|
Ananyino Culture
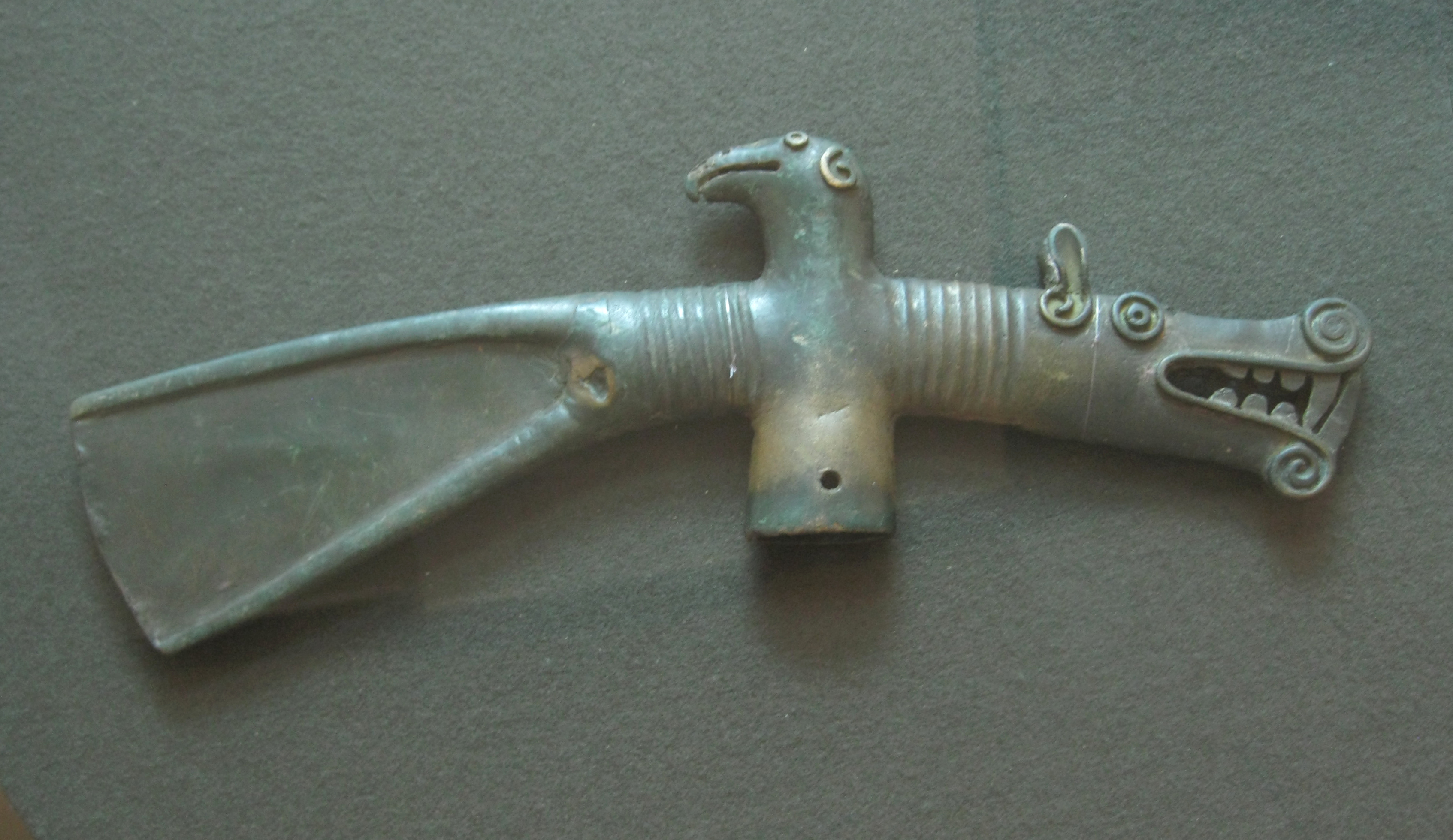
The Ananyino culture is an archeological culture of the late 8th to 3rd centuries BCE in present-day Tatarstan, Russian Federation. The name comes from the burials first discovered near the village Ananyino (Ананьино) in the vicinity of Elabuga, excavated by P.V.Alabin and I.V.Shishkin in 1858. It is located in the territory of the Middle Volga (from the Vetluga River to the town of Ulyanovsk) and the Kama River basin. In the southeast the culture stretches along the lower course of the Belaya River, from its mouth up to the town of Birsk (fortresses Novokabanov, Kakrykul, Peter-Tau, Anachev, Tra-Tau, Trikol, Novobiktov, Birsk settlement, Tash-Elga burials). In the Volga-Kama area and more northerly the culture extends to the Pechora River and Subarctic Ural. In the Volga and Lower Kama areas the traces of the Ananyino Culture fade in the 6th century BCE, in other areas in the 3rd to 2nd centuries BCE. Archeological monuments Unfortified settlements, fortresses and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ananyino Culture Axe
Ananyino (russian: links=no, Ананьино) is a rural locality (a selo) and the administrative center of Ananyinskoye Rural Settlement, Chernushinsky District, Perm Krai Perm Krai (russian: Пе́рмский край, r=Permsky kray, p=ˈpʲɛrmskʲɪj ˈkraj, ''Permsky krai'', , ''Perem lador'') is a federal subject of Russia (a krai) that came into existence on December 1, 2005 as a result of the 2004 refe ..., Russia. The population was 568 as of 2010.} There are 12 streets. Geography Ananyino is located 12 km north of Chernushka (the district's administrative centre) by road. Malanichi is the nearest rural locality. References Rural localities in Chernushinsky District {{Chernushinsky-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
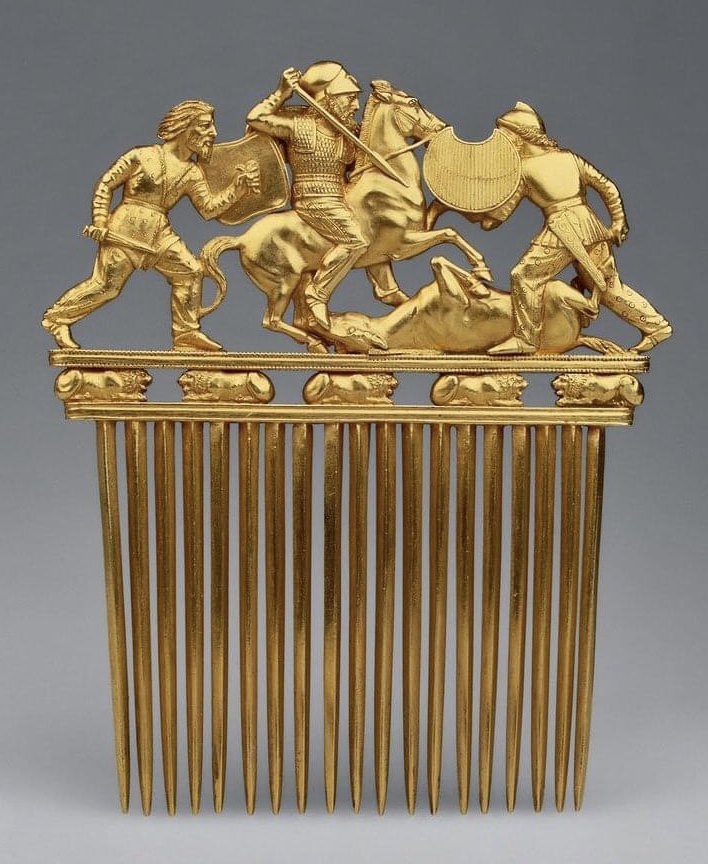
Colchian Culture
Colchian culture ( ka, კოლხური კულტურა; 8000 BCE to 600 BCE) is Neolithic - (Later Lazian culture) an early Bronze Age and Iron Age culture of the western Caucasus, mostly in western Georgia. It was partially succeeded by the Koban culture in northern and central Caucasus. It is named after the ancient geographic region of Colchis (Later Lazica), which covered a large area along the Black Sea coast. It is mainly known for highly developed bronze production and artistic craftsmanship. There are many items of copper and bronze found in ancient graves. Graves found and studied have been located in the Abkhazia region, the Sukhumi mountain complexes, the Racha highlands where brick tiles and graffiti have been found, and the Colchian plains () where collective graves have been found. Collective graves occurred during the last stages of the Colchian culture (c.8th millennium to 6th century BCE). In these graves bronze items were found that represented fore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finno-Ugric Archaeological Cultures
Finno-Ugric ( or ; ''Fenno-Ugric'') or Finno-Ugrian (''Fenno-Ugrian''), is a traditional grouping of all languages in the Uralic language family except the Samoyedic languages. Its formerly commonly accepted status as a subfamily of Uralic is based on criteria formulated in the 19th century and is criticized by some contemporary linguists such as Tapani Salminen and Ante Aikio as inaccurate and misleading. The three most-spoken Uralic languages, Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian, are all included in Finno-Ugric, although linguistic roots common to both branches of the traditional Finno-Ugric language tree ( Finno-Permic and Ugric) are distant. The term ''Finno-Ugric'', which originally referred to the entire family, is sometimes used as a synonym for the term ''Uralic'', which includes the Samoyedic languages, as commonly happens when a language family is expanded with further discoveries. Status The validity of Finno-Ugric as a phylogenic grouping is under challenge, with some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Cultures Of Eastern Europe
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vepsians
Veps, or Vepsians ( Veps: ''vepsläižed''), are a Finnic people who speak the Veps language, which belongs to the Finnic branch of the Uralic languages. According to the 2002 census, there were 8,240 Veps in Russia. Of the 281 Veps in Ukraine, 11 spoke Vepsian (Ukr. Census 2001). The most prominent researcher of the Veps in Finland is Eugene Holman. The self-designations of these people in various dialects are ''vepslaine'', ''bepslaane'' and (in northern dialects, southwest of Lake Onega) ''lüdinik'' and ''lüdilaine''. Almost all Vepsians are fluent in Russian. The younger generation, in general, does not speak Vepsian although many have an understanding of the language. Geography In modern times, they live in the area between Lake Ladoga, Lake Onega and Lake Beloye – in the Russian Republic of Karelia in the former Veps National Volost, in Leningrad Oblast along the Oyat River in the Podporozhsky and Lodeynopolsky Districts and further south in the Tikhvinsky and Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelians
Karelians ( krl, karjalaižet, karjalazet, karjalaiset, Finnish: , sv, kareler, karelare, russian: Карелы) are a Finnic ethnic group who are indigenous to the historical region of Karelia, which is today split between Finland and Russia. Karelians living in Russian Karelia are considered a distinct ethnic group closely related to Finnish Karelians, who are considered a subset of Finns. This distinction historically arose from Karelia having been fought over and eventually split between Sweden and Novgorod, resulting in Karelians being under different cultural spheres. In Russia, Karelians mostly live in the Republic of Karelia, where they are the designated ethnic group, and in other adjacent north-western parts of the country. They traditionally speak the Karelian language and are Eastern Orthodox Christians. There are also significant Karelian enclaves in the Tver and Novgorod oblasts, as some Karelians migrated to those areas after the Russo-Swedish War of 1656-16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
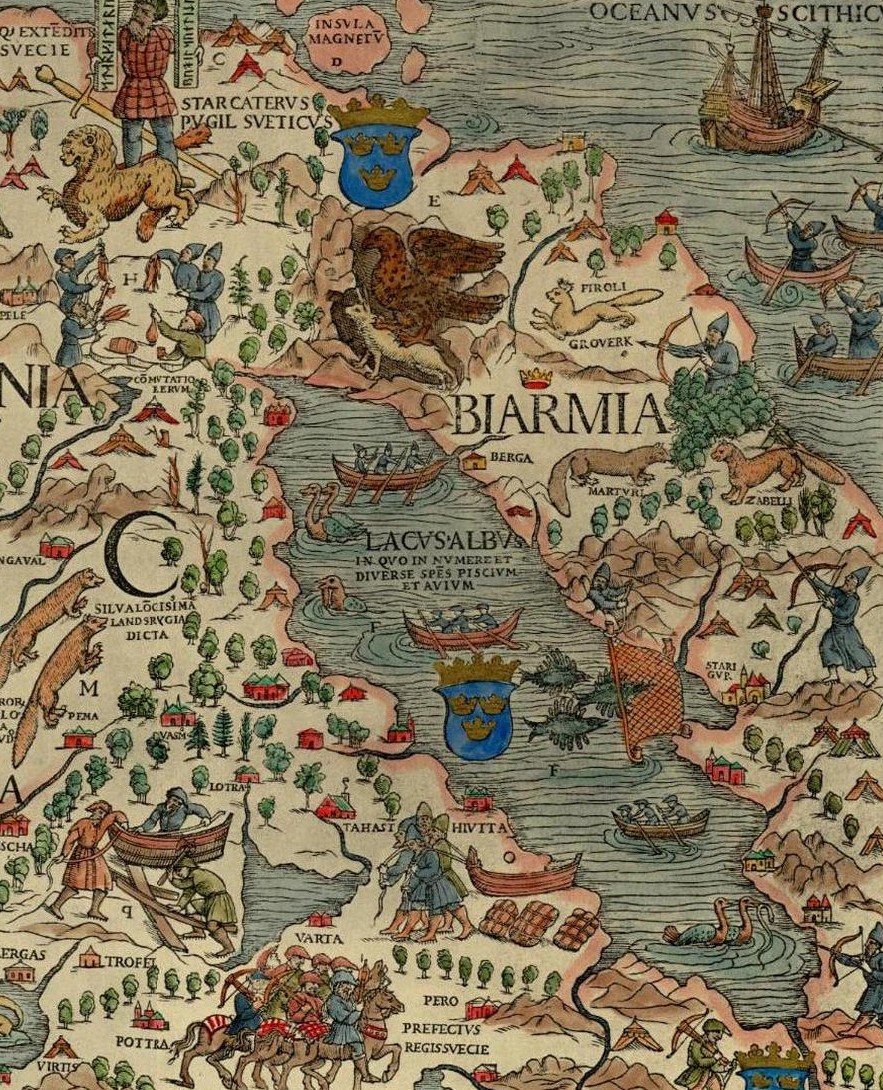
Bjarmaland
Bjarmaland (also spelt ''Bjarmland'' and ''Bjarmia''; Latin: ''Biarmia''; Old English: ''Beormaland,'' Komi: Биармия ''Biarmia,'' Old Permic: 𐍑𐍙𐍐𐍒𐍜𐍙𐍐) was a territory mentioned in Norse sagas since the Viking Age and in geographical accounts until the 16th century. The term is usually seen to have referred to the southern shores of the White Sea and the basin of the Northern Dvina River (''Vienanjoki'' in Finnish) as well as, presumably, some of the surrounding areas. Today, those territories comprise a part of the Arkhangelsk Oblast of Russia, as well as the Kola Peninsula. Norse voyagers in Bjarmaland According to the '' Voyage of Ohthere'' (c. 890 CE), the Norwegian merchant Ottar (Ohthere) reported to king Alfred the Great that he had sailed for 15 days along the northern coast and then southwards, finally arriving at a great river, probably the Northern Dvina. At the estuary of the river dwelt the ''Beormas'', who unlike the nom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga Finns
The Volga Finns (sometimes referred to as Eastern Finns) are a historical group of indigenous peoples of Russia living in the vicinity of the Volga, who speak Uralic languages. Their modern representatives are the Mari people, the Erzya and the Moksha Mordvins, as well as speakers of the extinct Merya, Muromian and Meshchera languages. The Permians are sometimes also grouped as Volga Finns. The modern representatives of Volga Finns live in the basins of the Sura and Moksha rivers, as well as (in smaller numbers) in the interfluve between the Volga and the Belaya rivers. The Mari language has two dialects, the Meadow Mari and the Hill Mari. Traditionally the Mari and the Mordvinic languages ( Erzya and Moksha) were considered to form a ''Volga-Finnic'' or ''Volgaic'' group within the Uralic language family, accepted by linguists like Robert Austerlitz (1968), Aurélien Sauvageot & Karl Heinrich Menges (1973) and Harald Haarmann (1974), but rejected by others like Björn Collin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian Languages
The Permic or Permian languages are a branch of the Uralic language family. They are spoken in several regions to the west of the Ural Mountains within the Russian Federation. The total number of speakers is around 950,000, of which around 550,000 speak the most widely spoken language, Udmurt. Like other Uralic languages, the Permic languages are primarily agglutinative and have a rich system of grammatical cases. Unlike many others, they do not have vowel harmony. The earliest Permic language to be preserved in writing was Old Permic or Old Zyryan, in the 14th century. The extant Permic languages division of the Finno-Ugric branch of the Uralic language family consists of the: * Udmurt (Votyak) * Komi (Zyryan) * Permyak (Komi-Permyak) The Permic languages have traditionally been classified as Finno-Permic languages, along with the Finnic, Saami, Mordvin, and Mari languages. The Finno-Permic and Ugric languages together made up the Finno-Ugric family. However, this taxonom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finno-Ugric Languages
Finno-Ugric ( or ; ''Fenno-Ugric'') or Finno-Ugrian (''Fenno-Ugrian''), is a traditional grouping of all languages in the Uralic language family except the Samoyedic languages. Its formerly commonly accepted status as a subfamily of Uralic is based on criteria formulated in the 19th century and is criticized by some contemporary linguists such as Tapani Salminen and Ante Aikio as inaccurate and misleading. The three most-spoken Uralic languages, Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian, are all included in Finno-Ugric, although linguistic roots common to both branches of the traditional Finno-Ugric language tree ( Finno-Permic and Ugric) are distant. The term ''Finno-Ugric'', which originally referred to the entire family, is sometimes used as a synonym for the term ''Uralic'', which includes the Samoyedic languages, as commonly happens when a language family is expanded with further discoveries. Status The validity of Finno-Ugric as a phylogenic grouping is under challenge, with some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern * : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Central Asia and Eastern Turkestan to distinguish them from the related Massagetae of the Aral region and the Scythians of the Pontic steppes. These tribes spoke Iranian languages, and their chief occupation was nomadic pastoralism." * : "Near the end of the 19th century V.F. Miller (1886, 1887) theorized that the Scythians and their kindred, the Sauromatians, were Iranian-speaking peoples. This has been a popular point of view and continues to be accepted in linguistics and historical science [...]" * : "From the end of the 7th century B.C. to the 4th century B.C. the Central- Eurasian steppes were inhabited by two large groups of kin Iranian-speaking tribes – the Scythians and Sarmatians [.. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically been considered as a natural barrier between Eastern Europe and Western Asia. Mount Elbrus in Russia, Europe's highest mountain, is situated in the Western Caucasus. On the southern side, the Lesser Caucasus includes the Javakheti Plateau and the Armenian highlands, part of which is in Turkey. The Caucasus is divided into the North Caucasus and South Caucasus, although the Western Caucasus also exists as a distinct geographic space within the North Caucasus. The Greater Caucasus mountain range in the north is mostly shared by Russia and Georgia as well as the northernmost parts of Azerbaijan. The Lesser Caucasus mountain range in the south is occupied by several independent states, mostly by Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia, but also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)