|
Anselm Of Capraia
Anselm of Capraia was a Pisan count. His political activity extended from the Republic of Pisa to Sardinia. Anselm was the son of Berthold, brother of William and Anselm, all three of whom went to the court of Peter II of Arborea to be educated. Anselm's mother was a daughter of Guelfo della Gherardesca, Count of Donoratico, and Uguccionella degli Uppezinghi. Anselm was sent by the Commune of Pisa in 1273 to Gallura to fight against the judge Giovanni Visconti, who had fled from Pisa recently. He defeated him in the hard-to-defend open plain between Trexenta and Gippi. Anselm occupied the Visconti estates, but it is not known if only those in the ''curatoria'' of Gippi or those in the third of Cagliari which Giovanni had acquired as well. However, Giovanni evaded capture and returned to Tuscany on a Sicilian ship. Anselm took over the reins of government in the Giudicato of Arborea after the imprisonment and assassination of his cousin Nicholas by the real judge, Marianus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisa
Pisa ( , or ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, central Italy, straddling the Arno just before it empties into the Ligurian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa. Although Pisa is known worldwide for its leaning tower, the city contains more than twenty other historic churches, several medieval palaces, and bridges across the Arno. Much of the city's architecture was financed from its history as one of the Italian maritime republics. The city is also home to the University of Pisa, which has a history going back to the 12th century, the Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa, founded by Napoleon in 1810, and its offshoot, the Sant'Anna School of Advanced Studies.Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna di Pisa Information statistics History ...
|
Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; it, Toscana ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of about 3.8 million inhabitants. The regional capital is Florence (''Firenze''). Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, artistic legacy, and its influence on high culture. It is regarded as the birthplace of the Italian Renaissance and of the foundations of the Italian language. The prestige established by the Tuscan dialect's use in literature by Dante Alighieri, Petrarch, Giovanni Boccaccio, Niccolò Machiavelli and Francesco Guicciardini led to its subsequent elaboration as the language of culture throughout Italy. It has been home to many figures influential in the history of art and science, and contains well-known museums such as the Uffizi and the Palazzo Pitti. Tuscany is also known for its wines, including Chianti, Vino Nobile di Montepulciano, Morellino di Scansano, Brunello di Montalcino and white Vernaccia di San Gimignano. Having a strong linguisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Pisa
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1287 Deaths
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divine Comedy
The ''Divine Comedy'' ( it, Divina Commedia ) is an Italian narrative poem by Dante Alighieri, begun 1308 and completed in around 1321, shortly before the author's death. It is widely considered the pre-eminent work in Italian literature and one of the greatest works of world literature. The poem's imaginative vision of the afterlife is representative of the medieval worldview as it existed in the Western Church by the 14th century. It helped establish the Tuscan language, in which it is written, as the standardized Italian language. It is divided into three parts: ''Inferno'', ''Purgatorio'', and '' Paradiso''. The narrative takes as its literal subject the state of the soul after death and presents an image of divine justice meted out as due punishment or reward, and describes Dante's travels through Hell, Purgatory, and Heaven. Allegorically, the poem represents the soul's journey towards God, beginning with the recognition and rejection of sin (''Inferno''), followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dante Alighieri
Dante Alighieri (; – 14 September 1321), probably baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante (, ), was an Italian poet, writer and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', originally called (modern Italian: ''Commedia'') and later christened by Giovanni Boccaccio, is widely considered one of the most important poems of the Middle Ages and the greatest literary work in the Italian language. Dante is known for establishing the use of the vernacular in literature at a time when most poetry was written in Latin, which was accessible only to the most educated readers. His ''De vulgari eloquentia'' (''On Eloquence in the Vernacular'') was one of the first scholarly defenses of the vernacular. His use of the Florentine dialect for works such as '' The New Life'' (1295) and ''Divine Comedy'' helped establish the modern-day standardized Italian language. His work set a precedent that important Italian writers such as Petrarch and Boccaccio would later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ugolino Della Gherardesca
Ugolino della Gherardesca (March 1289), Count of Donoratico, was an Italian nobleman, politician and naval commander. He was frequently accused of treason and features prominently in Dante's ''Divine Comedy''. Biography In the 13th century, the states of Italy were beset by the strife of two parties, the Ghibellines and the Guelphs. While the conflict was local and personal in origin, the parties had come to be associated with the two universal powers: the Ghibellines sided with the Holy Roman Emperor and his rule of Italy, while the Guelphs sided with the Pope, who supported self-governing city-states. Pisa was controlled by the Ghibellines, while most of the surrounding cities were controlled by the Guelphs, most notably Pisa's trading rivals Genoa and Florence. Under the circumstances, Pisa adopted the "strong and vigilant government" of a "armed with almost despotic power"."Count Ugolino of Pisa", ''Bentley’s Miscellany'' 55 (1864), p. 173–78. Ugolino was born in Pisa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gherardo Della Gherardesca
Gherardo is a given name. Notable people with the name include: *Gherardo Appiani (1370–1405), the lord of Piombino from 1398 until his death * Gherardo Bosio (1903–1941), Italian architect, engineer and urbanist *Gherardo III da Camino (1240–1306), Italian feudal lord and military leader * Giovanni Gherardo Dalle Catene (1520–1533), Italian painter of the Renaissance *Gherardo Cibo (1512–1600), artist and a herbalist from Italy *Gherardo Colombo (born 1946), Italian former magistrate and judge * Gherardo da Cremona (1114–1187), Italian translator of scientific books from Arabic into Latin * Gherardo D'Ambrosio (1930–2014), Italian magistrate and politician *Gherardo di Giovanni del Fora (1445–1497), Italian painter * Maffeo Gherardo (1406–1492), Italian Roman Catholic bishop and cardinal * Gherardo Gossi (born 1958), Italian cinematographer * Gherardo della Notte (1592–1656), Dutch Golden Age painter * Gherardo Perini, model for Michelangelo who came to work for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marianus II Of Arborea
Marianus II ( Sardinian: ''Marianu II'', Italian: ''Mariano II'') (died 1297) was the Judge of Arborea from 1241 to his death. With skilled military action, he came to control more than half of the island of Sardinia. By his control of the vast central plains and the rich deposits of precious metals, he increased the riches of his Judicate and staved off the general economic decline affecting the rest of Europe at the time. Biography He was the son and successor of Peter II of Arborea of the Bas-Serra family and a local woman named Sardinia. He succeeded to the throne at a young age under the regency of William of Capraia, a distant relative. William was the son of Bina de Lacon, widow of Peter I, and Hugh of Capraia, Count of Prato. William and his brothers Anselm and Berthold were pupils at the court of Peter II, who designated William regent for his son. On William's death in 1264, Marianus did not take the full reins of power, but instead had to recognize the co-dominion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Of Capraia
Nicholas of Capraia (died 1274) was the Judge of Arborea The Kings or ''Judges'' (from the Latin ''iudices'' and the Sardinian ', "judges," the title of the Byzantine officials left behind when Imperial power receded in the West) of the Arborea were the local rulers of the west of Sardinia during t ... from 1264 to his assassination ten years later. Nicholas was the eldest son and successor of William of Capraia, who had usurped the judicial office of Arborea from Marianus II in 1255. On William's death in 1264, Nicholas took up his authority, but he was imprisoned by Marianus in 1270 and remained in prison until Marianus decided to remove him permanently in 1274. His cousin Anselm tried to take his authority back in Cagliari. 1274 deaths Judges (judikes) of Arborea Year of birth unknown {{Italy-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
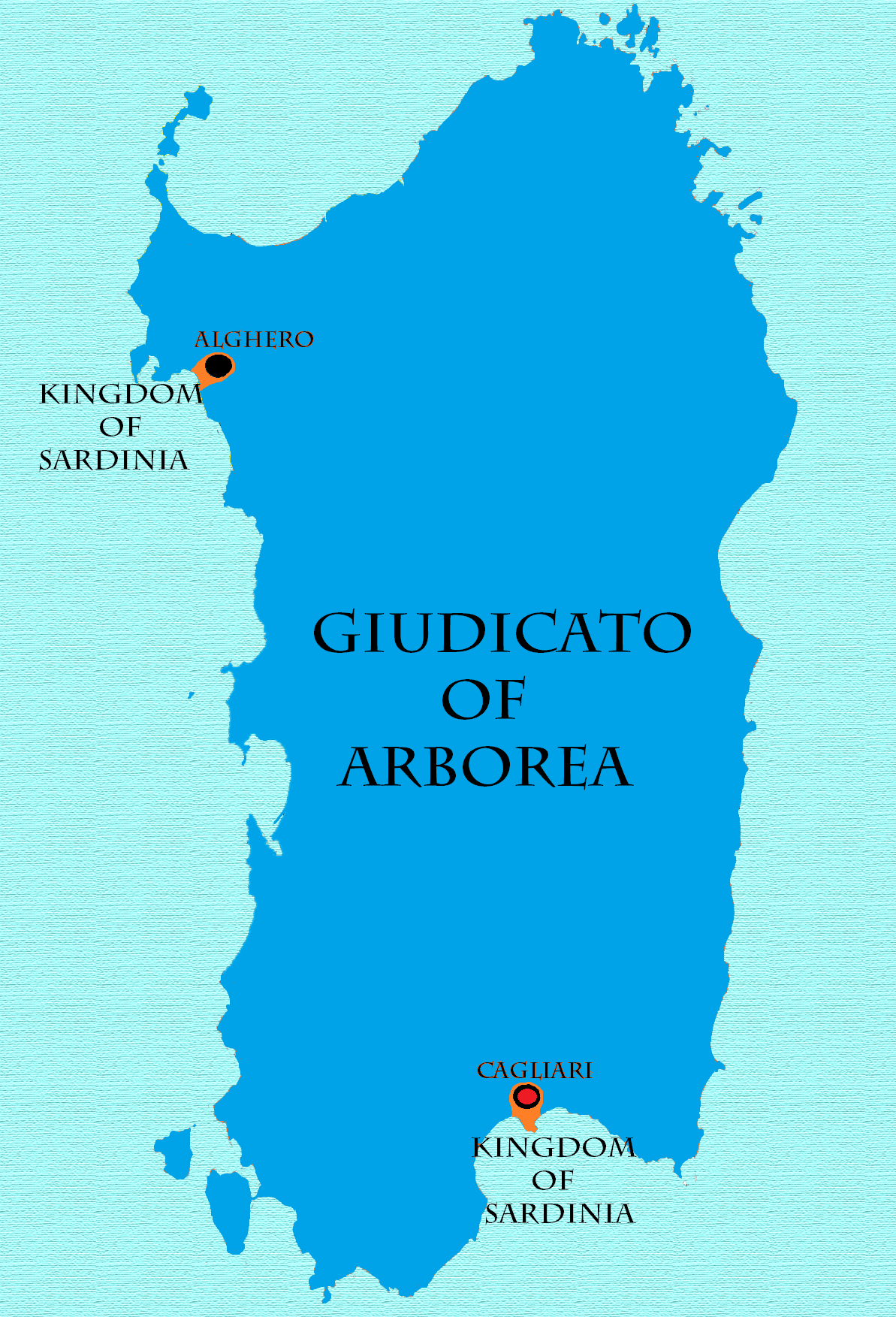
Giudicato Of Arborea
The Judicate of Arborea ( sc, Judicadu de Arbaree, it, Giudicato di Arborea, ) or the Kingdom of Arborea (, , ) was one of the four independent judicates into which the island of Sardinia was divided in the Middle Ages. It occupied the central-west portion of the island, wedged between Logudoro to the north and east, Cagliari to the south and east, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. To the north east and beyond Logudoro was located Gallura, with which Arborea had far less interaction. Arborea outlasted her neighbours, surviving well into the 15th century. The earliest known judicial seat was Tharros. The Judicate of Arborea at the times of its maximum expansion occupied the whole island's territory, except the cities of Alghero and Cagliari. Origins In the early 9th century, when the Arabs and Berbers of North Africa became aggressive in expansion and piracy, the central authorities of the Byzantine Empire were unable to effectively defend or consistently govern the imperia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 until 1816. It was a successor state of the County of Sicily, which had been founded in 1071 during the Norman conquest of the southern peninsula. The island was divided into three regions: Val di Mazara, Val Demone and Val di Noto. In 1282, a revolt against Angevin rule, known as the Sicilian Vespers, threw off Charles of Anjou's rule of the island of Sicily. The Angevins managed to maintain control in the mainland part of the kingdom, which became a separate entity also styled ''Kingdom of Sicily'', although it is commonly referred to as the Kingdom of Naples, after its capital. From 1282 to 1409 the island was ruled by the Spanish Crown of Aragon as an independent kingdom, then it was added permanently to the Crown. After 1302, the isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_1938.jpg)


.jpg)