|
Andrias Høgenni
''Andrias'' is a genus of giant salamanders. It includes the largest salamanders in the world, with ''A. japonicus'' reaching a length of , and ''A. sligoi'' reaching . While extant species are only known from East Asia, several extinct species in the genus are known from late Oligocene and Neogene aged fossils collected in Europe and North America North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ..., indicating that the genus formerly had a much wider range. Taxonomy The generic name derives from Ancient Greek ἀνδριάς, "statue". The former name was ''Megalobatrachus'', from Ancient Greek meaning "giant frog". Species Extant Based on genetic evidence, there may be more extant species in the genus. A study in 2018 found that ''A. davidianus'' '' sensu lato'' was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrias Japonicus
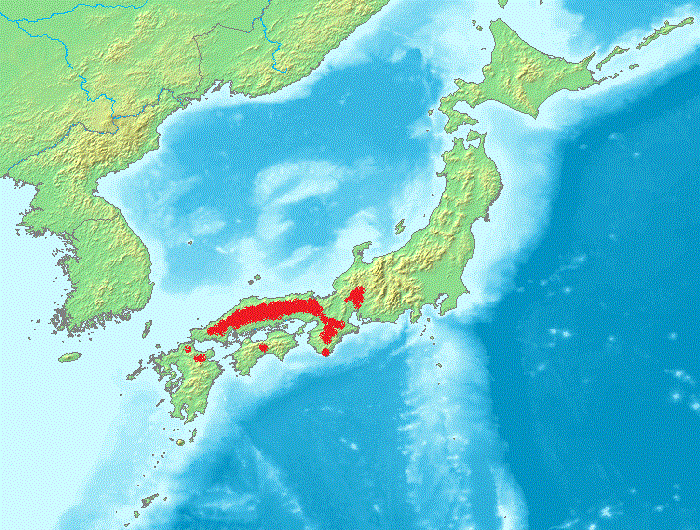
The Japanese giant salamander (''Andrias japonicus'') is a species of fully aquatic giant salamander endemic to Japan. With a length of up to ,''Andrias japonicus'' - Amphibiaweb it is the third-largest in the world, only being surpassed by the very similar and closely related (''A. davidianus''). It is known in Japanese as , literally meaning "giant salamander". Other local names include ''Hanzaki'''','' ''Hanzake','' and '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows in a generally easterly direction to the East China Sea. It is the seventh-largest river by discharge volume in the world. Its drainage basin comprises one-fifth of the land area of China, and is home to nearly one-third of the country's population. The Yangtze has played a major role in the history, culture, and economy of China. For thousands of years, the river has been used for water, irrigation, sanitation, transportation, industry, boundary-marking, and war. The prosperous Yangtze Delta generates as much as 20% of historical GDP of China, China's GDP. The Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze is the list of the largest hydroelectric power stations, largest hydro-electric power station in the world that is in use. In mid-2014, the Chine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrias Matthewi
''Andrias matthewi'', or Matthew's giant salamander, is an extinct species of giant salamander from the Miocene of North America. It belongs to the genus '' Andrias'', which contains the living Asian giant salamanders. It is the largest salamander to have ever existed, with a maximum estimated length of . Its fossils have been found in Nebraska, Colorado, and Saskatchewan. Taxonomy In 1917, Harold Cook named the new genus and species ''Plicagnathus matthewi'' for a dentary from the "lower Snake Creek beds" of Nebraska. The species was named in honor of William Diller Matthew, who first identified the specimen. In 1963, Joseph Tihen and Charles Chantell named the new species ''Cryptobranchus mccalli'' for two maxillae The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ... from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrias Matthewi Size Comparison
''Andrias'' is a genus of giant salamanders. It includes the largest salamanders in the world, with ''A. japonicus'' reaching a length of , and ''A. sligoi'' reaching . While extant species are only known from East Asia, several extinct species in the genus are known from late Oligocene and Neogene aged fossils collected in Europe and North America, indicating that the genus formerly had a much wider range. Taxonomy The generic name derives from Ancient Greek ἀνδριάς, "statue". The former name was ''Megalobatrachus'', from Ancient Greek meaning "giant frog". Species Extant Based on genetic evidence, there may be more extant species in the genus. A study in 2018 found that ''A. davidianus'' ''sensu lato'' was a species complex that consisted of at least 5 different species. ''A. sligoi'', which was formerly synonymized with ''A. davidianus'', was revived in 2019 for one of these populations, and in 2022, another of these was described as ''A. jiangxiensis''. Extinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the . The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Siberia
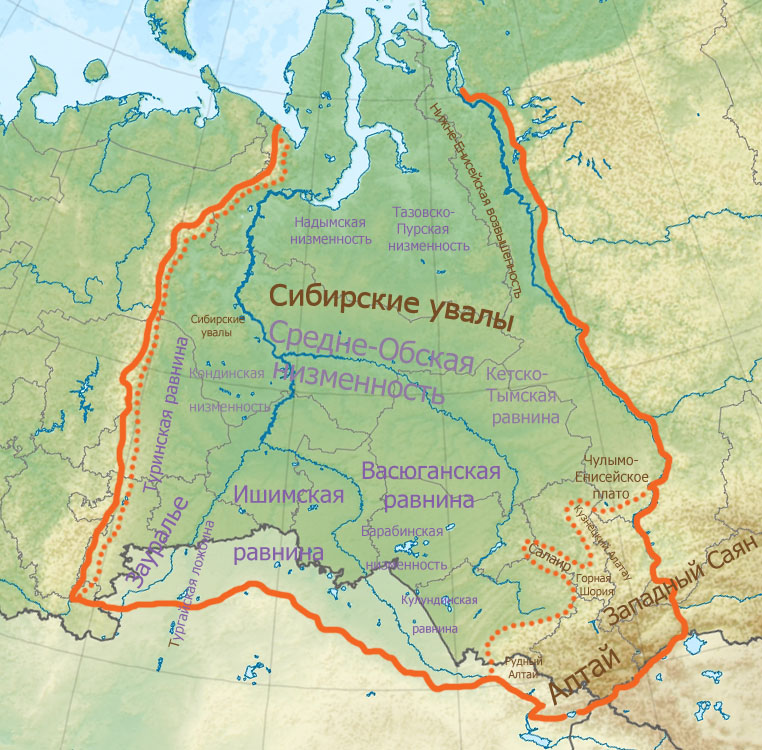
Western Siberia or West Siberia (russian: Западная Сибирь, Zapadnaya Sibir'; kk, Батыс Сібір) is a part of the larger region of Siberia that is mostly located in the Russian Federation. It lies between the Ural region and the Yenisei River, which conventionally divides Siberia into two halves. Western Siberia covers an area of , nearly 80% of which is located within the West Siberian Plain. The largest rivers of the region are the Irtysh and the Ob. The West Siberian petroleum basin is the largest hydrocarbon (petroleum and natural gas) basin in the world covering an area of about 2.2 million km2, and is also the largest oil and gas producing region in Russia. In medieval times, the region was part of the Golden Horde. After its gradual decline during the 15th century, the Khanate of Sibir, centered on Tyumen, was formed within the area. In the late 16th century, most of Western Siberia was conquered by the Russian Empire, while its southern region be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former Soviet Union, Soviet republics of the Soviet Union, republics of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, which are colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as the countries all have names ending with the Persian language, Persian suffix "-stan", meaning "land of". The current geographical location of Central Asia was formerly part of the historic region of Turkestan, Turkistan, also known as Turan. In the pre-Islamic and early Islamic eras ( and earlier) Central Asia was inhabited predominantly by Iranian peoples, populated by Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian-speaking Bactrians, Sogdians, Khwarezmian language, Chorasmians and the semi-nomadic Scythians and Dahae. After expansion by Turkic peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the area's history. The concept of "Central Europe" appeared in the 19th century. Central Europe comprised most of the territories of the Holy Roman Empire and those of the two neighboring kingdoms of Poland and Hungary. Hungary and parts of Poland were later part of the Habsburg monarchy, which also significantly shaped the history of Central Europe. Unlike their Western European (Portugal, Spain et al.) and Eastern European (Russia) counterparts, the Central European nations never had any notable colonies (either overseas or adjacent) due to their inland location and other factors. It has often been argued that one of the contributing causes of both World War I and World War II was Germany's lack of original overseas colonies. After World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrias Scheuchzeri
''Andrias scheuchzeri'' is an extinct species of giant salamander belonging to the genus ''Andrias'', which also contains the closely related living Asian giant salamanders. It is known from Oligocene to Pliocene aged deposits primarily from Central Europe, but possibly as far east as Western Siberia and eastern Kazakhstan. History In his book ''Lithographia Helvetica'' from 1726, Johann Jakob Scheuchzer described a Miocene fossil found in Öhningen as ''Homo diluvii testis'' (Latin: ''Man, witness of the Deluge''), believing it to be the remains of a human that drowned in the biblical Deluge. The fossil was about 1 m (3 ft) long, lacked its tail and hind legs, and could thus be interpreted as showing some resemblance to the remains of a violently trampled human child. In 1758, the first to doubt his theory in print was Johannes Gessner, who thought it was a giant catfish (Siluris). In 1787 Petrus Camper thought it was a lizard (Lacerta); at that time, scholars and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrias Schleuchzeri
''Andrias'' is a genus of giant salamanders. It includes the largest salamanders in the world, with ''A. japonicus'' reaching a length of , and ''A. sligoi'' reaching . While extant species are only known from East Asia, several extinct species in the genus are known from late Oligocene and Neogene aged fossils collected in Europe and North America, indicating that the genus formerly had a much wider range. Taxonomy The generic name derives from Ancient Greek ἀνδριάς, "statue". The former name was ''Megalobatrachus'', from Ancient Greek meaning "giant frog". Species Extant Based on genetic evidence, there may be more extant species in the genus. A study in 2018 found that ''A. davidianus'' ''sensu lato'' was a species complex In biology, a species complex is a group of closely related organisms that are so similar in appearance and other features that the boundaries between them are often unclear. The taxa in the complex may be able to hybridize readily with each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Complex
In biology, a species complex is a group of closely related organisms that are so similar in appearance and other features that the boundaries between them are often unclear. The taxa in the complex may be able to hybridize readily with each other, further blurring any distinctions. Terms that are sometimes used synonymously but have more precise meanings are cryptic species for two or more species hidden under one species name, sibling species for two (or more) species that are each other's closest relative, and species flock for a group of closely related species that live in the same habitat. As informal taxonomic ranks, species group, species aggregate, macrospecies, and superspecies are also in use. Two or more taxa that were once considered conspecific (of the same species) may later be subdivided into infraspecific taxa (taxa within a species, such as bacterial strains or plant varieties), that is complex but it is not a species complex. A species complex is in most cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensu Lato
''Sensu'' is a Latin word meaning "in the sense of". It is used in a number of fields including biology, geology, linguistics, semiotics, and law. Commonly it refers to how strictly or loosely an expression is used in describing any particular concept, but it also appears in expressions that indicate the convention or context of the usage. Common qualifiers ''Sensu'' is the ablative case of the noun ''sensus'', here meaning "sense". It is often accompanied by an adjective (in the same case). Three such phrases are: *''sensu stricto'' – "in the strict sense", abbreviation ''s.s.'' or ''s.str.''; *''sensu lato'' – "in the broad sense", abbreviation ''s.l.''; *''sensu amplo'' – "in a relaxed, generous (or 'ample') sense", a similar meaning to ''sensu lato''. Søren Kierkegaard uses the phrase ''sensu eminenti'' to mean "in the pre-eminent r most important or significantsense". When appropriate, comparative and superlative adjectives may also be used to convey the meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)

