|
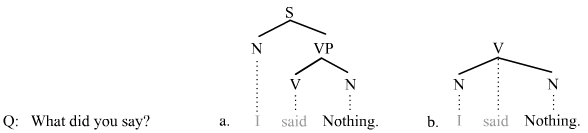
Answer Ellipsis
Answer ellipsis (= answer fragments) is a type of Ellipsis (linguistics), ellipsis that occurs in answers to questions. Answer ellipsis appears very frequently in any dialogue, and it is present in probably all languages. Of the types of ellipsis mechanisms, answer fragments behave most like sluicing, a point that shall be illustrated below. Examples Standard instances of answer ellipsis occur in answers to questions. A question is posed, and the answer is formulated in such a manner to be maximally efficient. Just the constituent that is focused by the question word is uttered. The elided material in the examples in this article is indicated using a smaller font and subscripts: ::Q: Who walked the dog? A: Tom walked the dog. - Subject noun as answer fragment ::Q: Whom did you call? A: I called Sam. - Object noun as answer fragment ::Q: What did you try to do? A: I tried to Fix the hard drive. - Verb phrase as answer fragment ::Q: Whose house is too big? A: Fred's house is too big. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsis (linguistics)
In linguistics, ellipsis () or an elliptical construction is the omission from a clause of one or more words that are nevertheless understood in the context of the remaining elements. There are numerous distinct types of ellipsis acknowledged in theoretical syntax. Theoretical accounts of ellipsis seek to explain its syntactic and semantic factors, the means by which the elided elements are recovered, and the status of the elided elements. Background Varieties of ellipsis have long formed a basis of linguistic theory that addresses basic questions of form–meaning correspondence: in particular, how the usual mechanisms of grasping a meaning from a form may be bypassed or supplanted via elliptical structures. In generative linguistics, the term ''ellipsis'' has been applied to a range of syntax in which a perceived interpretation is fuller than that which would be expected based solely on the presence of linguistic forms. One trait that many types and instances of ellipsis h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sluicing
In syntax, sluicing is a type of ellipsis that occurs in both direct and indirect interrogative clauses. The ellipsis is introduced by a ''wh''-expression, whereby in most cases, everything except the ''wh''-expression is elided from the clause. Sluicing has been studied in detail in the early 21st century and it is therefore a relatively well-understood type of ellipsis. Sluicing occurs in many languages. Basic examples Sluicing is illustrated with the following examples. In each case, an embedded question is understood though only a question word or phrase is pronounced. (The intended interpretations of the question-denoting elliptical clause are given in parentheses; parts of these are anaphoric to the boldface material in the antecedent.) ::Phoebe ate something, but she doesn't know what. (=what she ate) ::Jon doesn't like the lentils, but he doesn't know why. (=why he doesn't like the lentils) ::Someone has eaten the soup. Unfortunately, I don't know who. (=who has eaten th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gapping
In linguistics, gapping is a type of ellipsis that occurs in the non-initial conjuncts of coordinate structures. Gapping usually elides minimally a finite verb and further any non-finite verbs that are present. This material is "gapped" from the non-initial conjuncts of a coordinate structure. Gapping exists in many languages, but by no means in all of them, and gapping has been studied extensively and is therefore one of the more understood ellipsis mechanisms. Stripping is viewed as a particular manifestation of the gapping mechanism where just one remnant (instead of two or more) appears in the gapped/stripped conjunct. Basic examples Canonical examples of gapping have a true "gap", which means the elided material appears medially in the non-initial conjuncts, with a remnant to its left and a remnant to its right. The elided material of gapping in all the examples below is indicated with subscripts and a smaller font: ::Some ate bread, and others ate rice. ::Fred likes to pet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb Phrase Ellipsis
In linguistics, Verb phrase ellipsis (VP ellipsis or VPE) is a type of Ellipsis (linguistics), grammatical omission where a verb phrase is left out (elided) but its meaning can still be inferred from context. For example, "''She will sell sea shells, and he will too''" is understood as "''She will sell sea shells, and he will sell sea shells too''" (tree structure illustrated to the right). VP ellipsis is well-studied, particularly in English, where auxiliary verbs (e.g., will, can, do) play a crucial role in recovering the omitted verb phrase. The reliance on auxiliary verbs gives English a distinctive mechanism for VP ellipsis, making it one of the most researched languages in this area. VP ellipsis can occur partially (e.gargument ellipsis or as a whole verb phrase. For instance, Japanese employs a phenomenon known as verb-stranding VP ellipsis, where the verb remains while the rest of the phrase is elided. This cross-linguistic perspective reveals that VP ellipsis is not unique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudogapping
Pseudogapping is an ellipsis mechanism that elides most but not all of a non-finite verb phrase; at least one part of the verb phrase remains, which is called the ''remnant''. Pseudogapping occurs in comparative and contrastive contexts, so it appears often after subordinators and coordinators such as ''if'', ''although'', ''but'', ''than'', etc. It is similar to verb phrase ellipsis (VP-ellipsis) insofar as the ellipsis is introduced by an auxiliary verb, and many grammarians take it to be a particular type of VP-ellipsis. The distribution of pseudogapping is more restricted than that of VP-ellipsis, however, and in this regard, it has some traits in common with gapping. But unlike gapping (but like VP-ellipsis), pseudogapping occurs in English but not in closely related languages. The analysis of pseudogapping can vary greatly depending in part on whether the analysis is based in a phrase structure grammar or a dependency grammar. Pseudogapping was first identified, named, and exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constituent (linguistics)
In syntactic analysis, a constituent is a word or a group of words that function as a single unit within a hierarchical structure. The constituent structure of sentences is identified using ''tests for constituents''. These tests apply to a portion of a sentence, and the results provide evidence about the constituent structure of the sentence. Many constituents are phrases. A phrase is a sequence of one or more words (in some theories two or more) built around a head lexical item and working as a unit within a sentence. A word sequence is shown to be a phrase/constituent if it exhibits one or more of the behaviors discussed below. The analysis of constituent structure is associated mainly with phrase structure grammars, although dependency grammars also allow sentence structure to be broken down into constituent parts. Tests for constituents in English Tests for constituents are diagnostics used to identify sentence structure. There are numerous tests for constituents that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase Structure Grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammar studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue ( Post canonical systems). Some authors, however, reserve the term for more restricted grammars in the Chomsky hierarchy: context-sensitive grammars or context-free grammars. In a broader sense, phrase structure grammars are also known as ''constituency grammars''. The defining character of phrase structure grammars is thus their adherence to the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation of dependency grammars. History In 1956, Chomsky wrote, "A phrase-structure grammar is defined by a finite vocabulary (alphabet) Vp, and a finite set Σ of initial strings in Vp, and a finite set F of rules of the form: X → Y, where X and Y are strings in Vp." Constituency relation In linguistics, phrase structure grammars are all those grammars that are based on the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependency Grammar
Dependency grammar (DG) is a class of modern Grammar, grammatical theories that are all based on the dependency relation (as opposed to the ''constituency relation'' of Phrase structure grammar, phrase structure) and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency is the notion that linguistic units, e.g. words, are connected to each other by directed links. The (finite) verb is taken to be the structural center of clause structure. All other syntactic units (words) are either directly or indirectly connected to the verb in terms of the directed links, which are called ''dependencies''. Dependency grammar differs from phrase structure grammar in that while it can identify phrases it tends to overlook phrasal nodes. A dependency structure is determined by the relation between a word (a Head (linguistics), head) and its dependents. Dependency structures are flatter than phrase structures in part because they lack a finite verb, finite verb phrase constit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Answer Ellipsis1
Answer commonly refers to a response to a question. Answer may also refer to: Music * Answer, an element of a fugue Albums * ''Answer'' (Angela Aki album), 2009 * ''Answer'' (Supercar album), 2004 * ''Answers'' (album), 1994 * '' The Answers'', an album by Blue October Songs * "Answer" (Tohoshinki song) * "Answer" (Flow song), 2007 * "Answer" (Tyler, the Creator song), 2013 *"Answer", by Sarah McLachlan from her 2003 album '' Afterglow'' *"Answer", by Mayu Maeshima, opening song from the 2021 anime '' Full Dive'' *"Answer", by Ateez Publications * ''Answers'' (periodical), British weekly paper founded in 1888, initially titled ''Answers to Correspondents'' *''Answers'', an American magazine published by Answers in Genesis *"Answer", a 1954 science-fiction story by Fredric Brown Answer engines * Answers.com * Yahoo! Answers Other uses * Answer (law), any reply to a question, counter-statement or defense in a legal procedure * HMS ''Answer'', a British Royal Navy sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extraction Island
In linguistics, wh-movement (also known as wh-fronting, wh-extraction, or wh-raising) is the formation of syntactic dependencies involving interrogative words. An example in English is the dependency formed between ''what'' and the object position of ''doing'' in "What are you doing?". Interrogative forms are sometimes known within English linguistics as '' wh-words'', such as ''what, when, where, who'', and ''why'', but also include other interrogative words, such as ''how''. This dependency has been used as a diagnostic tool in syntactic studies as it can be observed to interact with other grammatical constraints. In languages with wh- movement, sentences or clauses with a wh-word show a non-canonical word order that places the wh-word (or phrase containing the wh-word) at or near the front of the sentence or clause ("''Whom'' are you thinking about?") instead of the canonical position later in the sentence ("I am thinking about ''you''"). Leaving the wh-word in its canonical posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |