|
Andrew Sutherland (mathematician)
Andrew Victor Sutherland is an American mathematician and Principal Research Scientist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. His research focuses on computational aspects of number theory and arithmetic geometry. He is known for his contributions to several projects involving large scale computations, including the Polymath project on bounded gaps between primes, the L-functions and Modular Forms Database, the sums of three cubes project, and the computation and classification of Sato-Tate distributions. Education and career Sutherland earned a bachelor's degree in mathematics from MIT in 1990. Following an entrepreneurial career in the software industry he returned to MIT and completed his doctoral degree in mathematics in 2007 under the supervision of Michael Sipser and Ronald Rivest, winning the George M. Sprowls prize for this thesis. He joined the MIT mathematics department as a Research Scientist in 2009, and was promoted to Principal Research Scientist in 2011. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics Of Computation
''Mathematics of Computation'' is a bimonthly mathematics journal focused on computational mathematics. It was established in 1943 as ''Mathematical Tables and other Aids to Computation'', obtaining its current name in 1960. Articles older than five years are available electronically free of charge. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Mathematical Reviews ''Mathematical Reviews'' is a journal published by the American Mathematical Society (AMS) that contains brief synopses, and in some cases evaluations, of many articles in mathematics, statistics, and theoretical computer science. The AMS also pu ..., Zentralblatt MATH, Science Citation Index, CompuMath Citation Index, and Current Contents/Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences. According to the '' Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 2.417. References External links * Delayed open access journals English-language journals Mathematics journals Public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number Field
In mathematics, an algebraic number field (or simply number field) is an extension field K of the field of rational numbers such that the field extension K / \mathbb has finite degree (and hence is an algebraic field extension). Thus K is a field that contains \mathbb and has finite dimension when considered as a vector space over The study of algebraic number fields, and, more generally, of algebraic extensions of the field of rational numbers, is the central topic of algebraic number theory. This study reveals hidden structures behind usual rational numbers, by using algebraic methods. Definition Prerequisites The notion of algebraic number field relies on the concept of a field. A field consists of a set of elements together with two operations, namely addition, and multiplication, and some distributivity assumptions. A prominent example of a field is the field of rational numbers, commonly denoted together with its usual operations of addition and multiplicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abelian Variety
In mathematics, particularly in algebraic geometry, complex analysis and algebraic number theory, an abelian variety is a projective algebraic variety that is also an algebraic group, i.e., has a group law that can be defined by regular functions. Abelian varieties are at the same time among the most studied objects in algebraic geometry and indispensable tools for much research on other topics in algebraic geometry and number theory. An abelian variety can be defined by equations having coefficients in any field; the variety is then said to be defined ''over'' that field. Historically the first abelian varieties to be studied were those defined over the field of complex numbers. Such abelian varieties turn out to be exactly those complex tori that can be embedded into a complex projective space. Abelian varieties defined over algebraic number fields are a special case, which is important also from the viewpoint of number theory. Localization techniques lead naturally fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Fields
In mathematics, a finite field or Galois field (so-named in honor of Évariste Galois) is a field that contains a finite number of elements. As with any field, a finite field is a set on which the operations of multiplication, addition, subtraction and division are defined and satisfy certain basic rules. The most common examples of finite fields are given by the integers mod when is a prime number. The ''order'' of a finite field is its number of elements, which is either a prime number or a prime power. For every prime number and every positive integer there are fields of order p^k, all of which are isomorphic. Finite fields are fundamental in a number of areas of mathematics and computer science, including number theory, algebraic geometry, Galois theory, finite geometry, cryptography and coding theory. Properties A finite field is a finite set which is a field; this means that multiplication, addition, subtraction and division (excluding division by zero) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
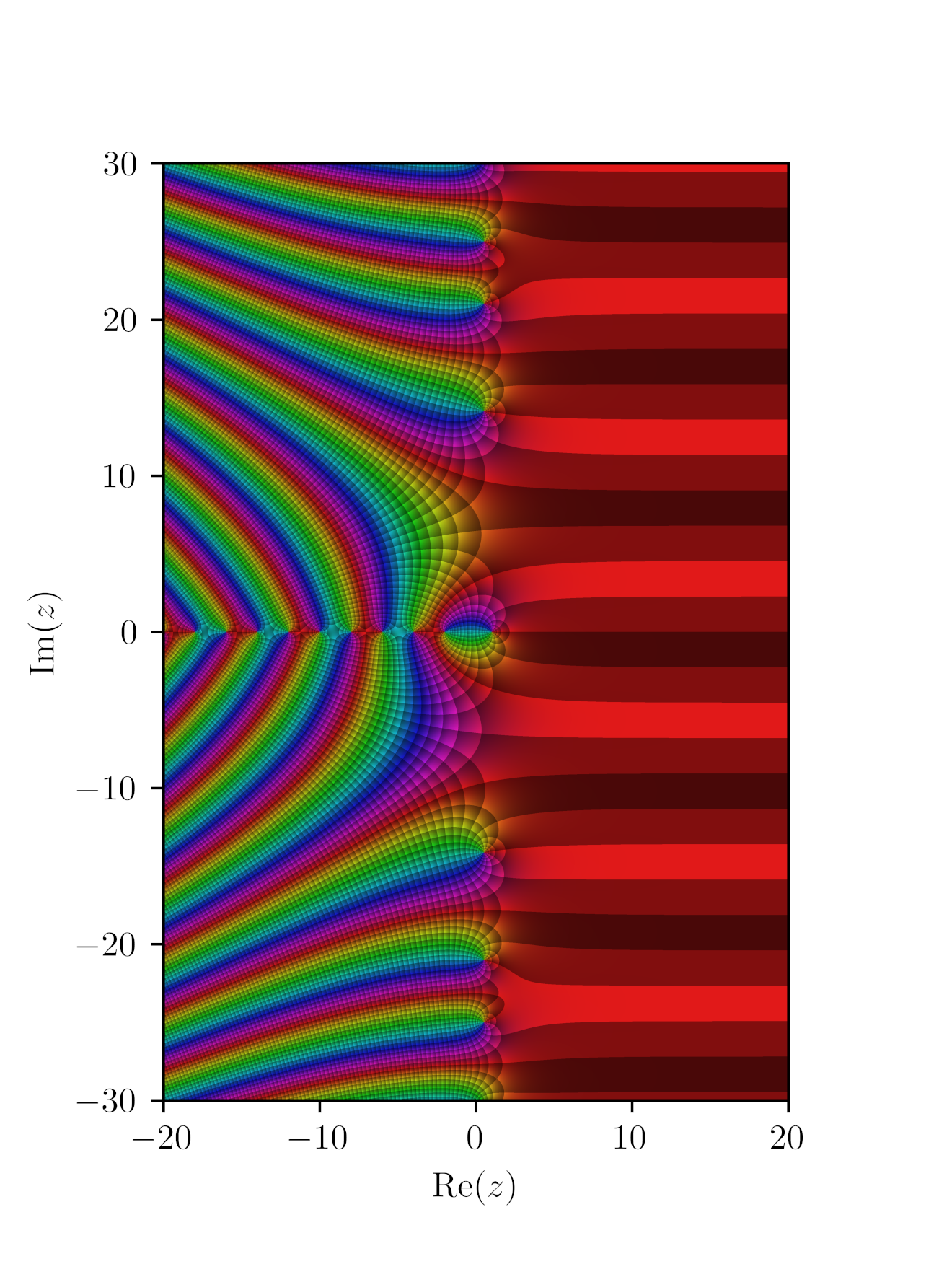
Zeta Functions
In mathematics, a zeta function is (usually) a function analogous to the original example, the Riemann zeta function : \zeta(s) = \sum_^\infty \frac 1 . Zeta functions include: * Airy zeta function, related to the zeros of the Airy function * Arakawa–Kaneko zeta function * Arithmetic zeta function * Artin–Mazur zeta function of a dynamical system * Barnes zeta function or double zeta function * Beurling zeta function of Beurling generalized primes * Dedekind zeta function of a number field * Duursma zeta function of error-correcting codes * Epstein zeta function of a quadratic form * Goss zeta function of a function field * Hasse–Weil zeta function of a variety * Height zeta function of a variety * Hurwitz zeta function, a generalization of the Riemann zeta function * Igusa zeta function * Ihara zeta function of a graph * ''L''-function, a "twisted" zeta function * Lefschetz zeta function of a morphism * Lerch zeta function, a generalization of the Riemann zeta function * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schoof–Elkies–Atkin Algorithm
The Schoof–Elkies–Atkin algorithm (SEA) is an algorithm used for finding the order of or calculating the number of points on an elliptic curve over a finite field. Its primary application is in elliptic curve cryptography. The algorithm is an extension of Schoof's algorithm by Noam Elkies and A. O. L. Atkin to significantly improve its efficiency (under heuristic assumptions). Details The Elkies-Atkin extension to Schoof's algorithm works by restricting the set of primes S = \ considered to primes of a certain kind. These came to be called Elkies primes and Atkin primes respectively. A prime l is called an Elkies prime if the characteristic equation: \phi^2-t\phi+ q = 0 splits over \mathbb_l, while an Atkin prime is a prime that is not an Elkies prime. Atkin showed how to combine information obtained from the Atkin primes with the information obtained from Elkies primes to produce an efficient algorithm, which came to be known as the Schoof–Elkies–Atkin algorithm. The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-functions
In mathematics, an ''L''-function is a meromorphic function on the complex plane, associated to one out of several categories of mathematical objects. An ''L''-series is a Dirichlet series, usually convergent on a half-plane, that may give rise to an ''L''-function via analytic continuation. The Riemann zeta function is an example of an ''L''-function, and one important conjecture involving ''L''-functions is the Riemann hypothesis and its generalization. The theory of ''L''-functions has become a very substantial, and still largely conjectural, part of contemporary analytic number theory. In it, broad generalisations of the Riemann zeta function and the ''L''-series for a Dirichlet character are constructed, and their general properties, in most cases still out of reach of proof, are set out in a systematic way. Because of the Euler product formula there is a deep connection between ''L''-functions and the theory of prime numbers. The mathematical field that studies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliptic Curve Primality Proving
In mathematics, elliptic curve primality testing techniques, or elliptic curve primality proving (ECPP), are among the quickest and most widely used methods in primality proving. It is an idea put forward by Shafi Goldwasser and Joe Kilian in 1986 and turned into an algorithm by A. O. L. Atkin the same year. The algorithm was altered and improved by several collaborators subsequently, and notably by Atkin and , in 1993. The concept of using elliptic curves in factorization had been developed by H. W. Lenstra in 1985, and the implications for its use in primality testing (and proving) followed quickly. Primality testing is a field that has been around since the time of Fermat, in whose time most algorithms were based on factoring, which become unwieldy with large input; modern algorithms treat the problems of determining whether a number is prime and what its factors are separately. It became of practical importance with the advent of modern cryptography. Although many curren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperelliptic Curve Cryptography
Hyperelliptic curve cryptography is similar to elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) insofar as the Jacobian of a hyperelliptic curve is an abelian group in which to do arithmetic, just as we use the group of points on an elliptic curve in ECC. Definition An (imaginary) hyperelliptic curve of genus g over a field K is given by the equation C : y^2 + h(x) y = f(x) \in K ,y/math> where h(x) \in K /math> is a polynomial of degree not larger than g and f(x) \in K /math> is a monic polynomial of degree 2g + 1. From this definition it follows that elliptic curves are hyperelliptic curves of genus 1. In hyperelliptic curve cryptography K is often a finite field. The Jacobian of C, denoted J(C), is a quotient group, thus the elements of the Jacobian are not points, they are equivalence classes of divisors of degree 0 under the relation of linear equivalence. This agrees with the elliptic curve case, because it can be shown that the Jacobian of an elliptic curve is isomorphic with the group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliptic Curve Cryptography
Elliptic-curve cryptography (ECC) is an approach to public-key cryptography based on the algebraic structure of elliptic curves over finite fields. ECC allows smaller keys compared to non-EC cryptography (based on plain Galois fields) to provide equivalent security.Commercial National Security Algorithm Suite and Quantum Computing FAQ U.S. National Security Agency, January 2016. Elliptic curves are applicable for key agreement, s, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperelliptic Curve
In algebraic geometry, a hyperelliptic curve is an algebraic curve of genus ''g'' > 1, given by an equation of the form y^2 + h(x)y = f(x) where ''f''(''x'') is a polynomial of degree ''n'' = 2''g'' + 1 > 4 or ''n'' = 2''g'' + 2 > 4 with ''n'' distinct roots, and ''h''(''x'') is a polynomial of degree 3. Therefore, in giving such an equation to specify a non-singular curve, it is almost always assumed that a non-singular model (also called a smooth completion), equivalent in the sense of birational geometry, is meant. To be more precise, the equation defines a quadratic extension of C(''x''), and it is that function field that is meant. The singular point at infinity can be removed (since this is a curve) by the normalization (integral closure) process. It turns out that after doing this, there is an open cover of the curve by two affine charts: the one already given by y^2 = f(x) and another one given by w^2 = v^f(1/v) . The glueing maps between the two charts are given by ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |