|
Andersen Island
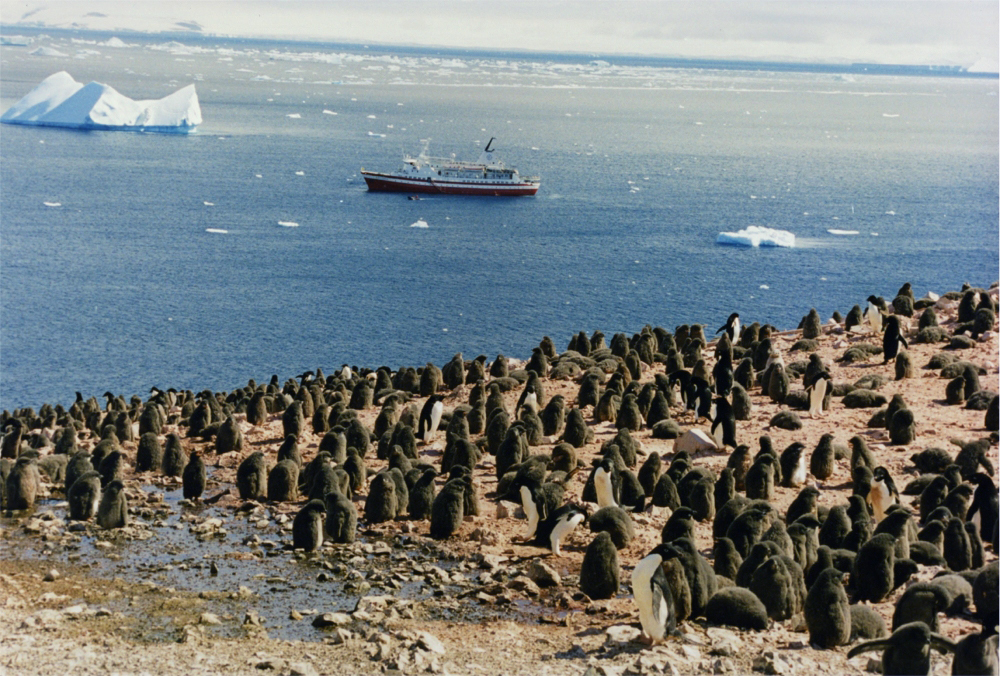
Andersen Island is an island west of Thorgaut Island, and east of Child Rocks, in the Robinson Group, Antarctica. It was mapped by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition under Douglas Mawson in February 1931. The island was also charted from the whaler ''Thorgaut'' about the same time. It was named after Captain Lars Andersen of the whaler ''Falk'' who had assisted the ''Discovery'' with coal. Important Bird Area A 111 ha site encompassing breeding colonies of some 13,000 pairs of Adélie penguins on Andersen Island and an unnamed island 1 km to the south-west has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding .... See also * List of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
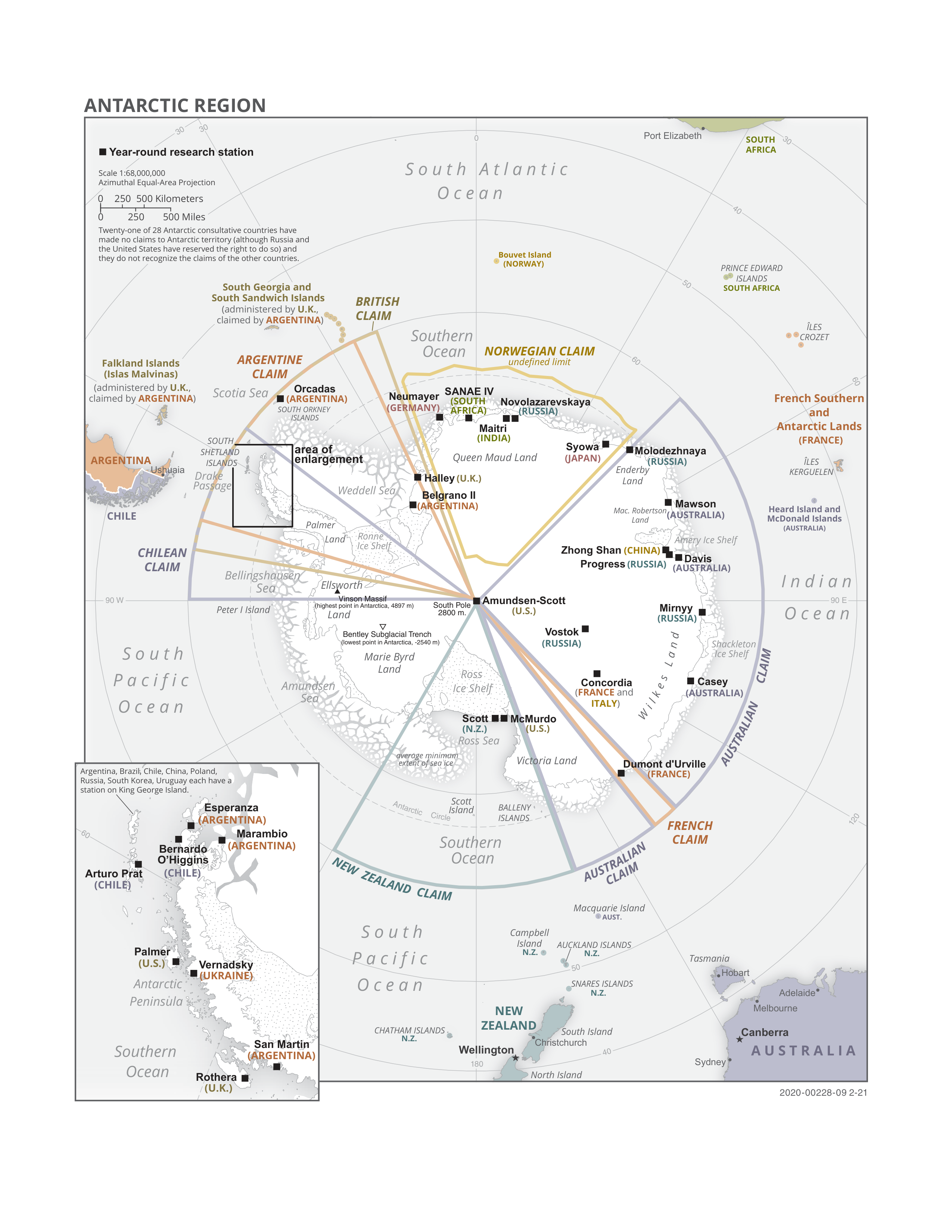
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Treaty System
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty System , type = Condominium , date_drafted = , date_signed = December 1, 1959"Antarctic Treaty" in ''The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 439. , location_signed = Washington, D.C., United States , date_sealed = , date_effective = June 23, 1961 , condition_effective = Ratification of all 12 signatories , date_expiration = , signatories = 12 , parties = 55 , depositor = Federal government of the United States , languages = English, French, Russian, and Spanish , wikisource = Antarctic Treaty The Antarctic Treaty an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorgaut Island
Thorgaut Island is an island off Antarctica, the largest island in the northeast part of the Robinson Group, lying 7 nautical miles (13 km) northwest of Cape Daly on the coast of Antarctica, 4 nautical miles (7 km) east of Andersen Island Andersen Island is an island west of Thorgaut Island, and east of Child Rocks, in the Robinson Group, Antarctica. It was mapped by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition under Douglas Mawson in February 1931. The isl ..., and 3 to 4 nautical miles (5 – 6 km) north-west of Kirton Island and Macklin Island, which are also part of the Robinson Group. The islands were sighted in 1931 by the crew of the Norwegian whaling ships ''Thorgaut'' and ''Robinson''. The name Robinson was applied to the group, and the name Thorgaut to its most conspicuous member. See also * List of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic islands Islands of Mac. Robertson Land {{MacRobertsonLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Child Rocks
The Child Rocks are a group of rocks at the west end of the Robinson Group off the coast of Mac. Robertson Land, west of Andersen Island. They were mapped by Norwegian cartographers from air photos taken by the Lars Christensen Expedition, 1936–37, and named "Vestskjera" (the west skerries). They were renamed by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia for J.B. Child, Third Officer of the RSS ''Discovery'' during the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition The British Australian (and) New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) was a research expedition into Antarctica between 1929 and 1931, involving two voyages over consecutive Austral summers. It was a British Commonwealth initiative, dr ..., 1929–31. References * Rock formations of Mac. Robertson Land {{MacRobertsonLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robinson Group
Robinson Group () is a group of small islands extending in an east–west direction, lying close northwest of Cape Daly. The group was observed by British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Mawson, 1931, who named it after W.S. Robinson of Melbourne, a patron of the expedition. Essentially the same islands were observed in 1931 by the crew of the Norwegian whale catcher ''Thorgaut'', who gave them the name "Thorgautoyane". In concurrence with the recommendations by Antarctic Names Committee of Australia (ANCA), the name "Robinson" has been assigned to the whole group and the name "Thorgaut" to the most conspicuous island. Robinson Group is made up of (running west-to-east) Child Rocks, Andersen Island Andersen Island is an island west of Thorgaut Island, and east of Child Rocks, in the Robinson Group, Antarctica. It was mapped by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition under Douglas Mawson in February 1931. The isl . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition
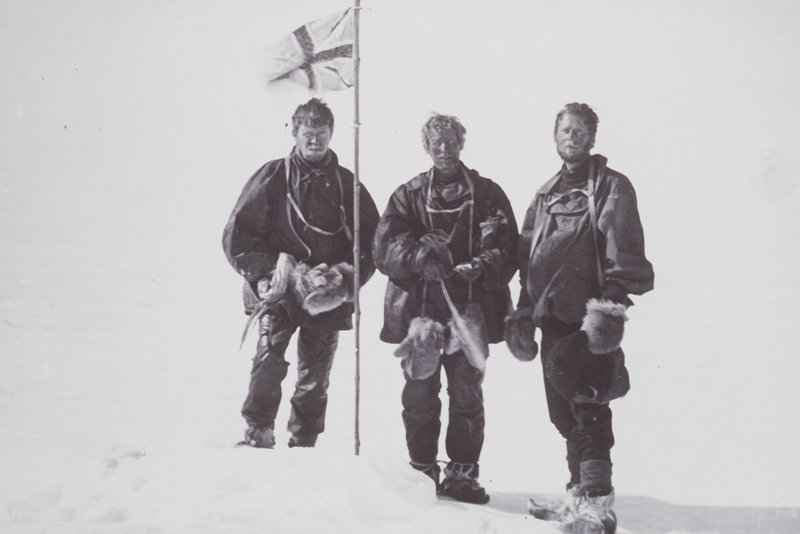
The British Australian (and) New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) was a research expedition into Antarctica between 1929 and 1931, involving two voyages over consecutive Austral summers. It was a British Commonwealth initiative, driven more by geopolitics than science, and funded by the United Kingdom, Australia and New Zealand. The leader of the BANZARE was Sir Douglas Mawson and there were several subcommanders (Captain K.N. MacKenzie, who replaced Captain John King Davis for the second summer) on board the RRS Discovery, the ship previously used by Robert Falcon Scott. The BANZARE, which also made several short flights in a small plane, mapped the coastline of Antarctica and discovered Mac. Robertson Land and Princess Elizabeth Land (which later was claimed as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory). The voyages primarily comprised an "acquisitive exploratory expedition", with Mawson making proclamations of British sovereignty over Antarctic lands at each o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Mawson
Sir Douglas Mawson OBE FRS FAA (5 May 1882 – 14 October 1958) was an Australian geologist, Antarctic explorer, and academic. Along with Roald Amundsen, Robert Falcon Scott, and Sir Ernest Shackleton, he was a key expedition leader during the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration. Mawson was born in England and came to Australia as an infant. He completed degrees in mining engineering and geology at the University of Sydney. In 1905 he was made a lecturer in petrology and mineralogy at the University of Adelaide. Mawson's first experience in the Antarctic came as a member of Shackleton's ''Nimrod'' Expedition (1907–1909), alongside his mentor Edgeworth David. They were part of the expedition's northern party, which became the first to attain the South Magnetic Pole and to climb Mount Erebus. After his participation in Shackleton's expedition, Mawson became the principal instigator of the Australasian Antarctic Expedition (1911–1914). The expedition explored thousand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lars Andersen (captain)
{{human name disambiguation, Andersen, Lars ...
Lars Andersen may refer to: * Lars Andersen (archer) (born 1964), Danish archer and a speed world record holder * Lars Andersen (captain), namesake of Andersen Island * Lars Andersen (footballer), Danish footballer in 2008–09 Danish Cup * Lars Håkon Andersen (born 1974), Norwegian ice hockey player * Lars Hedegaard Andersen (born 1975), Danish cricketer * Lars B. Andersen (born 1970), Norwegian-British businessman See also *Lars Anderson (other) Lars Anderson may refer to: * Lars Anderson (baseball) (born 1987), American baseball player *Lars Anderson (wrestler) (born 1939), American former professional wrestler See also *Larz Anderson Larz Anderson (August 15, 1866 – April 13, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RRS Discovery
The RRS ''Discovery'' is a barque-rigged auxiliary steamship built in Dundee, Scotland for Antarctic research. Launched in 1901, she was the last traditional wooden three-masted ship to be built in the United Kingdom. Her first mission was the British National Antarctic Expedition, carrying Robert Falcon Scott and Ernest Shackleton on their first, and highly successful, journey to the Antarctic, known as the ''Discovery'' Expedition. After service as a merchant ship before and during the First World War, ''Discovery'' was taken into the service of the British government in 1923 to carry out scientific research in the Southern Ocean, becoming the first Royal Research Ship. The ship undertook a two-year expedition – the Discovery Investigations – recording valuable information on the oceans, marine life and being the first scientific investigation into whale populations. From 1929 to 1931 ''Discovery'' served as the base for the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adélie Penguin
The Adélie penguin (''Pygoscelis adeliae'') is a species of penguin common along the entire coast of the Antarctic continent, which is the only place where it is found. It is the most widespread penguin species, and, along with the emperor penguin, is the most southerly distributed of all penguins. It is named after Adélie Land, in turn named for Adèle Dumont d'Urville, who was married to French explorer Jules Dumont d'Urville, who first discovered this penguin in 1840. Adélie penguins obtain their food by both predation and foraging, with a diet of mainly krill and fish. Taxonomy and systematics The first Adélie penguin specimens were collected by crew members of French explorer Jules Dumont d'Urville on his expedition to Antarctica in the late 1830s and early 1840s. Jacques Bernard Hombron and Honoré Jacquinot, two French surgeons who doubled as naturalists on the journey, described the bird for science in 1841, giving it the scientific name ''Catarrhactes adeli� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Important Bird Area
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations. IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife International. There are over 13,000 IBAs worldwide. These sites are small enough to be entirely conserved and differ in their character, habitat or ornithological importance from the surrounding habitat. In the United States the Program is administered by the National Audubon Society. Often IBAs form part of a country's existing protected area network, and so are protected under national legislation. Legal recognition and protection of IBAs that are not within existing protected areas varies within different countries. Some countries have a National IBA Conservation Strategy, whereas in others protection is completely lacking. History In 1985, following a specific request from the European Economic Community, Birdlife International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BirdLife International
BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding important sites for birds, maintaining and restoring key bird habitats, and empowering conservationists worldwide. It has a membership of more than 2.5 million people across 116 country partner organizations, including the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds, the Wild Bird Society of Japan, the National Audubon Society and American Bird Conservancy. BirdLife International has identified 13,000 Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas and is the official International Union for Conservation of Nature’s Red List authority for birds. As of 2015, BirdLife International has established that 1,375 bird species (13% of the total) are threatened with extinction ( critically endangered, endangered or vulnerable). BirdLife International p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |