|
Anem (ancient City)
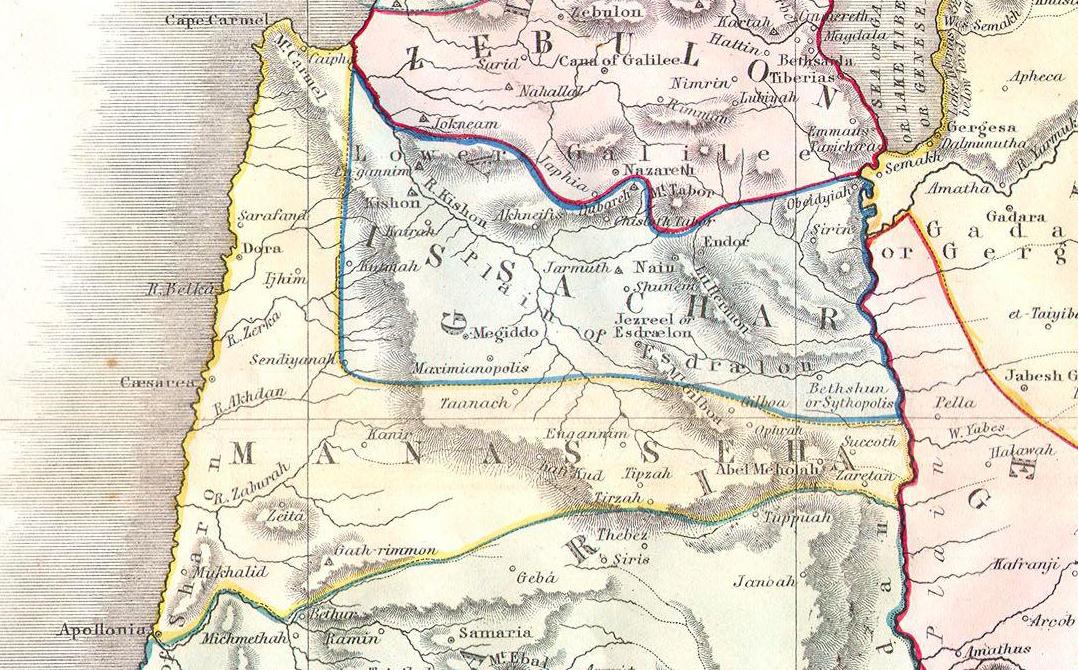
Anem or Anim was a Levitical city in Israel allocated to the Gershonites, according to the Hebrew Bible, from the land of the tribe of Issachar () (6:58 in some Bibles). In the parallel location in the Book of Joshua, the name ''En-gannim'' or ''Engannim'' appears, and the two names may refer to the same town. The location of Anem is unknown. William F. Albright William Foxwell Albright (May 24, 1891– September 19, 1971) was an American archaeologist, biblical scholar, philologist, and expert on ceramics. He is considered "one of the twentieth century's most influential American biblical scholars." ... suggested that Anem was the same location as En-gannim, the two spellings being variants of a single original site ''ʕen-ʕonam''. But Hagen Martino (in 1907), claimed that Anem is 'probably a distinct site', near En-gannim.e.g., Martino (Ed.). ''Atlas Biblicus. Continens Duas Et Viginti Tabulas Quibus Accedit. Index topographicus in Universam Geographam Biblicam'', Paris (S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levitical City
In the Hebrew Bible, the Levitical cities were 48 cities in ancient Israel set aside for the tribe of Levi, who were not allocated their own territorial land when the Israelites entered the Promised Land. Numbers 35:1-8 relates God's command to Moses to establish 48 cities for the Levites, of which six would also function as Cities of Refuge to which manslayers could flee. Each settlement was to comprise a walled city and the common land around it for pasture, measured radially as one thousand cubits in each direction, or as a square measuring two thousand cubits along each side. The land for the cities was to be 'donated' by the host tribe and was allocated to the Levites according to their tribal sub-divisions. 13 cities were for the Aaronites. 13 cities were for the Gershonites. 10 cities were for the Kohathites. 12 cities were for the Merarites. The six cities which were to be Cities of Refuge were Golan, Ramoth, and Bezer, on the east of the Jordan River, and Kedesh, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Israel
The history of ancient Israel and Judah begins in the Southern Levant during the Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age. "Israel" as a people or tribal confederation (see Israelites) appears for the first time in the Merneptah Stele, an inscription from ancient Egypt that dates to about 1208 BCE. According to modern archaeology, ancient Israelite culture developed as an outgrowth from the Canaanites. Two related Israelite polities known as the Kingdom of Israel and the Kingdom of Judah had emerged in the region by Iron Age II. According to the Hebrew Bible, a "United Monarchy" (consisting of Israel and Judah) existed as early as the 11th century BCE, under the reigns of Saul, David, and Solomon; the country later would have split into two separate kingdoms: Israel (containing the cities of Shechem and Samaria) in the north and Judah (containing Jerusalem and the Jewish Temple) in the south. The historicity of the United Monarchy is debated as there are no archaeological remai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gershonite
The Gershonites were one of the four main divisions among the Levites in Biblical times. The Bible claims that the Gershonites were all descended from the eponymous ''Gershon'' a son of Levi (not to be confused with Moses' son Gershom), although some biblical scholars regard this as a postdictional metaphor providing an aetiology of the connectedness of the clan to others in the Israelite confederation. '' Peake's Commentary on the Bible''''Jewish Encyclopedia'' The Bible lists 2 major family divisions of the Gershonites, the Libnites and the Shimeites (Numbers 3:21). The Bible ascribes a specific religious function to the Gershonites, namely care of the curtains, hangings, and ropes of the sanctuary. This differentiation of religious activity between the Gershonites and other Levites, in particular the Aaronids, is found only in the Priestly Code, and not in passages that textual scholars attribute to other authors. According to the Book of Joshua, rather than possessing a cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach" ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tānāḵh''), also known in Hebrew as Miqra (; Hebrew: ''Mīqrā''), is the Biblical canon, canonical collection of Hebrew language, Hebrew scriptures, including the Torah, the Nevi'im, and the Ketuvim. Different branches of Judaism and Samaritanism have maintained different versions of the canon, including the 3rd-century Septuagint text used by Second-Temple Judaism, the Syriac language Peshitta, the Samaritan Torah, the Dead Sea Scrolls, and most recently the 10th century medieval Masoretic Text, Masoretic text created by the Masoretes currently used in modern Rabbinic Judaism. The terms "Hebrew Bible" or "Hebrew Canon" are frequently confused with the Masoretic text, however, this is a medieval version and one of several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe Of Issachar
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Issachar () was one of the twelve tribes of Israel and one of the ten lost tribes. In Jewish tradition, the descendants of Issachar were seen as being dominated by religious scholars and influential in proselytism. The sons of Issachar, ancestors of the tribe, were Tola, Phuvah, Job and Shimron. Biblical narrative In the biblical narrative of the Book of Joshua, following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes, Joshua allocated the land among the twelve tribes. The territory allocated to Issachar stretched from the Jordan River in the east to Mount Carmel on the west, near to the Mediterranean coast, including the fertile Esdraelon plain between present-day Lower Galilee and Samaria. It was bounded on the east by East Manasseh, the south by West Manasseh, and the north by Zebulun and Naphtali. There is a consensus among scholars that the accounts in the Book of Judges are not historically reliable. Alternati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Joshua
The Book of Joshua ( he, סֵפֶר יְהוֹשֻׁעַ ', Tiberian: ''Sēp̄er Yŏhōšūaʿ'') is the sixth book in the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament, and is the first book of the Deuteronomistic history, the story of Israel from the conquest of Canaan to the Babylonian exile. It tells of the campaigns of the Israelites in central, southern and northern Canaan, the destruction of their enemies, and the division of the land among the Twelve Tribes, framed by two set-piece speeches, the first by God commanding the conquest of the land, and, at the end, the second by Joshua warning of the need for faithful observance of the Law (''torah'') revealed to Moses. Almost all scholars agree that the Book of Joshua holds little historical value for early Israel and most likely reflects a much later period. The earliest parts of the book are possibly chapters 2–11, the story of the conquest; these chapters were later incorporated into an early form of Joshua likely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William F
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German ''Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the name shoul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Minor Biblical Places
This is a list of places mentioned in the Bible, which do not have their own Wikipedia articles. See also the list of biblical places for locations which do have their own article. A Abana Abana, according to 2 Kings 5:12, was one of the "rivers of Damascus", along with the Pharpar river. Abdon Abdon was a Levitical city in Asher allocated to the Gershonites according to Joshua 21:30 and 1 Chronicles 6:74. Abel-Shittim Abel-Shittim, the last Israelite encampment before crossing into the Promised Land, is identified by Josephus with Abila in Peraea, probably the site of modern Tell el-Hammam in Jordan. Adam Adam was a location which, according to Joshua 3:16, was along the Jordan River, near Zarethan. According to Cheyne and Black, it may be a scribal error for "Adamah". Adadah Adadah is the name of a town mentioned in Joshua 15:22, in a list of towns inside the territory of the Tribe of Judah. The name "Adadah" appears nowhere else in the Bible."Adadah", in According to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |