|
Anthedon (Boeotia)
Anthedon (Ἀνθηδών) was a town in Boeotia, Ancient Greece, located on the coast of the Gulf of Euboea, about west of Chalcis, at the foot of Mount Messapius. It was member of the Amphictyonic League, and served as port for Thebes. In ancient times, it was believed to have had one of the mythical characters named Anthedon as its eponym. The ruins of the town are situated 1 1/2 mile from the village Loukisia. Ancient accounts The oldest mention of the city is found in Homer's ''Iliad'', Catalogue of Ships, where it is given the epithet "furthermost", i. e. the most geographically remote town of Boeotia to the northern Gulf of Euboea. Ancient inhabitants of Anthedon derived their origin from the sea-god Glaucus, who was believed to have been originally a native of the place. A surviving ancient coin now stored in the Archaeological Museum of Chalkis bears on one side a representation of Glaucus. The Anthedonians appear to have been a different race from the other people o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Boeotia
Boeotia ( ), sometimes Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia ( el, Βοιωτία; modern: ; ancient: ), formerly known as Cadmeis, is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, and its largest city is Thebes. Boeotia was also a region of ancient Greece, from before the 6th century BC. Geography Boeotia lies to the north of the eastern part of the Gulf of Corinth. It also has a short coastline on the Gulf of Euboea. It bordered on Megaris (now West Attica) in the south, Attica in the southeast, Euboea in the northeast, Opuntian Locris (now part of Phthiotis) in the north and Phocis in the west. The main mountain ranges of Boeotia are Mount Parnassus in the west, Mount Helicon in the southwest, Cithaeron in the south and Parnitha in the east. Its longest river, the Cephissus, flows in the central part, where most of the low-lying areas of Boeotia are found. Lake Copais was a large lake in the center ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
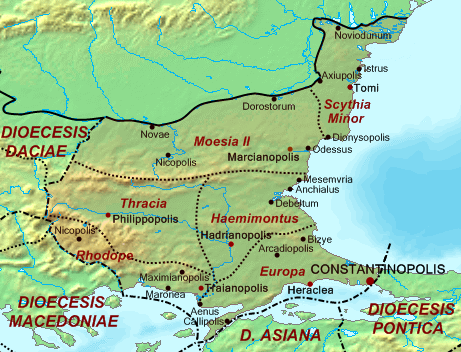
Thracia
Thracia or Thrace ( ''Thrakē'') is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical and Hellenistic eras, and briefly by the Greek Diadochi ruler Lysimachus, but became a client state of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire as the Sapaean kingdom. Roman emperor Claudius annexed the kingdom as a Roman province in 46 AD. Confines From the perspective of classical Greece, Thracia included the territory north of Thessaly, with no definite boundaries, sometimes to the inclusion of Macedonia and Scythia Minor. Later, Thracia proper was understood to include the territory bordered by the Danube on the north, by the Black Sea on the east, by Macedonia in the south and by Illyria to the west, roughly equivalent with the territory of the Thracian kingdom as it stood during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. With the annexation of the Thracian kingdom by the Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cities In Ancient Boeotia
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequences for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name to the architectural form of the basilica. Originally, a basilica was an ancient Roman public building, where courts were held, as well as serving other official and public functions. Basilicas are typically rectangular buildings with a central nave flanked by two or more longitudinal aisles, with the roof at two levels, being higher in the centre over the nave to admit a clerestory and lower over the side-aisles. An apse at one end, or less frequently at both ends or on the side, usually contained the raised tribunal occupied by the Roman magistrates. The basilica was centrally located in every Roman town, usually adjacent to the forum and often opposite a temple in imperial-era forums. Basilicas were also built in private residences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aloadae
__NOTOC__ In Greek mythology, the Aloadae () or Aloads (Ancient Greek: Ἀλωάδαι ''Aloadai'') were Otus or Otos (Ὦτος means "insatiate") and Ephialtes (Ἐφιάλτης "nightmare"), Thessalian sons of Princess Iphimedia, wife of Aloeus, by Poseidon, whom she induced to make her pregnant by going to the seashore and disporting herself in the surf or scooping seawater into her bosom. From Aloeus, sometimes their real father, they received their patronymic, the Aloadae. They had a sister Pancratis ( Pancrato) who was renowned for her great beauty. Mythology The Aloads were strong and aggressive giants, growing by nine fingers every month. Nine fathoms tall at age of nine, they were only outshone in beauty by Orion. War with the gods The brothers wanted to storm Mt. Olympus and gain Artemis for Otus and Hera for Ephialtes. Their plan, or construction, of a pile of mountains atop which they would confront the gods is described differently according to the aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iphimedeia
In Greek mythology, Iphimedeia (; Ancient Greek: Ἰφιμέδεια) or Iphimede (Ἰφιμέδη) was a Thessalian princess. She was attested in Homer's ''Odyssey'' in the Catalogue of women as being a mortal. Family Iphimedia was the daughter of Triopas of Thessaly (a son of Poseidon and Canace) and probably by Hiscilla, daughter of King Myrmidon of Phthia. Her possible brothers were Erysichthon and Phorbas. Iphimedea had by Poseidon the twins Otus and Ephialtes who were called the Aloadae after their stepfather.Homer, ''Odyssey'11.305 Pindar, ''Pythian Ode'4.89 Hyginus, ''Fabulae'28/ref> One account called these men's natural father as Aloeus, husband and paternal uncle of Iphimede. The latter mothered as well Pancratis (or Pancrato) to Aloeus. She was probably also the mother of Elate and Platanus, the sisters of the Aloadae. Mythology Early years Iphimedeia also fell in love with Poseidon, god of the sea, and would often come to the sea shore where she po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans called him Bacchus ( or ; grc, Βάκχος ) for a frenzy he is said to induce called ''bakkheia''. As Dionysus Eleutherios ("the liberator"), his wine, music, and ecstatic dance free his followers from self-conscious fear and care, and subvert the oppressive restraints of the powerful. His '' thyrsus'', a fennel-stem sceptre, sometimes wound with ivy and dripping with honey, is both a beneficent wand and a weapon used to destroy those who oppose his cult and the freedoms he represents. Those who partake of his mysteries are believed to become possessed and empowered by the god himself. His origins are uncertain, and his cults took many forms; some are described by ancient sources as Thracian, others as Greek. In Orphic religion, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone ( ; gr, Περσεφόνη, Persephónē), also called Kore or Cora ( ; gr, Κόρη, Kórē, the maiden), is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld after her abduction by and marriage to her uncle Hades, the king of the underworld.Martin Nilsson (1967). ''Die Geschichte der Griechische Religion'' Vol I pp 462–463, 479–480 The myth of her abduction, her sojourn in the underworld, and her temporary return to the surface represents her functions as the embodiment of spring and the personification of vegetation, especially grain crops, which disappear into the earth when sown, sprout from the earth in spring, and are harvested when fully grown. In Classical Greek art, Persephone is invariably portrayed robed, often carrying a sheaf of grain. She may appear as a mystical divinity with a sceptre and a little box, but she was mostly represented in the process of being carried off by Hades. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demeter
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Demeter (; Attic Greek, Attic: ''Dēmḗtēr'' ; Doric Greek, Doric: ''Dāmā́tēr'') is the Twelve Olympians, Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over crops, grains, food, and the fertility (soil), fertility of the earth. Although she is mostly known as a grain goddess, she also appeared as a goddess of health, birth, and marriage, and had connections to the Greek Underworld, Underworld. She is also called Deo (). In Greek tradition, Demeter is the second child of the Titans Rhea (mythology), Rhea and Cronus, and sister to Hestia, Hera, Hades, Poseidon, and Zeus. Like her other siblings but Zeus, she was swallowed by her father as an infant and rescued by Zeus. Through her brother Zeus, she became the mother of Persephone, a fertility goddess. One of the most notable Homeric Hymns, the ''Homeric Hymn to Demeter'', tells the story of Persephone's abduction by Hades and Demeter's search for her. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabeiri
In Greek mythology, the Cabeiri or Cabiri ( grc, Κάβειροι, ''Kábeiroi''), also transliterated Kabeiri or Kabiri, were a group of enigmatic chthonic deities. They were worshiped in a mystery cult closely associated with that of Hephaestus, centered in the north Aegean islands of Lemnos and possibly Samothrace—at the Samothrace temple complex—and at Thebes. In their distant origins the Cabeiri and the Samothracian gods may include pre-Greek elements, or other non-Greek elements, such as Thracian, Tyrrhenian, Pelasgian, Phrygian or Hittite. The Lemnian cult was always local to Lemnos, but the Samothracian mystery cult spread rapidly throughout the Greek world during the Hellenistic period, eventually initiating Romans. The ancient sources disagree about whether the deities of Samothrace were Cabeiri or not; and the accounts of the two cults differ in detail. But the two islands are close to each other, at the northern end of the Aegean, and the cults are at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pausanias (geographer)
Pausanias ( /pɔːˈseɪniəs/; grc-gre, Παυσανίας; c. 110 – c. 180) was a Greek traveler and geographer of the second century AD. He is famous for his ''Description of Greece'' (, ), a lengthy work that describes ancient Greece from his firsthand observations. ''Description of Greece'' provides crucial information for making links between classical literature and modern archaeology. Biography Not much is known about Pausanias apart from what historians can piece together from his own writing. However, it is mostly certain that he was born c. 110 AD into a Greek family and was probably a native of Lydia in Asia Minor. From c. 150 until his death in 180, Pausanias travelled through the mainland of Greece, writing about various monuments, sacred spaces, and significant geographical sites along the way. In writing ''Description of Greece'', Pausanias sought to put together a lasting written account of "all things Greek", or ''panta ta hellenika''. Living in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |