|
Animal Attack
Animal attacks are violent attacks caused by non-human animals against humans, one of the most common being bites. These attacks are a cause of human injuries and fatalities worldwide. According to the ''2012 U.S. Pet Ownership & Demographics Sourcebook'', 56% of United States citizens owned a pet. In the United States in 1994, approximately 4.7 million people were bitten by dogs. The frequency of animal attacks varies with geographical location, as well as hormonal secretion. Gonad glands found on the anterior side of the pituitary gland secrete androgens and estrogens hormones. Animals with high levels of these hormones tend to be more aggressive, which leads to a higher frequency of attacks not only to humans but among themselves. In the United States, a person is more likely to be killed by a domesticated dog than they are to die from being hit by lightning according to the National Safety Council. Animal attacks have been identified as a major public health problem. In 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Report Dog Bites LCCN93511152
A report is a document that presents information in an organized format for a specific audience and purpose. Although summaries of reports may be delivered orally, complete reports are almost always in the form of written documents. Usage In modern business scenario, reports play a major role in the progress of business. Reports are the backbone to the thinking process of the establishment and they are responsible, to a great extent, in evolving an efficient or inefficient work environment. The significance of the reports includes: * Reports present adequate information on various aspects of the business. * All the skills and the knowledge of the professionals are communicated through reports. * Reports help the top line in decision making. * A rule and balanced report also helps in problem solving. * Reports communicate the planning, policies and other matters regarding an organization to the masses. News reports play the role of ombudsman and levy checks and balances on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents ( pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. ''Mycobacterium tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capnocytophaga Canimorsus
''Capnocytophaga canimorsus'' is a Fastidious organism, fastidious, slow-growing, Gram-negative rod of the genus ''Capnocytophaga''.Pers C, Gahrn-Hansen B, and Frederiksen W. 1996. ''Capnocytophaga canimorsus'' Septicemia in Denmark, 1982-1995: Review of 39 Cases. ''Clinical Infectious Diseases'' 23: 71-75.Brenner DJ, Hollis DG, Fanning GR, and Weaver RE. 1989. ''Capnocytophaga canimorsus'' sp. nov. (Formerly CDC Group DF-2), a Cause of Septicemia following Dog Bite, and ''C. cynodegmi'' sp. nov., a Cause of Localized Wound Infection following Dog Bite. ''Journal of Clinical Microbiology'' 27 (2): 231-235. It is a Commensalism, commensal bacterium in the normal gingival flora of canine and feline species, but can cause illness in humans. Transmission may occur through bites, licks, or even close proximity with animals.Fischer LJ, Weyant RS, White EH and Quinn FD. Intracellular Multiplication and Toxic Destruction of Cultured Macrophages by ''Capnocytophaga canimorsus''. ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteroides
''Bacteroides'' is a genus of Gram-negative, obligate anaerobic bacteria. ''Bacteroides'' species are non endospore-forming bacilli, and may be either motile or nonmotile, depending on the species. The DNA base composition is 40–48% GC. Unusual in bacterial organisms, ''Bacteroides'' membranes contain sphingolipids. They also contain meso-diaminopimelic acid in their peptidoglycan layer. ''Bacteroides'' species are normally mutualistic, making up the most substantial portion of the mammalian gastrointestinal microbiota, where they play a fundamental role in processing of complex molecules to simpler ones in the host intestine. As many as 1010–1011 cells per gram of human feces have been reported. They can use simple sugars when available; however, the main sources of energy for ''Bacteroides'' species in the gut are complex host-derived and plant glycans. Studies indicate that long-term diet is strongly associated with the gut microbiome composition—those who eat ple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusobacterium
''Fusobacterium'' is a genus of anaerobic, Gram-negative, non-sporeforming bacteria belonging to Gracilicutes. Individual cells are slender, rod-shaped bacilli with pointed ends. Strains of ''Fusobacterium'' cause several human diseases, including periodontal diseases, Lemierre's syndrome, and topical skin ulcers. Although older sources state that ''Fusobacterium'' is part of the normal flora of the human oropharynx, the current consensus is that ''Fusobacterium'' should always be treated as a pathogen. ''F. prausnitzii'', a gut commensal associated with healthy patients, was completely reclassified as '' Faecalibacterium'' (''Clostridiales'':''Ruminococcaceae'') in 2002. Clinical relevance ''Fusobacterium'' is often associated with ulcerative colitis. Research of colon cancer has also shown an overrepresentation of ''Fusobacterium'', both in feces of patients and tumor issue itself. Whether ''Fusobacterium'' causes these diseases or only colonizes existing tumours, remains unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
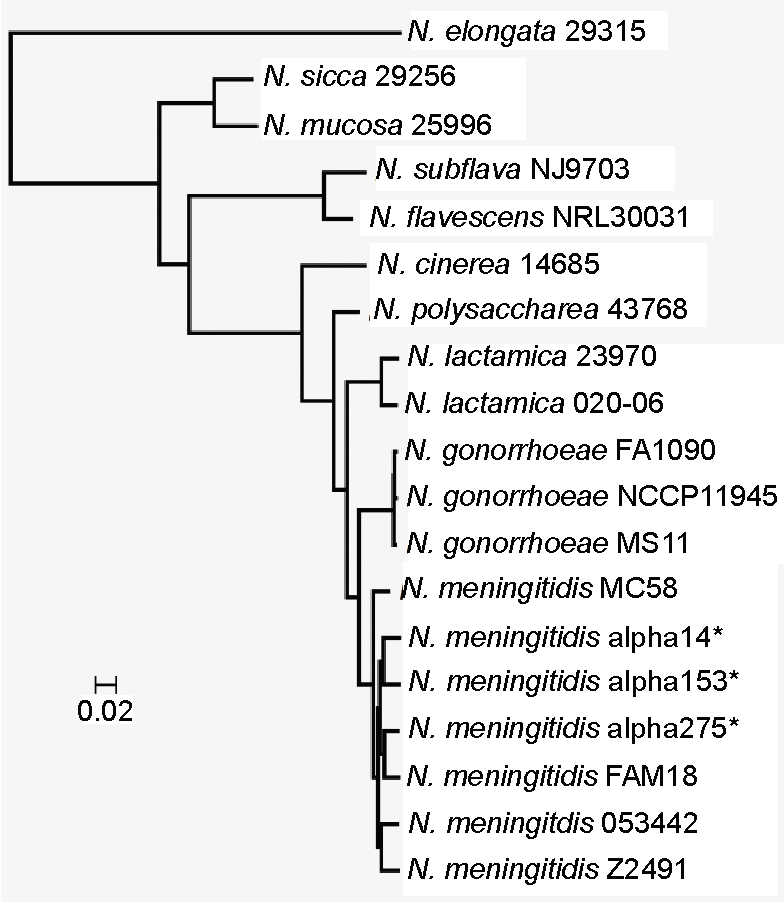
Neisseria
''Neisseria'' is a large genus of bacteria that colonize the mucosal surfaces of many animals. Of the 11 species that colonize humans, only two are pathogens, ''N. meningitidis'' and '' N. gonorrhoeae''. ''Neisseria'' species are Gram-negative bacteria included among the Pseudomonadota, a large group of Gram-negative forms. ''Neisseria'' diplococci resemble coffee beans when viewed microscopically. Pathogenesis and classification Pathogens Species of this genus (family Neisseriaceae) of parasitic bacteria grow in pairs and occasionally tetrads, and thrive best at 98.6 °F (37 °C) in the animal body or serum media. The genus includes: * '' N. gonorrhoeae'' (also called the gonococcus) causes gonorrhea. * ''N. meningitidis'' (also called the meningococcus) is one of the most common causes of bacterial meningitis and the causative agent of meningococcal septicaemia. These two species have the ability of 'breaching' the barrier. Local cytokines of the area become sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corynebacterium
''Corynebacterium'' () is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria and most are aerobic. They are bacilli (rod-shaped), and in some phases of life they are, more specifically, club-shaped, which inspired the genus name ('' coryneform'' means "club-shaped"). They are widely distributed in nature in the microbiota of animals (including the human microbiota) and are mostly innocuous, most commonly existing in commensal relationships with their hosts. Some, such as '' C. glutamicum'', are commercially useful. Others can cause human disease, including, most notably, diphtheria, which is caused by ''C. diphtheriae''. As with various species of amicrobiota (including their relatives in the genera '' Arcanobacterium'' and ''Trueperella''), they usually are not pathogenic, but can occasionally opportunistically capitalize on atypical access to tissues (via wounds) or weakened host defenses. Taxonomy The genus ''Corynebacterium'' was created by Lehmann and Neumann in 1896 as a taxono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moraxella
''Moraxella'' is a genus of gram-negative bacteria in the family Moraxellaceae. It is named after the Swiss ophthalmologist Victor Morax. The organisms are short rods, coccobacilli, or as in the case of ''Moraxella catarrhalis'', diplococci in morphology, with asaccharolytic, oxidase-positive, and catalase-positive properties.Ala'Aldeen, D. A. A. (2007). "Neisseria and moraxella". In Greenwood, David; Slack, Richard; Peitherer, John; & Barer, Mike (Eds.), ''Medical Microbiology'' (17th ed.), p. 258. Elsevier. . ''M. catarrhalis'' is the clinically most important species under this genus. Roles in disease The organisms are commensals of mucosal surfaces and sometimes give rise to opportunistic infection. * ''M. catarrhalis'' usually resides in respiratory tract, but can gain access to the lower respiratory tract in patients with chronic chest disease or compromised host defenses, thus causing tracheobronchitis and pneumonia. For example, it causes a significant proportion of lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus
''Staphylococcus'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical ( cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically). The name was coined in 1880 by Scottish surgeon and bacteriologist Alexander Ogston (1844–1929), following the pattern established five years earlier with the naming of '' Streptococcus''. It combines the prefix "staphylo-" (from grc, σταφυλή, staphylē, bunch of grapes), and suffixed by the Modern (from ). Staphylococcus was one of the leading infections in hospitals and many strains of this bacterium have become antibiotic resistant. Despite strong attempts to get rid of them, staph bacteria stay present in hospitals, where they can infect people who are most at risk of infection. Staphylococcus includes at least 43 species. Of these, nine have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive ' (plural ) or spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs along a single axis, so as they grow, they tend to form pairs or chains that may appear bent or twisted. This differs from staphylococci, which divide along multiple axes, thereby generating irregular, grape-like clusters of cells. Most streptococci are oxidase-negative and catalase-negative, and many are facultative anaerobes (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically). The term was coined in 1877 by Viennese surgeon Albert Theodor Billroth (1829–1894), by combining the prefix "strepto-" (from ), together with the suffix "-coccus" (from Modern , from .) In 1984, many bacteria formerly grouped in the genus ''Streptococcus'' were separated out into the genera '' Enterococcus'' and '' Lactococcus''. Currently, over 50 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasturella
''Pasteurella multocida'' is a Gram-negative, nonmotile, penicillin-sensitive coccobacillus of the family Pasteurellaceae. Strains of the species are currently classified into five serogroups (A, B, D, E, F) based on capsular composition and 16 somatic serovars (1–16). ''P. multocida'' is the cause of a range of diseases in mammals and birds, including fowl cholera in poultry, atrophic rhinitis in pigs, and bovine hemorrhagic septicemia in cattle and buffalo. It can also cause a zoonotic infection in humans, which typically is a result of bites or scratches from domestic pets. Many mammals (including domestic cats and dogs) and birds harbor it as part of their normal respiratory microbiota. History ''Pasteurella multocida'' was first found in 1878 in cholera-infected birds. However, it was not isolated until 1880, by Louis Pasteur, in whose honor ''Pasteurella'' is named. Disease :''See: Pasteurellosis'' ''P. multocida'' causes a range of diseases in wild and domesticate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |