|
Anan (Karaite Prince)
Anan Ben David (c. 715 - c. 795) ( he, ענן בן דוד) is widely considered to be a major founder of the Karaite movement of Judaism. His followers were called Ananites and, like modern Karaites, did not believe the Rabbinic Jewish oral law (such as the Mishnah) to be authoritative. History From the second third of the 7th century and until middle of the 8th, as a result of the tremendous intellectual commotion produced throughout the Western Asia by the swift Early Muslim conquests of the Arabs and the collision of Islam with the older religions and cultures of the world, there arose a large number of religious sects, especially in Persia, Babylonia (Iraq), and Syria. Judaism did not escape this general fomentation; the remnants of Second Temple sects picked up new life and flickered once more before their final extinction, and new sects also arose. "Anan" (which means "Cloud") was never a very common name among Jews, but it is attested in the Bible - the original Anan wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karaite Judaism
Karaite Judaism () or Karaism (, sometimes spelt Karaitism (; ''Yahadut Qara'it''); also spelt Qaraite Judaism, Qaraism or Qaraitism) is a Jewish religious movement characterized by the recognition of the written Torah alone as its supreme authority in '' halakha'' (Jewish religious law) and theology. Karaites believe that all of the divine commandments which were handed down to Moses by God were recorded in the written Torah without any additional Oral Law or explanation. Unlike mainstream Rabbinic Judaism, which considers the Oral Torah, codified in the Talmud and subsequent works, to be authoritative interpretations of the Torah, Karaite Jews do not believe that the written collections of the oral tradition in the Midrash or the Talmud are binding. When they read the Torah, Karaites strive to adhere to the plain or most obvious meaning ('' peshat'') of the text; this is not necessarily the literal meaning of the text, instead, it is the meaning of the text that would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Hanifah
Nuʿmān ibn Thābit ibn Zūṭā ibn Marzubān ( ar, نعمان بن ثابت بن زوطا بن مرزبان; –767), commonly known by his '' kunya'' Abū Ḥanīfa ( ar, أبو حنيفة), or reverently as Imam Abū Ḥanīfa by Sunni Muslims, was a Persian Sunni Muslim theologian and juristPakatchi, Ahmad and Umar, Suheyl, "Abū Ḥanīfa", in: ''Encyclopaedia Islamica'', Editors-in-Chief: Wilferd Madelung and, Farhad Daftary. who became the eponymous founder of the Hanafi school of Sunni jurisprudence, which has remained the most widely practiced law school in the Sunni tradition, predominates in Central Asia, Afghanistan, Iran (until the 16th century), Balkans, Russia, Chechnya, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Muslims in India, Turkey, and some parts of the Arab world. Some followers call him ''al-Imām al-Aʿẓam'' ("The Greatest Imam") and ''Sirāj al-Aʾimma'' ("The Lamp of the Imams") in Sunni Islam. Born to a Muslim family in Kufa, Abu Hanifa is known to hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Al-Rawandi
Abu al-Hasan Ahmad ibn Yahya ibn Ishaq al-Rawandi ( ar, أبو الحسن أحمد بن يحيى بن إسحاق الراوندي), commonly known as Ibn al-Rawandi ( ar, ابن الراوندي; 827–911 CEAl-Zandaqa Wal Zanadiqa, by Mohammad Abd-El Hamid Al-Hamad, First edition 1999, Dar Al-Taliaa Al-Jadida, Syria (Arabic)), was an early Persian scholar and theologian. In his early days, he was a Mu'tazilite scholar, but then rejected the Mu'tazilite doctrine. Afterwards, he became a Shia scholar; there is some debate about whether he stayed a Shia until his death or became a skeptic, though most sources confirm his eventual rejection of all religion and becoming an atheist. Although none of his works have survived, his opinions had been preserved through his critics and the surviving books that answered him. His book with the most preserved fragments (through an Ismaili book refuting Al-Rawandi's ideology) is the '' Kitab al-Zumurrud'' (''The Book of the Emerald''). L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagoreans
Pythagoreanism originated in the 6th century BC, based on and around the teachings and beliefs held by Pythagoras and his followers, the Pythagoreans. Pythagoras established the first Pythagorean community in the ancient Greek colony of Kroton, in modern Calabria (Italy). Early Pythagorean communities spread throughout Magna Graecia. Pythagoras' death and disputes about his teachings led to the development of two philosophical traditions within Pythagoreanism. The ''akousmatikoi'' were superseded in the 4th century BC as a significant mendicant school of philosophy by the Cynics. The ''mathēmatikoi'' philosophers were absorbed into the Platonic school in the 4th century BC. Following political instability in Magna Graecia, some Pythagorean philosophers fled to mainland Greece while others regrouped in Rhegium. By about 400 BC the majority of Pythagorean philosophers had left Italy. Pythagorean ideas exercised a marked influence on Plato and through him, on all of Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
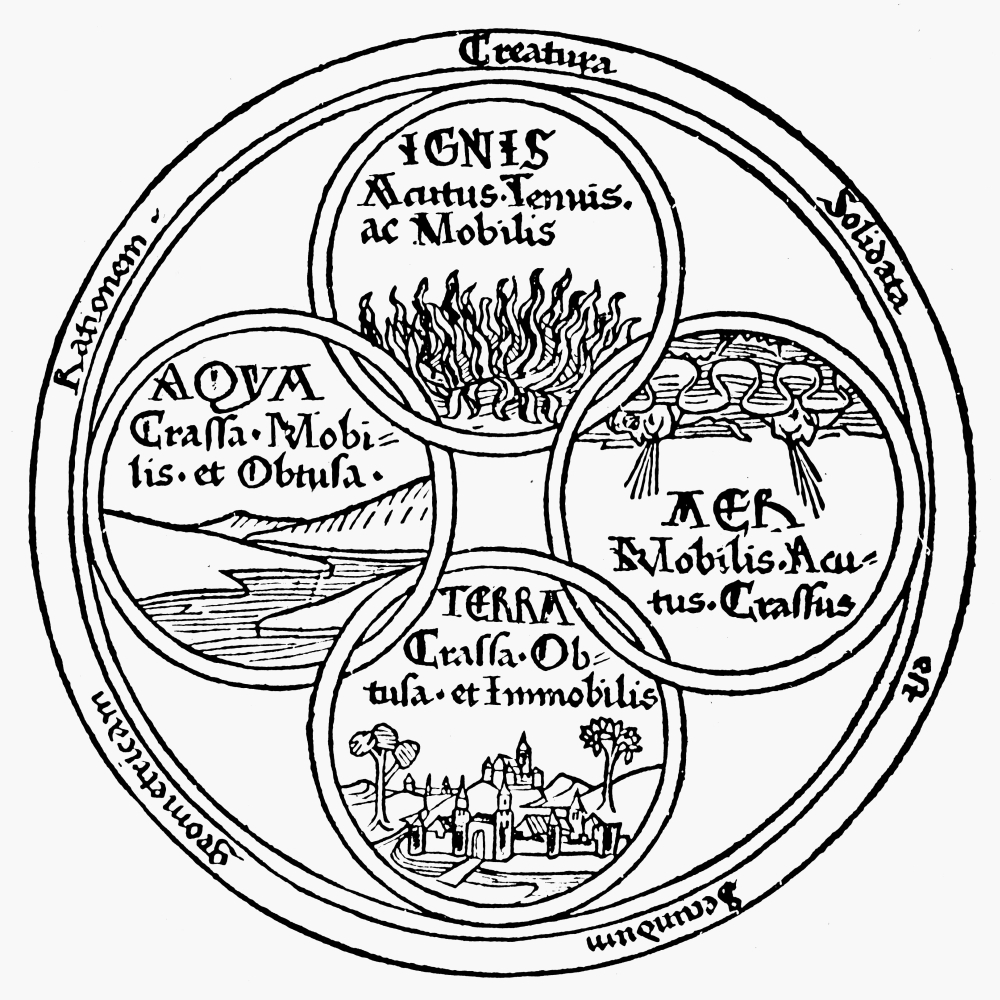
Empedocles
Empedocles (; grc-gre, Ἐμπεδοκλῆς; , 444–443 BC) was a Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a native citizen of Akragas, a Greek city in Sicily. Empedocles' philosophy is best known for originating the cosmogonic theory of the four classical elements. He also proposed forces he called Love and Strife which would mix and separate the elements, respectively. Empedocles challenged the practice of animal sacrifice and killing animals for food. He developed a distinctive doctrine of reincarnation. He is generally considered the last Greek philosopher to have recorded his ideas in verse. Some of his work survives, more than is the case for any other pre-Socratic philosopher. Empedocles' death was mythologized by ancient writers, and has been the subject of a number of literary treatments. Life Although the exact dates of Empedocles birth and death are unknown and ancient accounts of his life conflict on the exact details, they agree that he was born in the early 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metempsychosis
Metempsychosis ( grc-gre, μετεμψύχωσις), in philosophy, is the transmigration of the soul, especially its reincarnation after death. The term is derived from ancient Greek philosophy, and has been recontextualised by modern philosophers such as Arthur Schopenhauer and Kurt Gödel; otherwise, the term ''transmigration'' is more appropriate. The word plays a prominent role in James Joyce's '' Ulysses'' and is also associated with Nietzsche. Another term sometimes used synonymously is '' palingenesis''. History It is unclear how the doctrine of metempsychosis arose in Greece. It is easiest to assume that earlier ideas which had never been extinguished were used for religious and philosophic purposes. Orphism The Orphic religion, which held it, first appeared in Thrace upon the semi-barbarous northeastern frontier. Orpheus, its legendary founder, is said to have taught that soul and body are united by a compact unequally binding on either; the soul is divine, imm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmudical Hermeneutics
Talmudical hermeneutics (Hebrew: מידות שהתורה נדרשת בהן) defines the rules and methods for investigation and exact determination of meaning of the scriptures in the Hebrew Bible, within the framework of Rabbinic Judaism. This includes, among others, the rules by which the requirements of the Oral Law and the Halakha are derived from and established by the written law. These rules relate to: * grammar and exegesis * the interpretation of certain words and letters and apparently superfluous and/or missing words or letters, and prefixes and suffixes * the interpretation of those letters which, in certain words, are provided with points * the interpretation of the letters in a word according to their numerical value (see Gematria) * the interpretation of a word by dividing it into two or more words (see Notarikon) * the interpretation of a word according to its consonantal form or according to its vocalization * the interpretation of a word by transposing its lette ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qiyas
In Islamic jurisprudence, qiyas ( ar, قياس , " analogy") is the process of deductive analogy in which the teachings of the hadith are compared and contrasted with those of the Quran, in order to apply a known injunction ('' nass'') to a new circumstance and create a new injunction. Here the ruling of the Sunnah and the Quran may be used as a means to solve or provide a response to a new problem that may arise. This, however, is only the case providing that the set precedent or paradigm and the new problem that has come about will share operative causes (, ''ʿillah''). The ʿillah is the specific set of circumstances that trigger a certain law into action. An example of the use of qiyās is the case of the ban on selling or buying of goods after the last call for Friday prayers until the end of the prayer stated in the . By analogy this prohibition is extended to other transactions and activities such as agricultural work and administration. Among Sunni Muslims, Qiyas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levirate Marriage
Levirate marriage is a type of marriage in which the brother of a deceased man is obliged to marry his brother's widow. Levirate marriage has been practiced by societies with a strong clan structure in which exogamous marriage (i.e. marriage outside the clan) is forbidden. Etymology The term ''levirate'' is derived from the Latin ''levir'', meaning "husband's brother". Background and rationale Levirate marriage can, at its most positive, serve as protection for the widow and her children, ensuring that they have a male provider and protector. Levirate marriage can be a positive in a society where women must rely on men to provide for them, especially in societies where women are under the authority of, dependent on, in servitude to or regarded as possessions of their husbands, and to ensure the survival of the clan. The practice of levirate marriage is strongly associated with patriarchal societies. The practice was extremely important in ancient times (e.g., Ancient Near Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The term ''Talmud'' normally refers to the collection of writings named specifically the Babylonian Talmud (), although there is also an earlier collection known as the Jerusalem Talmud (). It may also traditionally be called (), a Hebrew abbreviation of , or the "six orders" of the Mishnah. The Talmud has two components: the Mishnah (, 200 CE), a written compendium of the Oral Torah; and the Gemara (, 500 CE), an elucidation of the Mishnah and related Tannaitic writings that often ventures onto other subjects and expounds broadly on the Hebrew Bible. The term "Talmud" may refer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esoteric Interpretation Of The Quran
Esoteric interpretation of the Quran ( ar, تأويل, taʾwīl) is the allegorical interpretation of the Quran or the quest for its hidden, inner meanings. The Arabic word ''taʾwīl'' was synonymous with conventional interpretation in its earliest use, but it came to mean a process of discerning its most fundamental understandings. "Esoteric" interpretations do not usually contradict the conventional (in this context called " exoteric") interpretations; instead, they discuss the inner levels of meaning of the Quran. The Arabic words ''taʾwīl'' and '' tafsīr'' both mean roughly "explanation, elucidation, interpretation, and commentary"; but from the end of the 8th century CE onwards, ''taʾwīl'' was commonly regarded as the esoteric or mystical interpretation of the Quran, while the conventional exegesis of the Quran was referred to using the term ''tafsīr''. The term '' batin'' refers to the inner or esoteric meaning of a sacred text, and '' zahīr'' to the apparent or exo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing.: ), which consist of verses (pl.: , sing.: , cons.: ). In addition to its religious significance, it is widely regarded as the finest work in Arabic literature, and has significantly influenced the Arabic language. Muslims believe that the Quran was orally revealed by God to the final prophet, Muhammad, through the archangel Gabriel incrementally over a period of some 23 years, beginning in the month of Ramadan, when Muhammad was 40; and concluding in 632, the year of his death. Muslims regard the Quran as Muhammad's most important miracle; a proof of his prophethood; and the culmination of a series of divine messages starting with those revealed to Adam, including the Torah, the Psalms and the Gospel. The word ''Quran'' oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |