A Greek inscription on the wall of one of the town's oldest churches (Saint John the Baptist) testifies to the existence of an ancient Greek settlement under the name Aiginion. In the 10th century AD, it was known as Stagoi (Σταγοί), a Byzantine fortress and bishopric (the name is still in use for the town by the Greek Orthodox Church). Of its medieval monuments, only the cathedral, the Church of the Dormition, survives. It was a late 11th- or early 12th-century building, built on the remains of an earlier, late antique ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previously used term and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles permitted. After the Nazi rise to power in 1933, one of Adolf Hitler's most overt and audacious moves was to establish the ''Wehrmacht'', a modern offensively-capable armed force, fulfilling the Nazi régime's long-term goals of regaining lost territory as well as gaining new territory and dominating its neighbours. This required the reinstatement of conscription and massive investment and defense spending on the arms industry. The ''Wehrmacht'' formed the heart of Germany's politico-military power. In the early part of the Second World War, the ''Wehrmacht'' employed combined arms tactics (close- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |